To stop asthma from interfering with school, work or play. Salbutamol for 24 to 48 hours (2 to 4 puffs every 4 to 6 hours depending on clinical evolution) and prednisolone po (1 to 2 mg/kg once daily) to complete 3 days of treatment.
A dose of systemic corticosteroids should be administered within the first hour of treatment for acute asthma for all but patients with the mildest form of the disease.
Acute asthma attack treatment. In general, symptoms of asthma are easily controlled in most people by making lifestyle changes and using medications, so they can have normal lives. Asthma is one of the most frequently encountered problems in clinical practice [ 1, 2 ]. Salbutamol for 24 to 48 hours (2 to 4 puffs every 4 to 6 hours depending on clinical evolution) and prednisolone po (1 to 2 mg/kg once daily) to complete 3 days of treatment.
An acute asthma attack is not to be taken lightly. Wheezing with fluids or mucus. Consider early addition of a single bolus dose of intravenous salbutamol (15 micrograms/kg over 10 minutes) in a severe asthma attack where the patient has not responded to initial inhaled therapy.
To establish the presence of an acute asthma attack. Second line treatment of acute asthma. Professional with a severe or life threatening acute exacerbation of asthma should receive oral or iv steroids within one hour (2013, 2018 local target not national priority) • people who receive hospital or ooh rx for acute asthma exacerbation should be followed up by their own gp practice within 2 working days (2018 national priority)
Patients should have inhaled corticosteroid therapy started if new diagnosis or treatment increased if poorly controlled prior to admission. The cornerstones of acute asthma management in childhood are oxygen, inhalation of bronchodilators and systemic corticosteroids. A dose of systemic corticosteroids should be administered within the first hour of treatment for acute asthma for all but patients with the mildest form of the disease.
Additional treatment should be included as required. Observe the patient for 1 hour (4 hours if he lives far from the health centre) then give outpatient treatment: Even when the fast acting medicine is used the medicine might not work creating an emergency situation for the individual.
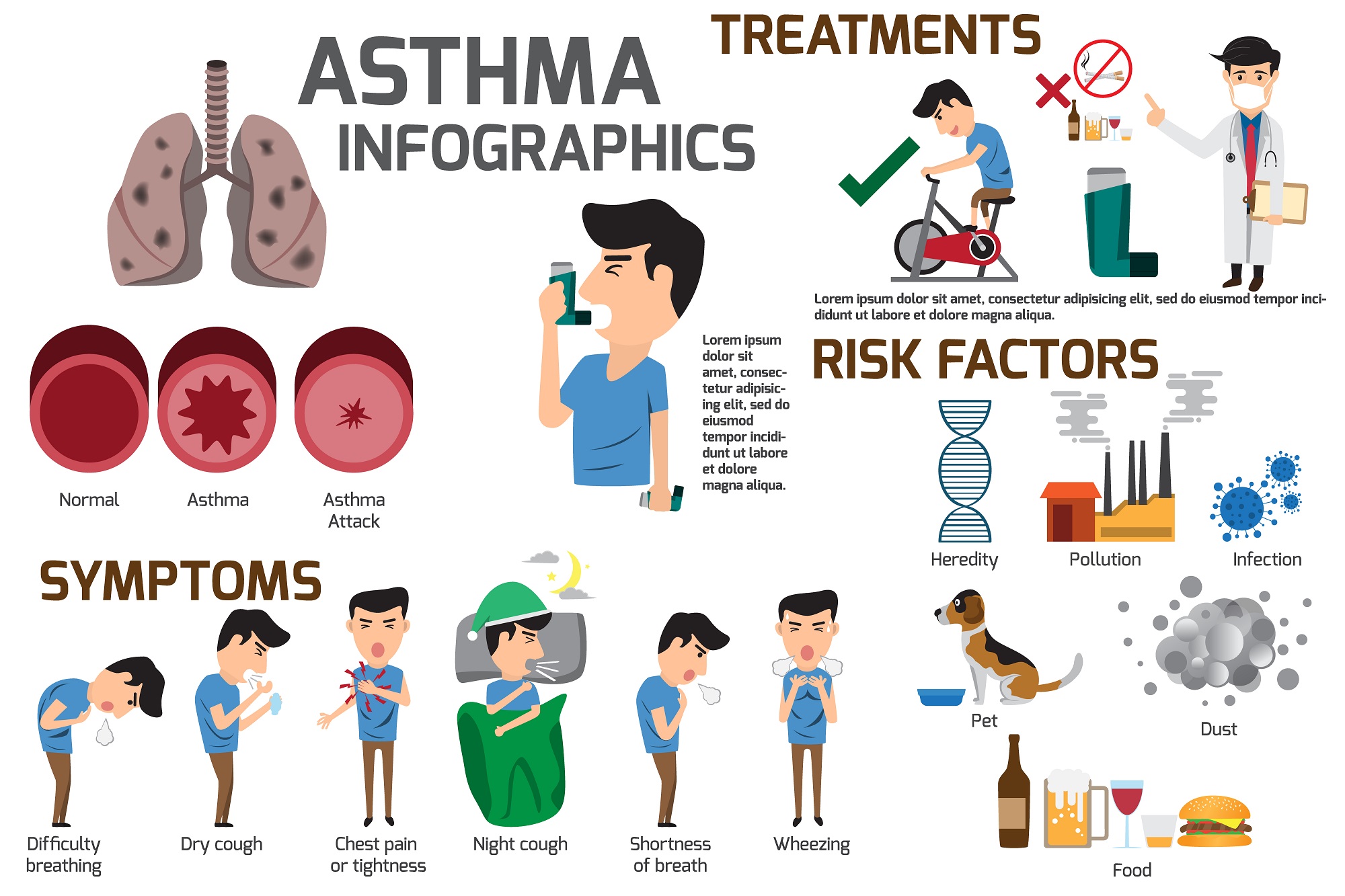
The main aims of asthma treatments are: General references the goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function. A greater awareness of the severity.
To stop asthma from interfering with school, work or play. 141 this therapy is particularly important for patients with severe asthma and those already receiving systemic corticosteroids, as recently confirmed by a large prospective study of asthma care. Symptoms of an acute asthma attack in pregnancy include:.
Patients with acute asthma will exhibit increasing shortness of breath, chest tightness, coughing, and/or wheezing. Treatment of acute attacks of asthma in children. During an asthma attack, the muscles that surround the bronchial tubes constrict, narrowing the air passages and making it extremely difficult to breathe.
The danger of acute asthma attacks is that they can be deadly. Appendix 2.2 emergency treatment care bundles for management of acute adult asthma 56 appendix 2.3 discharge letter, fax, email template for management of acute adult asthma 59 appendix 2.4 audit form for emergency asthma care 60 appendix 2.5 asthma management plan 61 appendix 2.6 peak flow measurements 63 appendix 2.7 medications in acute. Intramuscular (im) or intravenous (iv) corticosteroids may be used in the initial treatment of acute asthma;
Theophylline has very little role in treatment of an acute asthma exacerbation. However, there is no evidence that these routes have a more rapid onset of action or are more effective than is oral administration [17]. Other common symptoms are wheezing and a rattling sound in the.
Acute asthma is often associated with anxiety, which may further increase dyspnoea and bronchopulmonary obstruction. If this occurs then the individual should head to the nearest hospital for immediate treatment. Routine prescription of antibiotics is not indicated for patients with acute asthma.
In contrast, poor asthma control typically presents with a diurnal variability in airflow and is a characteristic that is usually not seen during an acute exacerbation. Acute asthma should be differentiated from poor asthma control.