Intramuscular (im) or intravenous (iv) corticosteroids may be used in the initial treatment of acute asthma; An asthma exacerbation is an acute or subacute episode of increased dyspnea, cough, chest tightness, or wheezing associated with decreased lung function (decreased forced expiratory volume or peak expiratory flow rate compared with baseline parameters).
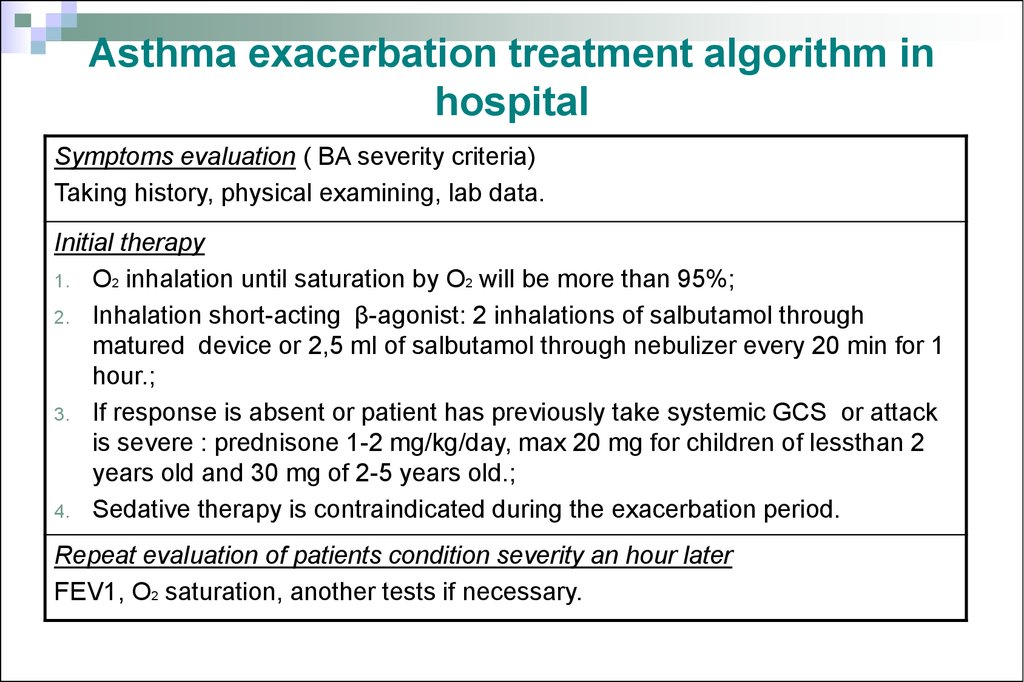
Summary of treatment modalities for asthma exacerbation.
Acute asthma exacerbation treatment. Global initiative for asthma (gina). Acute asthma should be differentiated from poor asthma control. An asthma exacerbation is an acute or subacute episode of progressive worsening of symptoms of asthma, including shortness of breath, wheezing, cough, and chest tightness.
Defining an exacerbation an exacerbation is a deterioration in the level of control experienced by a person with asthma. Older, frail patients and patients with comorbidities, a history of respiratory failure, or acute changes in blood gas measurements are admitted to the hospital for observation and treatment. An asthma exacerbation is an acute or subacute episode of increased dyspnea, cough, chest tightness, or wheezing associated with decreased lung function (decreased forced expiratory volume or peak expiratory flow rate compared with baseline parameters).
The role of ipratropium bromide in the emergency management of acute asthma exacerbation: It’s important to go over each step of this plan with your doctor to make sure you understand what to do in these cases. However, if a person’s symptoms are very severe, they.
(2) early administration of corticosteroids; Treatment after discharge from the hospital: However, there is no evidence that these routes have a more rapid onset of action or are more effective than is oral administration [17].
Important factors in the prevention of asthma exacerbations include adequate adherence to inhaled corticosteroid controller therapy, early and appropriate exacerbation treatment, and biologic therapy if indicated. For the treatment of exacerbations, the current update: Professional with a severe or life threatening acute exacerbation of asthma should receive oral or iv steroids within one hour (2013, 2018 local target not national priority) • people who receive hospital or ooh rx for acute asthma exacerbation should be followed up by their own gp practice within 2 working days (2018 national priority)
Theophylline has very little role in treatment of an acute asthma exacerbation. Key predictors of asthma exacerbations include recent exacerbations, low lung function, poor asthma control, and relevant biomarkers. (1) treatment of hypoxemia (if needed);
Oxygen therapy, bronchodilators, and if needed, corticosteroids form the basis of initial therapy of an acute asthma exacerbation. Intubation in acute severe asthma is risky and challenging. These plans usually include instructions for treating acute asthma exacerbations.
Acute exacerbations of asthma are very common reasons for a presentation to emergency departments. Anticholinergics in the treatment of children and adults with acute asthma: Summary of treatment modalities for asthma exacerbation.
In contrast, poor asthma control typically presents with a diurnal variability in airflow and is a characteristic that is usually not seen during an acute exacerbation. Agonists are the cornerstones of treatment for acute asthma. Mild exacerbations often can be treated on an outpatient basis in patients with adequate home support.
A metaanalysis of randomized clinical trials. It should be performed by an experienced practitioner whenever possible. Do not delay immediate treatment measures for.
— adds levalbuterol as a saba treatment for asthma exacerbations. Agonist therapy in children and adults. 1,143 people died from acute asthma in 2010 (asthma uk, 2013).
Intramuscular (im) or intravenous (iv) corticosteroids may be used in the initial treatment of acute asthma; Exacerbations are marked by decreases from baseline in objective measures of pulmonary function, such as peak expiratory flow rate. General references the goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function.
Treatments, thus underscoring the distinction between acute and chronic asthma management. Treatment of acute asthma exacerbation in the outpatient setting: — acknowledges the limited value of pulmonary function measures in very severe exacerbations.
Patients with acute asthma will exhibit increasing shortness of breath, chest tightness, coughing, and/or wheezing. In the acute setting, the use of class 1 medications for symptom relief is standard, in addition to class 2 to target inflammation at the heart of an acute exacerbation and prevent relapse. 2 in general, the goals of treatment for adults with an acute asthma exacerbation include.