Acute or chronic failure can begin on either the left or right side of your heart, or both sides may fail at the same time. I50.43 is a billable icd code used to specify a diagnosis of acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure.
Acute or chronic failure can begin on either the left or right side of your heart, or both sides may fail at the same time.
Acute on chronic systolic heart failure. Heart failure may also be classified as acute or chronic. Unspecified, acute, chronic, acute on chronic, due to left heart failure. Acute systolic heart failure occurs more suddenly and often is considered a medical emergency.
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Dorland�s medical dictionary defines exacerbation as an increase in the severity of disease or any of its symptoms. 222 cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock with mcc
Swelling in feet, ankles, legs, or abdomen; Acute heart failure resulting from cardiomyopathy has. • 428.43, acute on chronic combined systolic and.
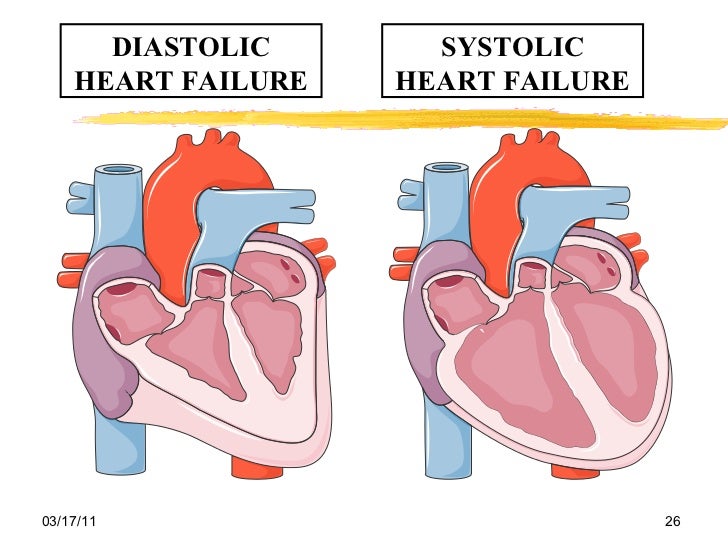
Systolic heart failure means that. Systolic heart failure, also known as a systolic dysfunction, is one of the most common types of heart failure and it typically affects the left ventricle of the heart. I50.23 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure.
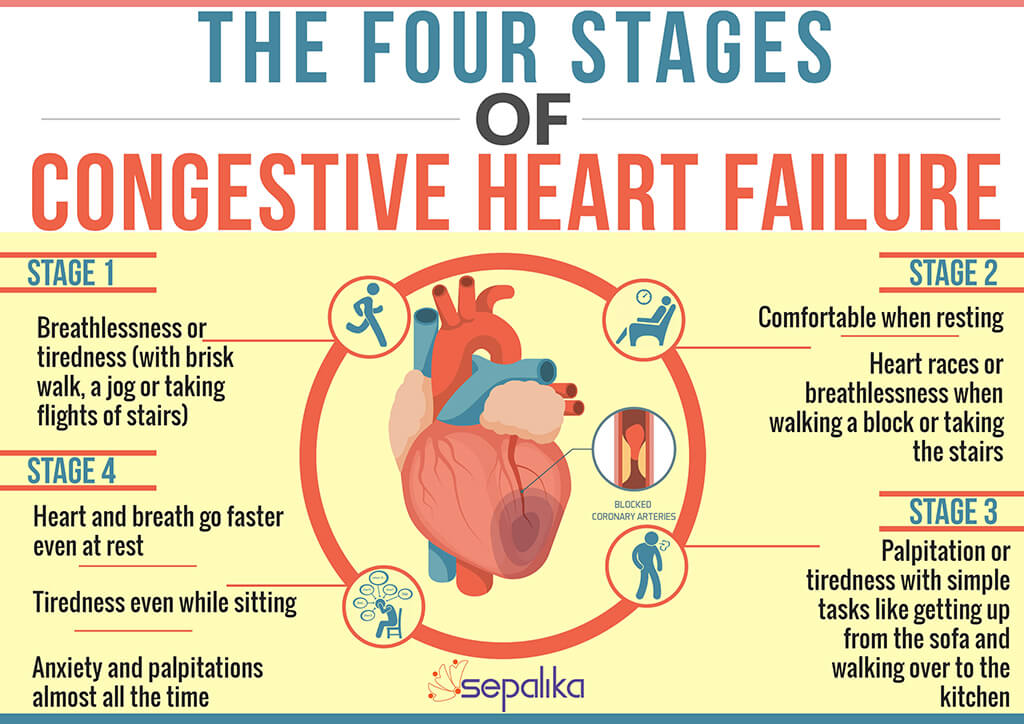
New onset chf is also seen in er. Heart failure is a common form of heart disease associated with progressive exercise intolerance and high risk of adverse clinical outcome events. Acute heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterised by signs and symptoms of fluid overload which require hospitalisation.
A �billable code� is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Chronic systolic heart failure occurs over a period of time, typically caused by other heart conditions such as high blood pressure, a damaged heart, or coronary artery disease. Acute decompensated heart failure is a worsening of chronic heart failure symptoms, which can result in acute respiratory distress.
Chronic treatment addresses the underlying conditions that. The pathophysiology of chronic systolic heart failure is fundamentally determined by the failure of the circulatory system to. Acute or chronic failure can begin on either the left or right side of your heart, or both sides may fail at the same time.
I50.23 is a billable icd code used to specify a diagnosis of acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure. A �billable code� is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Systolic heart failure is characterized by ventricular dilation and reduced ejection fraction, and this syndrome may be either chronic or acute.
If you have systolic heart failure, you can have: I50.43 is a billable icd code used to specify a diagnosis of acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure. Coding clinic’s answer was that if the “provider links acute chf with diastolic dysfunction, assign code i50.31, acute diastolic (congestive) heart failure, as the principal diagnosis.
Acute on chronic systolic heart failure (443253003) recent clinical studies. Patients have a history of chf most of the time. They develop pedal edema gradually at home but recently they might have had more shortness of breath, tiredness, more swelling, cough, pnd or orthopnea, etc.
Acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure. With chronic systolic heart failure (17). Assign code 428.33, diastolic heart failure, acute on chronic, and code 428.0, congestive heart failure, unspecified.
Treatment for systolic heart failure. The physician is responsible for documenting acute or chronic before the appropriate code can be assigned. Left ventricular remodeling is the principal cause of progression of systolic heart failure.
I50.83, high output heart failure Coughing, wheezing, difficulty laying flat to sleep, as well as an irregular heartbeat can also be symptoms. When the provider has linked either diastolic or systolic dysfunction with acute or chronic heart failure, it should be coded as ‘acute/chronic diastolic or systolic heart failure.’