Covers the initial management of suspected ankylosing spondylitis in primary care, when to refer, and what advice to give. Ankylosing spondylitis (as) is a systemic inflammatory rheumatic disease involving spinal and sacroiliac joints.
Physical therapy is strongly recommended for patients with active or stable ankylosing spondyloarthritis.
Ankylosing spondylitis treatment guidelines. Summary of the main recommendations for the treatment of patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (panel a) and stable ankylosing spondylitis (panel b). Treatment for as aims to achieve several goals, including: A common treatment regimen for the various forms of spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, enteropathic arthritis, reactive arthritis, juvenile spondyloarthritis, and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis) involves medication, exercise, physical therapy, good posture practices, and other options such as applying heat/cold to help relax muscles and reduce joint.
We conducted updated systematic literature reviews for 20 clinical questions on pharmacologic treatment addressed in the 2015 guidelines, and for 26 new questions on pharmacologic. Treatment for ankylosing spondylitis (as) is tailored to each person since there is a wide variety in how as affects different people. Physical therapy is strongly recommended for patients with active or stable ankylosing spondyloarthritis.
Current guidelines for the drug treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. The guidelines were published in. Several drugs are currently available in the management of as, and may be divided into 3 groups.
Methods we conducted updated systematic literature reviews for 20 clinical questions on pharmacologic treatment addressed in the 2015 guidelines, and for 26 new questions on pharmacologic. Covers the initial management of suspected ankylosing spondylitis in primary care, when to refer, and what advice to give. “key acr recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis:
In adults with active as, strongly recommend treatment with nsaids over no treatment with nsaids; Ankylosing spondylitis (as) is a systemic inflammatory rheumatic disease involving spinal and sacroiliac joints. Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis this guideline is intended to provide guidance for the evaluation of new medicinal products in ankylosing spondylitis this guideline should be read in conjunction with directive 2001/83/ec and all
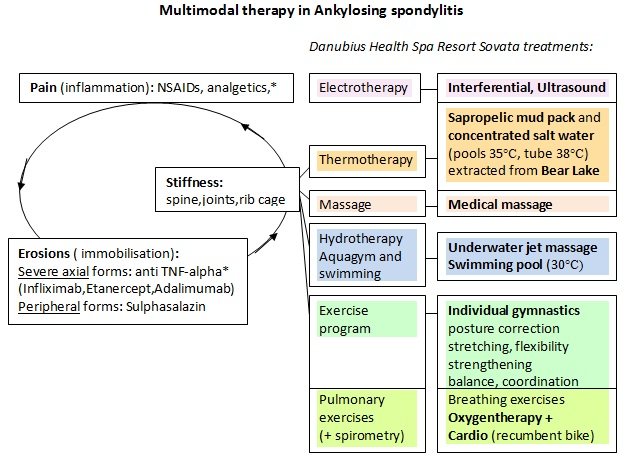
There�s no cure for ankylosing spondylitis (as), but treatment is available to help relieve the symptoms. The reviewers conditionally recommend active interventions like supervised exercise over passive interventions like massage, ultrasound, and heat. Although home exercise is known to be effective, group physical therapy under appropriate supervision is more efficient than individual exercise 6).
Infliximab is recommended only if treatment is started with the least. Discussion this update was primarily motivated by the availability of new treatment options, notably secukinumab, ixekizumab, tofacitinib, and tnfi biosimilars, for patients with axspa. Covers what advice to give and the treatment, follow up, and referral of someone with confirmed ankylosing spondylitis.
Treatment can also help delay or prevent the process of the spine joining up (fusing) and stiffening. The frequency of the measurements depends on the level of disease activity. 1.4.3 adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab and infliximab are recommended, within their marketing authorisations, as options for treating severe active ankylosing spondylitis in adults whose disease has responded inadequately to, or who cannot tolerate, nsaids.
In most cases treatment involves a. It is important to educate patients that proper exercise not only alleviates pain but also relaxes. In adults with active as, despite treatment with nsaids, strongly recommend treatment with tnfi over no tnfi
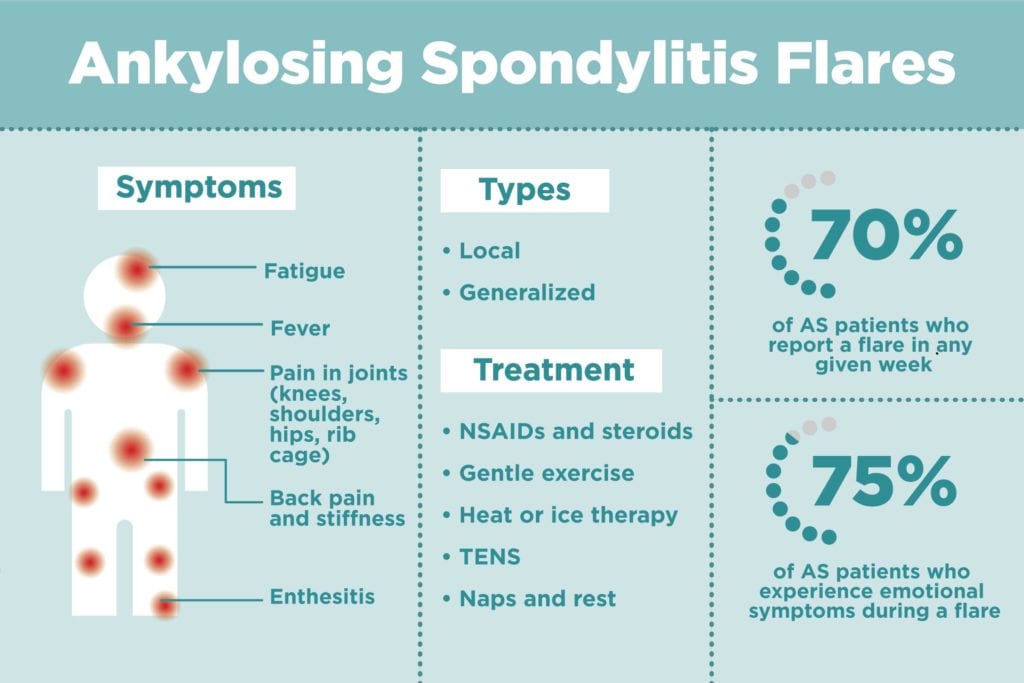
As with any chronic disease, patient education is vital to familiarize the patient with the symptoms, course, and treatment of the disease. This condition is responsible for back pain, stiffness and discomfort. Reducing symptoms, such as pain and stiffness;