If during dobutamine infusion up to 20 μg/kg there is an increase of more than 20% in the vti of the lvot (ie cardiac output ) and the calculated valve area remains below 1 cm 2 then there is a true aortic stenosis. Nevertheless, assessment of as severity is still challenging.

Areas of less than 0.6 cm2 constitute severe aortic.
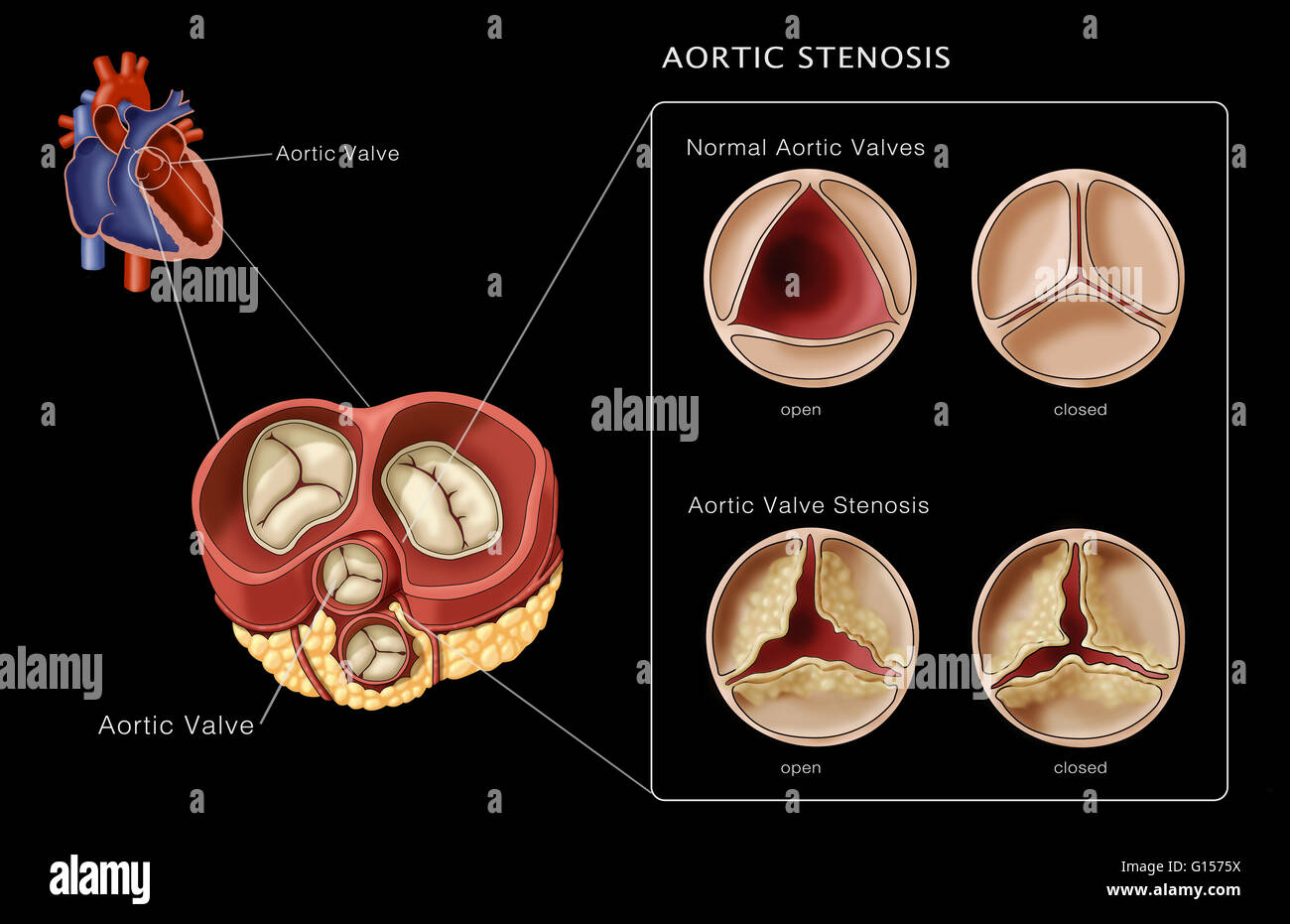
Aortic stenosis valve area. Aortic valve area (vti) aortic valve area can be calculated by using the principle of conservation of mass — what comes in must go out. Ava can be underestimated at low transvalvular flow rate. A normal aortic valve area is greater than or equal to 2.0 cm2.
Recently, an aortic valve area (ava) index (avai) <0.6 cm (2)/m (2) was proposed as an indicator of severe aortic stenosis. However, measurement of aortic valve area directly by planimetry is a much simpler method which have been widely used and validated. These proportions were 3.1% and 9.3% for ava ≤1.5 cm 2 , respectively.
Yet, the impact of flow rate on prognostic value of ava ≤1.0cm 2 is unknown and is. We identified 103 consecutive asymptomatic patients (mean age 72 ± 11 years) with severe aortic stenosis, defined by an ava of <1.0 cm. What is normal aortic valve area?
As aortic stenosis develops, minimal valve gradient is present until the orifice area becomes less than half of normal. Background to account for differences in body size in patients with aortic stenosis, aortic valve area (ava) is divided by body surface area (bsa) to calculate indexed ava (ava index). A straight tipped wire is placed in the catheter.
In people with normal aortic valves, the normal aortic valve area range is 2.0 cm2 and greater. Valvular aortic stenosis (as) is the most frequent valvular disease in developed countries. Aortic velocity and mean pressure gradient are also utilized to determine the severity of your aortic stenosis.
Assessment of low flow, low gradient severe aortic stenosis: Severity of aortic stenosis a normal sized aorta has a valve area of approximately 3.0cm2 (3.0 centimeters squared) and 4.0cm2. • obstruction to lv outflow • decrease in aortic valve area • normal:
As the area is reduced, transvalvular flow resistance increases. In adult individuals with normal aortic valves, the valve area is 3.0 to 4.0 cm 2. As the severity of aortic stenosis increases, increases in valve gradients aren’t really present until the aortic valve area narrows down to less than half of its normal size.
Measure the lvot diameter in centimeters. In patients with moderate to severe aortic stenosis, the pigtail catheter will generally not cross the aortic valve in the traditional fashion. Areas of less than 0.6 cm2 constitute severe aortic.
The recent concept of parodoxical low flow, low gradient severe. The aortic valve area is normally 3.0 to 4.0 cm 2. How to get an ava by continuity equation.
Aortic valve area indexed to body surface area should be considered for the large and small extremes of body surface area. Valve area by continuity equation. Aortic stenosis aortic valve gradient aortic valve area by continuity equation aortic valve area by gorlin equation aortic valve area by pisa aortic valve area by planimetry aortic valve area by velocity ratio.
< 1.0 cm2 valvular hear disease, chapter 63, braunwarld’s heart disease 10th edition 2014 Specific to size, a normal aortic valve area is >2 centimeters squared (cm2). Values of ava ≤1.0 cm 2 were found in 0.5% of studies with normal valves and 1.8% of studies with ascl.
If the valve area is between 1.0 and 1.5 cm2, the stenosis is moderate; This results in increased left ventricular load, while simultaneously affecting systemic perfusion. Crossing the stenosed aortic valve.
Aortic valve area (ava) ≤1.0cm 2 is a defining characteristic of severe aortic stenosis (as). Vratio ≤0.25 were found in 0.1% of patients without obstruction. A study has shown the validity of this approach to calculate the aortic valve area.
Aortic stenosis is a progressive disease that leads to a gradual reduction in the orifice area. The pressure gradient across a stenotic valve is directly related to the valve orifice area and the transvalvular flow. The purpose of the present study was to clarify the prognostic value of the avai.
If during dobutamine infusion up to 20 μg/kg there is an increase of more than 20% in the vti of the lvot (ie cardiac output ) and the calculated valve area remains below 1 cm 2 then there is a true aortic stenosis. The diagnosis of as is classically confirmed by echocardiography, the standard tool for detecting and assessing the severity of the disease. Nevertheless, assessment of as severity is still challenging.
To gain more insight into the aortic valve or a true or stenosis has a pseudo stenosis seems dobutamine stress worthwhile. If the valve area is between 1.5 and 2.0 cm2, the stenosis is mild; Methods we prospectively measured indices of as in all consecutive echocardiograms performed in a