
After developing in the bone marrow, some lymphocyte cells travel to the thymus, where they become t cells. The key difference between t lymphocytes and b lymphocytes is that the t lymphocytes originate in bone marrows and mature in the thymus while b lymphocytes originate and mature in bone marrows.
Some of them also develop into nk cells.
B lymphocyte vs t lymphocyte. Lymphocytes in peripheral blood (circulation) are heterogeneous and can be broadly classified into t cells, b cells, and natural killer (nk) cells. Agranulocytes → monocytes and lymphocytes. So, lymphocytes are one of the five types of wbcs and belong to granular leukocytes.
T lymphocytes recognise the antigens of the pathogen on the surface of the cell and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death). A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the immune system of jawed vertebrates. Their most salient role is in immune system.
However, these antibodies are not secreted. B lymphocytes can connect to the antibodies directly on the surface of the attacking virus or infection while the t lymphocytes can only connect to the virus antibodies on the outside of the infected cells. One such part is called macrophages.
They arise from bone marrow, bursa of fabricus (in fowl), gut associated lymphoid tissue (peyer’s patches). Other lymphocytes stay in the bone marrow, where they become b cells. The main two types of cells in blood are red blood cells (rbc) and white blood cells (wbc).
All lymphocytes are leukocytes but all leukocytes are not lymphocytes. A portion of b cells become memory b cells. B and t lymphocytes later differentiate into effector and memory cells on exposure to antigens.
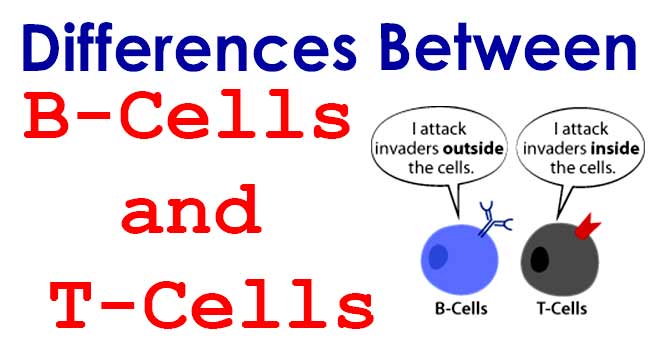
B cells produce antibody molecules that can latch on and destroy invading viruses or bacteria. T cells start growing in bone marrow and then travel to the thymus gland to mature. 059543 % cd 4 pos.
059568 % cd 8 pos. The main difference between monocytes and lymphocytes is the role in the immune system. The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs).
Sometimes, however, and as demonstrated in this case, bone marrow and peripheral blood involvement occur. There are two main types lymphocytes: T cells and b cells contribute to our specific immunity and develop from the same progenitor stem cell.
T cells are direct fighters of foreign invaders and also produced cytokines, which are biological substances that help activate other parts of the immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules; B lymphocytes (b cells) and t lymphocytes (t cells) are two types of lymphocytes.
Monocytes are the tools for innate immunity. However, they have many differences. Natural killer cells (nk cells).
T cells and b cells. The level of igm peaks in 10 days after the infection. Classification of lymphomas includes delineation of lymphocyte subset, either t or b cell.
Difference between b lymphocytes and t lymphocytes (b cells vs t cells) 1. B lymphocytes differentiate inside the bone marrow; B cells vs t cells.
The key difference between t lymphocytes and b lymphocytes is that the t lymphocytes originate in bone marrows and mature in the thymus while b lymphocytes originate and mature in bone marrows. These are the primary lymphoid organs. They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which.
A failure to express cd40 ligand has been associated with an. T lymphocytes differentiate in the thymus. 059527 % cd 3 pos.
They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. After developing in the bone marrow, some lymphocyte cells travel to the thymus, where they become t cells. Lymphocytes are tools for adaptive immunity.
Some of them also develop into nk cells. B cells also present antigens of digested pathogens along with mhc ii complexes. B lymphocytes lie outside the lymph node while the t lymphocytes lie inside the lymph nodes.
These make antibodies that help your body fight infections. Lymphocytes mainly constitute t cells, b cells, and natural killer (nk) cells. These attack foreign cells, cancer cells, and cells infected with a virus.
B lymphocyte responses to protein antigens are dependent on cytokines produced by activated t lymphocytes (cd4 +). B cells, also known as b lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. The three main types of lymphocytes are the t cells, b cells, and the natural killer cells.
T lymphocytes appear more discrete and separated one from another, while b lymphocytes exhibit close cellular association to form a syncytial array. These proteins are called antibodies.