
While vemurafenib results in a response in about 80% of melanoma patients, the clinical response among crc patients is not greater than 5%. Activated raf proteins trigger the activation of mek1/2 and further activate erk.
The braf activating mutation, harbored by approximately 10% of colorectal cancers (crc), confers dramatic prognosis to advanced diseases.
Braf mutation colon cancer. Braf mutation in colorectal cancer: This mutation is also present in more than 60% of melanoma patients. Braf mutation testing has a role in (1) differentiating sporadic colorectal cancer from lynch syndrome, (2) identifying cancers lacking braf mutation that are more likely to respond to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor therapy, and (3) conferring worse prognosis in colorectal cancer that is microsatellite stable.
A subgroup harboring a braf mutation has been described, and represents approximately 10% of the patients diagnosed with colon cancer. Therefore, knowing about a braf gene. Activated raf proteins trigger the activation of mek1/2 and further activate erk.
The braf v600e mutation is a prognostic biomarker of aggressive tumor growth. The braf v600e mutation occurs in approximately 10% of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, with recent estimates ranging from as low as 5% to as high as 21%. Braf mutation is an inclusion criterion in 11 clinical trials for colorectal carcinoma, of which 8 are open and 3 are closed.
2 globally, there are ~774,000 deaths each year from crc. Braf mutations in colorectal cancer. Consecutive cases of primary colorectal cancer (n = 137) were analyzed for mlh1 protein expression using immunohistochemistry (ihc).braf v600e mutation was detected by ihc using a specific.
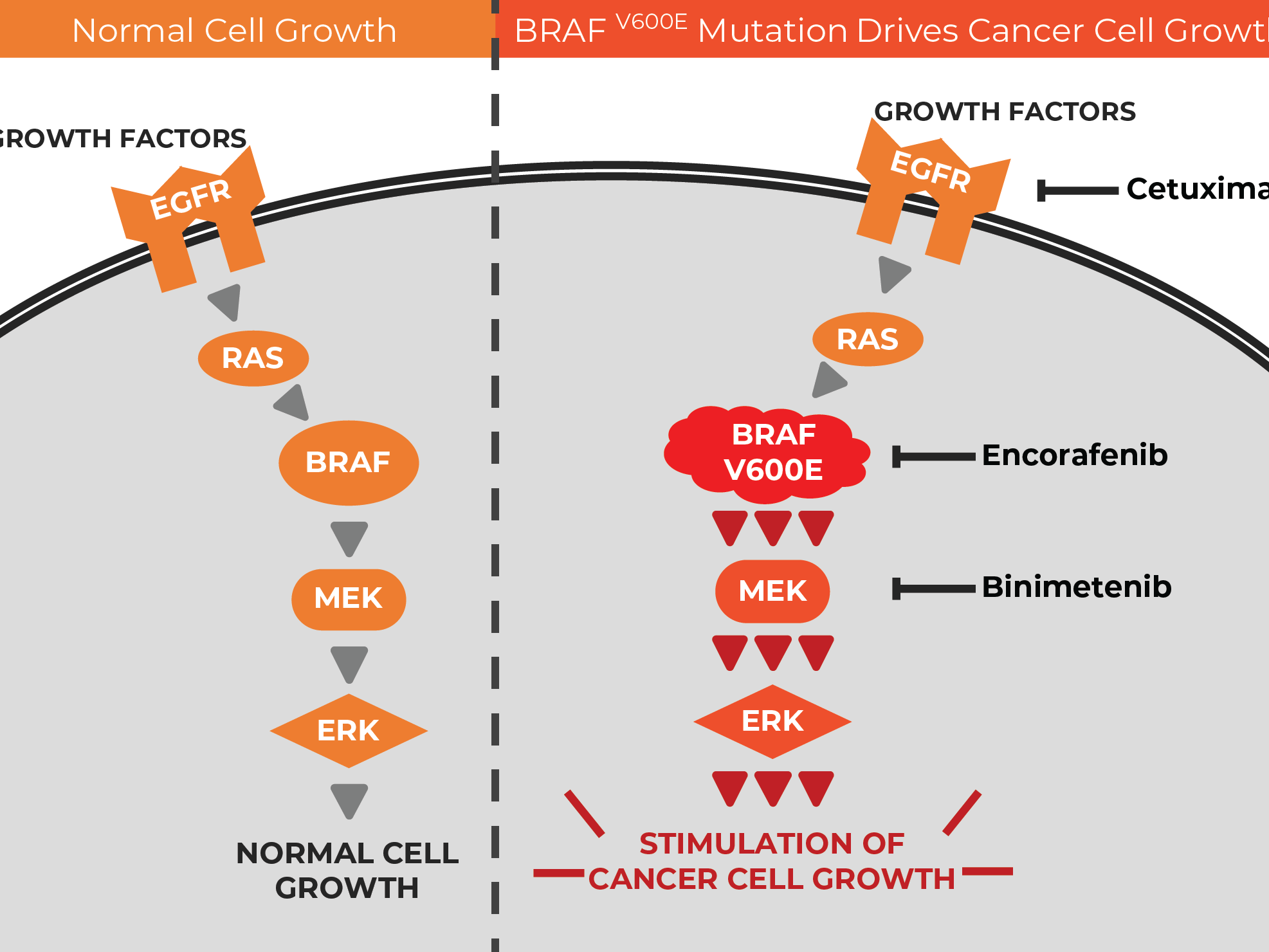
Fortunately, substantial activity is emerging from the current clinical trials. For people with colorectal cancer with braf mutations, a treatment regimen that consists of three targeted cancer drugs—encorafenib (braftovi), cetuximab (erbitux), and binimetinib (mektovi)—can improve how long they live without increasing their risk of serious side effects, results from the beacon crc trial show. The aim of the study was to detect mutations of braf oncogene in colorectal cancer and to use this information to identify lynch syndrome patients.
More than 30 mutations of the braf gene associated with human cancers have been identified. The mortality risk for patients with a braf mutation is more than two times higher than for those with a normal braf gene. Yet, the braf mutation could be considered as a stratifi.
Braf mutation is seen in nearly one in ten patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Of the trials that contain braf mutation and colorectal carcinoma as inclusion criteria, 7 are phase 1 (6 open), 1 is phase 1/phase 2 (1 open), and 3. The mapk cascade plays a crucial role in tumor cell proliferation and survival.
This subgroup has morphological, clinical, and therapeutic characteristics that differ substantially from patients who do not carry this genetic alteration. Mutation in the braf oncogene is a key step in malignant transformation within the methylator pathway to colorectal cancer. However, there is a paucity of information about braf mutant colorectal tumors.
Colorectal cancer (crc) is the third most common cancer worldwide 1 and the fourth most common cancer in the usa. We found that cultured human crc cells harboring kras or braf mutations are selectively killed when exposed to high levels of vitamin c. Colorectal cancers can also have a braf v600e mutation, although the incidence is less frequent, estimated at about 10% of colorectal cancer (crc) patients.
Colorectal cancer is a heterogeneous disease with multiple underlying genetic mutations causing different clinical phenotypes. While vemurafenib results in a response in about 80% of melanoma patients, the clinical response among crc patients is not greater than 5%. The roles of braf mutation in colorectal cancer.
More than half of human colorectal cancers (crcs) carry either kras or braf mutations and are often refractory to approved targeted therapies. This mutation is also present in more than 60% of melanoma patients. This effect is due to increased uptake of the oxidized form of vitamin c,.
Despite major improvements in survival for advanced colorectal cancer overall, patients with braf mutation continue to have a very poor prognosis often with median survival of less than 12 months. The braf activating mutation, harbored by approximately 10% of colorectal cancers (crc), confers dramatic prognosis to advanced diseases. The braf mutant (mt) colorectal cancer (crc) population is a small and unique subgroup noted for its association with poor prognosis and survival.