New data demonstrates >90% year 1 success rate for radiofrequency ablation in treating patients with atrial fibrillation. Blandino et al 15 compared catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs in a subset of persistent af patients (>70 years old) and found that ablation (including a second procedure) yielded a higher success rate in maintaining nsr than did.

Nonetheless, after the introduction of pulmonary vein targeting for af in 1998, the expectation of a.
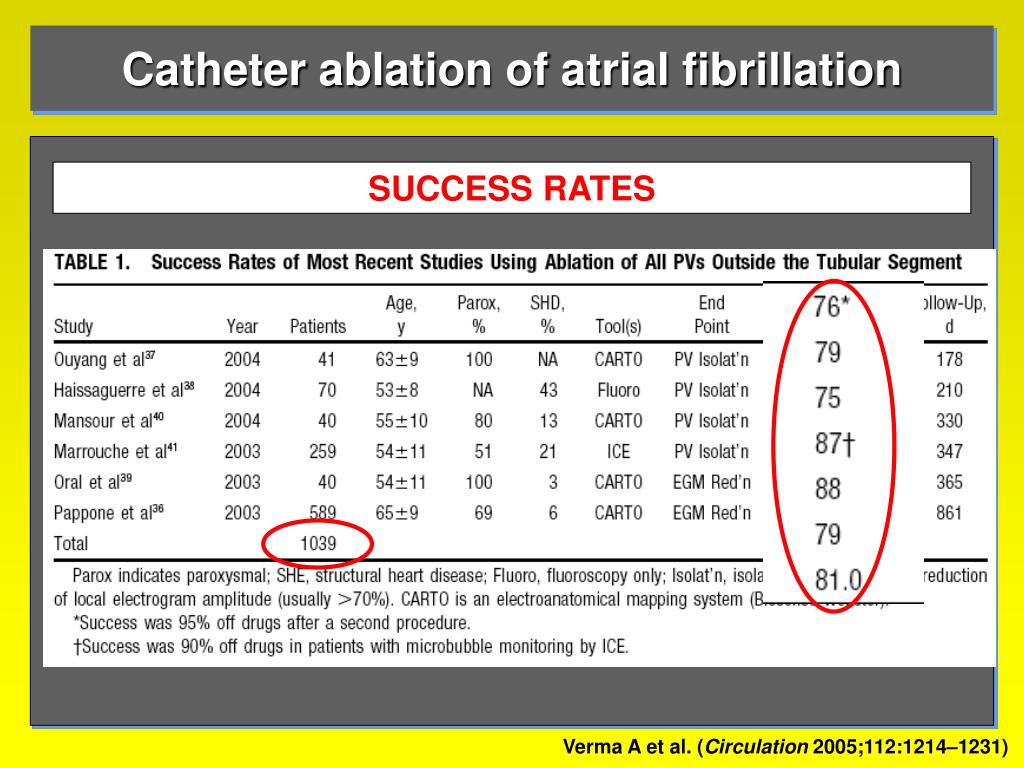
Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation success rate. When only patients who are younger and have no heart disease that could be causing the issue are. New data demonstrates >90% year 1 success rate for radiofrequency ablation in treating patients with atrial fibrillation. The success rate of catheter ablation in the treatment of af varies depending on the type and duration of af (ie, paroxysmal vs persistent), structural remodeling of the heart, and the technique.
Publish your vascular medicine research or review with hindawi. However, rate control strategy remained the predominant mantra in af management for the majority of patients in clinical practice. Background data on procedural characteristics and clinical outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation (af) in adults younger than 35 years has not been sufficiently addressed.
Though this is a study from only one center, the conclusion is clear: These limitations include not only the durability of the pulmonary vein isolation (pvi) lines, but also the pathophysiological understanding of the arrhythmia�s substrate. Catheter ablations done right do work.
Yes, it may require a “repeat” procedure. Recurrent af after catheter ablation occurs in at least 20 to 40% of patients. The aim is to assess procedural characteristics and clinical outcome of catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in young adults in comparison to older adults.
3 calkins, hugh, et al., hrs/ehra/ecas expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: In this review, we summarize the current state of the art of catheter ablation of af and describe future perspectives. This increases to around 80 per cent with multiple procedures (two or more).
If it does not, you may need a second catheter ablation procedure to eliminate the flutter. For the last two decades, the management of patients with atrial fibrillation (af) had stayed in an “equipoise” between rate and rhythm control as shown by affirm and race trials 1,2. Your success rates may be lower if you have been in af for a long time and have a large left atrium.
For nonparoxysmal af ablation studies, unadjusted success rate summary estimates ranged from 70.0% in 2010 to 64.3% in 2016 (1.1%/year; I 2 = 85%), with no improvement in multivariate analyses. Single procedure success rate was 33% (10 patients), and repeat ablation procedures were performed in 13 patients.
In early studies, the majority of centers reported single procedure success rates of 60% or more for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and 30% or less for persistent atrial fibrillation. Publish your vascular medicine research or review with hindawi. Blandino et al 15 compared catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs in a subset of persistent af patients (>70 years old) and found that ablation (including a second procedure) yielded a higher success rate in maintaining nsr than did.
Effect of left atrial enlargement on success rates of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in women. Catheter ablation success rates have improved over time based on a better understanding of atrial fibrillation, new techniques and technology, and greater doctor experience. If you have persistent af your success rates are around 40 to 50 per cent with one procedure.
Nonetheless, after the introduction of pulmonary vein targeting for af in 1998, the expectation of a. The procedure has a high success rate. Although catheter ablation is a safe procedure with a low periprocedural complication rate 16, several variables need to be considered when identifying patients with potentially lower success.