
Unfortunately, there are many reasons someone might develop heart failure. Heart failure occurs when something damages the heart muscle or reduces the heart�s ability to pump effectively.
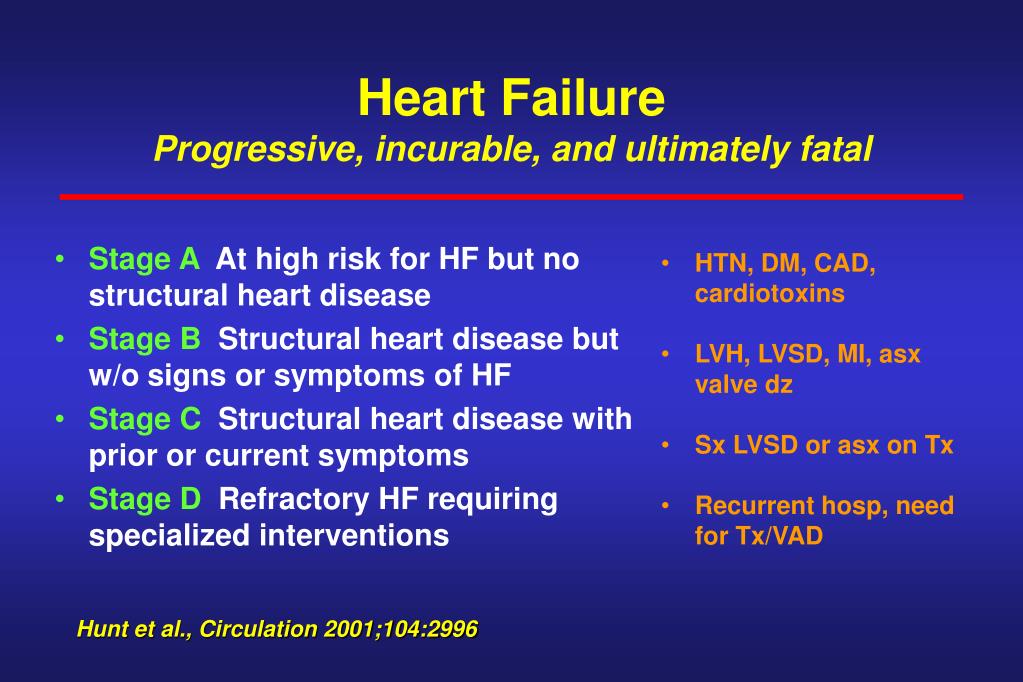
A person has a structural heart disorder but is not presenting symptoms.
Chronic heart failure stages. Heart failure occurs when something damages the heart muscle or reduces the heart�s ability to pump effectively. In time, patients will reach the final stages of congestive heart failure. Patients in the end stages of heart failure want to know what to expect.
Is a problem individuals develop when their heart struggles to pump blood the way it usually does and should do. Treatment of acute and chronic heart failure the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the european society of cardiology (esc) developed with the special contribution of the heart failure association (hfa) of the esc authors/task force members: Ask your healthcare provider what stage of heart failure you are in.
No matter what the cause, the. The stages range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure, and provide treatment plans. Normal physical activity like walking or taking a flight of stairs does not lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations.
- left ventricular (lv) remodeling; In the initial stages of congestive heart failure, cardiac physiology attempts to adapt via several compensatory mechanisms to maintain cardiac output and meet the systemic demands. People at high risk for developing hf in the future, but no functional or structural heart disorder;
Stage a, stage b, stage c, and stage d. No limitation of physical activity. Unfortunately, there are many reasons someone might develop heart failure.
Predicting the illness trajectory can be difficult. It occurs when the arteries cannot. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system increases heart.
Loss of appetite and nausea. Heart failure is classified into four stages: Most often, the damage stems from coronary artery disease or heart attack.
The four stages of congestive heart failure depending on the functional capabilities of the heart. Chronic heart failure (chf) remains the only cardiovascular disease with an increasing hospitalization burden and an ongoing drain on health care expenditures. Heart failure is the end result of a number of different pathophysiological processes in which there is injury to the heart with loss or impairment of functioning myocardial cells.
What are the stages of heart failure? A person has a structural heart disorder but is not presenting symptoms. Coronary artery disease is one of the leading causes of heart failure.
Skip to accessibility menu skip to login skip to content skip to footer Ordinary physical activity does not cause undue fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea (shortness of breath). There are four stages or classes of chf, and each is based on the severity of your symptoms.
Their body struggles as a result. A structural heart disorder, but no symptoms at any stage Structural heart disease and symptoms of heart failure;
Their heart is slower and does not work well. The prevalence of chf increases with advancing life span, with diastolic heart failure predominating in. Although symptoms can be managed, this is a chronic condition with no cure.
Class i is no problem, and class iv has symptoms of chest pain and physical activity with discomfort. The four stages are set up as follows: In its 2001 guidelines, the american college of cardiology/american heart association working group introduced four stages of heart failure:
A person has a high risk of heart failure but currently has no identifiable disorders. These stages help guide treatment options including taking medication and getting surgery. The american college of cardiology (acc) and the american heart association (aha) have identified the stages of heart failure.
You’ll be grouped into class 1 if a weakness has been discovered in your. A—high risk of heart failure but no structural disease or symptoms;. 5 compensatory neurohormonal mechanisms are activated in order to maintain adequate cardiac function and tissue perfusion.
The development of heart failure has been divided into four stages : The stages of congestive heart failure based on this approach are: A, b, c, and d.
Refractory heart failure requiring specialized interventions; But faulty heart valves, longstanding high blood pressure, or genetic disease may also be to blame. There are four stages of heart failure (stage a, b, c and d).
Slight limitation of physical activity. 2) clinical heart failure and 3) low cardiac output state. Ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea (shortness of breath).