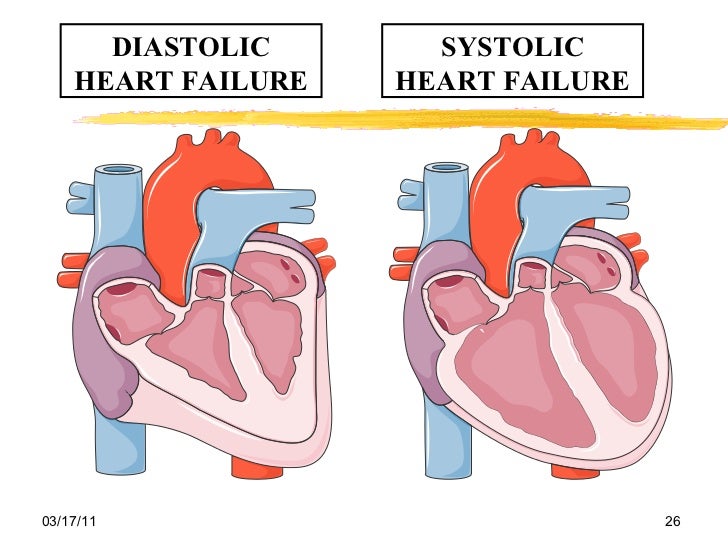
Both affect the lower left chamber of your heart, known. Although there is some overlap in the pathophysiology of heart failure related to primary systolic or diastolic dysfunction, this review is focused on a discussion of chronic systolic.
If you have systolic heart failure, it means your heart isn’t contracting well during heartbeats.
Chronic systolic and diastolic heart failure. Of the 7788 patients in the digitalis investigation group trial, 6800 had systolic hf (ejection fraction >45%) and 988 had diastolic hf (ejection fraction >45%). I50.41 acute combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure. If there is no provider documentation linking the two conditions, assign code i50.9, heart failure, unspecified.”.
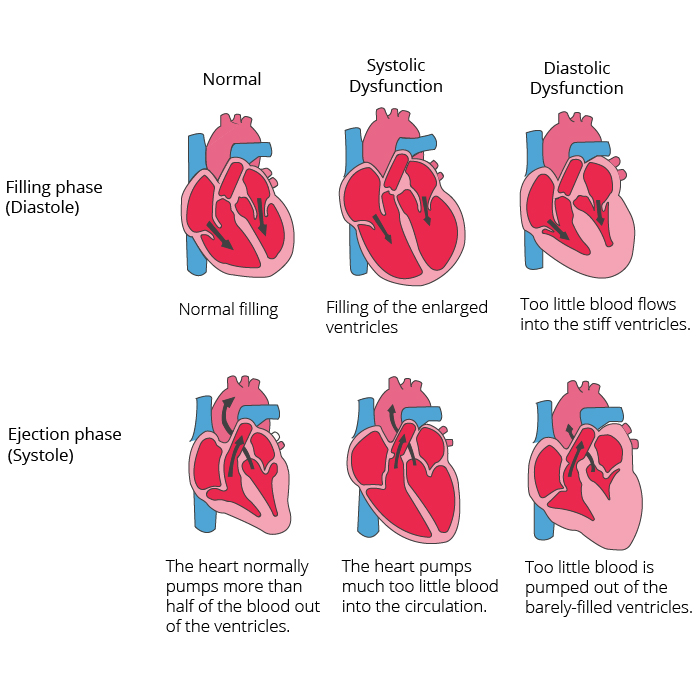
Chronic combined systolic and diastolic heart failure (153941000119100) recent clinical studies. The left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally (because the muscle has become stiff). Combined ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction it is not uncommon in chronic heart failure to have a combination of both systolic and diastolic dysfunction.
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (hfpef), also called diastolic failure (or diastolic dysfunction): Chronic systolic heart failure occurs over a period of time, typically caused by other heart conditions such as high blood pressure, a damaged heart, or coronary artery disease. If you have diastolic heart failure, it means.
They develop pedal edema gradually at home but recently they might have had more shortness of breath, tiredness, more swelling, cough, pnd or orthopnea, etc. Diastolic heart failure (dhf) and systolic heart failure (shf) are 2 clinical subsets of the syndrome of chronic heart failure that are most commonly encountered in clinical practice. Efficacy and safety of shenfu injection combined with sodium nitroprusside in the treatment of chronic heart failure in patients with coronary heart disease:
However, the effects of dhf on mortality and hospitalization have not been adequately defined. Chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure. Although there is some overlap in the pathophysiology of heart failure related to primary systolic or diastolic dysfunction, this review is focused on a discussion of chronic systolic.
When the provider has linked either diastolic or systolic dysfunction with acute or chronic heart failure, it should be coded as ‘acute/chronic diastolic or systolic heart failure.’. The heart can�t properly fill with. Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after october 1,.
Cdr132l thus should be explored as treatment for the broad area of chronic heart failure. I50.42 chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure. The clinically overt dhf and shf appear to be 2 separate syndromes with distinctive morphologic and functional changes although signs, symptoms, and prognosis are.
Underlying causes, risk factors, and precipitating causes of heart failure (hf) should be treated. Systolic heart failure occurs during a heartbeat and relates to the pumping function, whereas diastolic heart failure occurs between heartbeats. Patients have a history of chf most of the time.
If you have systolic heart failure, it means your heart isn’t contracting well during heartbeats. Systolic heart failure, also known as a systolic dysfunction, is one of the most common types of heart failure and it typically affects the left ventricle of the heart. Acute systolic heart failure occurs more suddenly and often is considered a medical emergency.
A protocol of randomized controlled trial. New onset chf is also seen in er. In addition to the systolic recovery, diastolic function was also ameliorated in this chronic model of hf.
Heart failure due primarily to systolic dysfunction (also known as heart failure with reduced ejection) accounts for approximately 50% of the heart failure cases. Both affect the lower left chamber of your heart, known. 222 cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock with mcc.