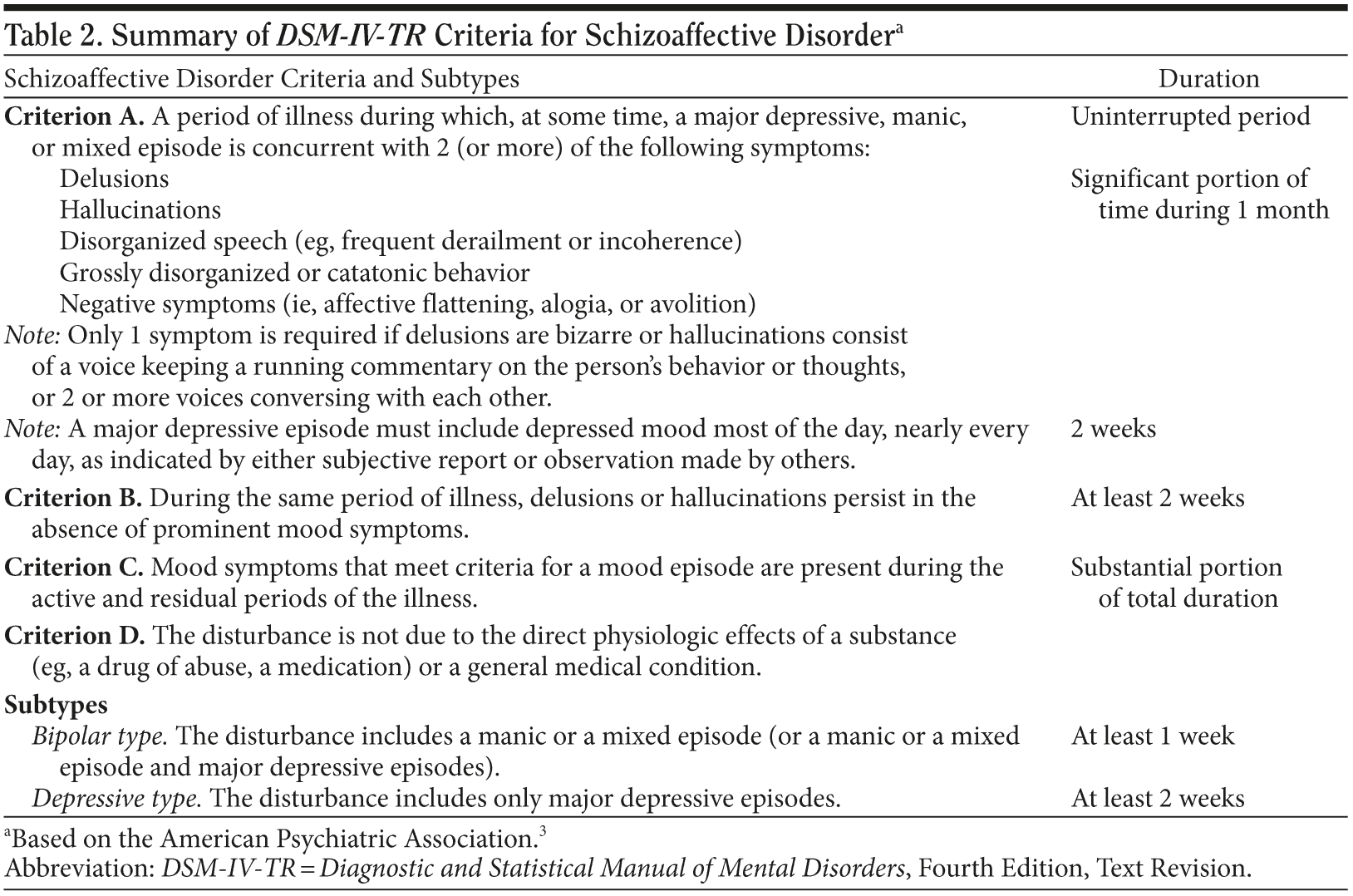
An uninterrupted duration of illness during which there is a major mood episode (manic or depressive) in addition to criterion a for schizophrenia; Diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder.

Some have suggested the removal of schizoaffective disorder, because of poor reliability and limited validity [15].
Criteria for schizoaffective disorder. The formal diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder, depressive type, rests on these symptoms, which can be evaluated by psychiatrists and other mental health professionals. Again, schizoaffective disorder requires a period of at least 2 weeks in which there are only psychotic symptoms without mood symptoms. Schizoaffective disorder is a condition where symptoms of both psychotic.
A disorder in which the individual suffers from both symptoms that qualify as schizophrenia and symptoms that qualify as a mood disorder (e.g., depression or bipolar disorder) for a substantial portion (but not all) of the active period of the illness; An uninterrupted duration of illness during which there is a major mood episode (manic or depressive) in addition to criterion a for schizophrenia; F25.1 schizoaffective disorder, depressive type.
Delusions or hallucinations for two or more consecutive weeks without mood symptoms sometime during the life of the. An uninterrupted duration of illness during which there is a major mood episode (manic or depressive) in addition to criterion a for schizophrenia; Diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder expert rev neurother.
Symptoms of schizoaffective disorder schizoaffective disorder is, in effect, a cross between a disturbance in thought and a disturbance in mood. Some have suggested the removal of schizoaffective disorder, because of poor reliability and limited validity [15]. Diagnostic criteria for 295.70 schizoaffective disorder.
For the remainder of the active period of the illness, the individual suffers from delusions or hallucinations in the absence of prominent. The diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorder s, fifth edition, helps to clarify the diagnosis, but issues related to validity and reliability remain. Diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder.
Again, patients also do not meet criterion a of schizoaffective disorder. The major depressive episode must include depressed mood. The major depressive episode must include criterion a1:
Schizoaffective disorder is recognised as a separate diagnosis to both schizophrenia and bipolar, despite sharing many similar symptoms. A major mood episode (either major depression or mania) that lasts for an uninterrupted period of time A major mood episode (either major depression or mania) that lasts for an uninterrupted period of time.
An uninterrupted duration of illness during which there is a major mood episode (manic or depressive) in addition to criterion a for schizophrenia; Diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder. The major depressive episode must include depressed mood.
Making this determination is critical to accurately diagnosing schizoaffective vs. Dsm criteria (paragraphs) dsm version. The word schizoaffective has two parts:
With regard to treatment, only a small and heterogeneous. An uninterrupted period of illness during which, at some time, there is either a. Delusions or hallucinations for ≥2 weeks
Both symptom clusters (depressive/manic and schizophrenic) must exist at the same time (comorbid) to justify a diagnosis of this disorder. The major depressive episode must include depressed mood. Keep in mind that one of the primary criteria for a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder is the presence of delusions or hallucinations for two weeks in the absence of a mood disorder (such as depression or mania).
An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive or manic) concurrent with criterion a of schizophrenia note: