The genetic test is only going to reveal an association or a probability that someone might get type 1 or type 2 diabetes, because the disease is not only caused by genetic variation. However, these variants are also found in the general population, and only about 5 percent of individuals with the gene variants develop type 1 diabetes.
The environmental determinants of diabetes in the young (teddy) study group, 2008), combined by genetic predisposition (bluestone et al., 2010;
Diabetes type 1 genetics. Type 1 diabetes develops through the interaction of complex genetic and environmental influences. Brother or sister with diabetes increases risk by 10%. Diabetes mellitus type 1 (dm1) itself is not inherited, but a predisposition to developing the condition can run in families.
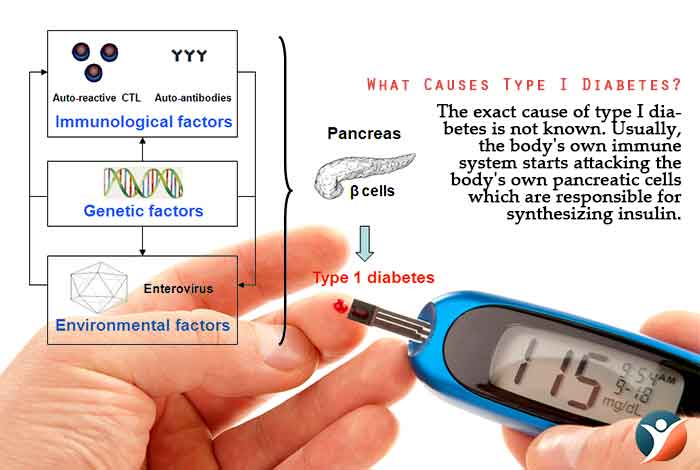
The pathology of type 1 diabetes is discussed in more detail in part 2.1 (ii), but to summarise, consensus opinion is that type 1 dm is caused by environmental factors (maclaren and atkinson, 1992; This article reviews the current knowledge on the genetics of t1d. Estimated contribution of genetic factors to type 1 diabetes risk is ~50%.
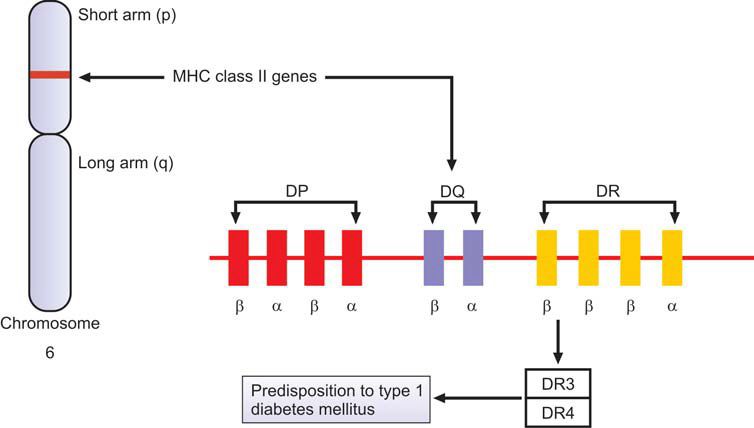
Hla variations account for approximately 40 percent of the genetic risk for the condition. In the general population, the risk of developing type 1 diabetes is around 1 in 250. This can include both family history, as well as the presence of certain genes.
Both parents with diabetes increases risk by 30%. Genetics and diabetes background diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by persistent hyperglycemia. Other hla variations appear to be protective against the disease.
Mother with diabetes increases risk of diabetes by 2%. Twin studies provide one line of evidence. The disease is most likely triggered at an early age by autoantibodies primarily directed against insulin or glutamic acid decarboxylase, or both, but rarely
There are several groups of genes that play a role in type 1 diabetes risk. Some genes make you more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, while others protect you from it. It is the most common form of diabetes in children, and its incidence is on the rise.
The role of genes in susceptibility to t1d. Genetic analysis of chromosome 2 in type 1 diabetes: Genetics of diabetes type 1 📋treatment guidelines
There are several lines of evidence indicating a strong genetic component causing susceptibility to the disease. Genetics of diabetes type 1 herbal teas are gaining popularity in the united states and this could be due to the infusion of western and eastern medicine techniques being blended together. Many of these are called hla genes, which are related to the immune system.
Yet when one twin has type 1 diabetes, the other gets the disease, at most, only half the time. While the exact cause is not known, some genetic risk factors have been found. The combination of these genes determines your risk.
However, it is not yet fully understood how genetic variation relates to the underlying mechanism of disease. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that has a very significant genetic component. The greatest genetic risk (both increased risk, susceptible, and decreased risk, protective) for type 1 diabetes is conferred by specific alleles, genotypes, and haplotypes of the hla class ii (and class i) genes.
While some people with a family history of dm1 may be at an increased risk, most will not have the condition. Evidence for the contribution of genetics to type 1 diabetes. Dr john mordes, university of massachusetts medical school, studies genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes.
Identical twins have identical genes. Such mixed family history is associated with an intermediate phenotype of diabetes: The overall risk of t1d in the general population is 0.4%, but it is higher in relatives of patients.
Type 1 diabetes is the most common autoimmune disorder in childhood, characterized by the development of autoimmunity through unknown environmental insults in genetically susceptible individuals. The environmental determinants of diabetes in the young (teddy) study group, 2008), combined by genetic predisposition (bluestone et al., 2010; Type 1 diabetes is partially caused by genetics, and family members of type 1 diabetics have a higher risk of developing the disease themselves.
In most cases of type 1 diabetes, people need to inherit risk factors from both parents. When one twin has type 2 diabetes, the other�s risk is three in four at most. The genetic test is only going to reveal an association or a probability that someone might get type 1 or type 2 diabetes, because the disease is not only caused by genetic variation.
Join leading researchers in the field and publish with us. One proof of this is identical twins. Type 1 diabetes, a multifactorial disease with a strong genetic component, is caused by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β cells.
However, these variants are also found in the general population, and only about 5 percent of individuals with the gene variants develop type 1 diabetes. Father with diabetes increases risk of diabetes by 8%. Genetic predisposition is thought to be a major risk factor in the development of type 1 diabetes.