We agree that understanding the population effect of these guidelines is important. All of the ada recommendations and the following:
The guidelines also give specific recommendations regarding statin therapy when planning or during pregnancy.
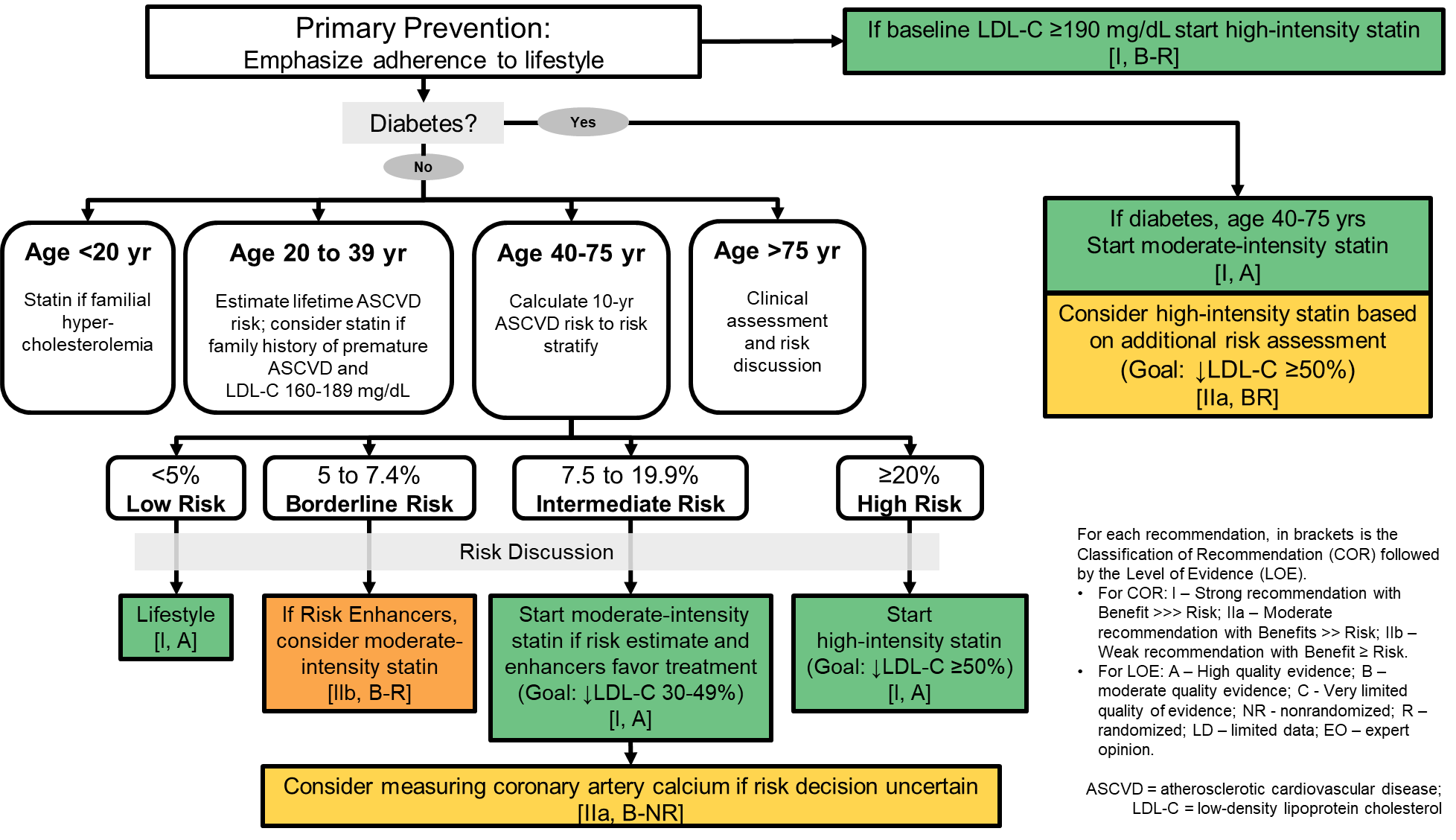
Guidelines for statin therapy. All of the ada recommendations and the following: The primary goal is an ldl cholesterol <100 mg/dl (<2.6 mmol/l) (a). We agree that understanding the population effect of these guidelines is important.
Statin therapy should be added to lifestyle therapy, regardless of baseline lipid levels, for diabetic patients: The findings were consistent for men and women. Use a maximally tolerated statin to lower ldl‐c levels by ≥50%.
The extent to which patients with new or worsening pad symptoms are offered guideline therapy is unknown. 24 in response, the mayo clinic established a task force, which. We wish to emphasize that the uspstf issued 2 recommendations.
Guideline & other references the following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: They were particularly important for people at intermediate risk, for whom deciding when to begin statin therapy is challenging. Nearly, all who qualified for statin therapy by the 2016 esc/eas guidelines also did so with the 2019 guidelines (figure 1 and table 2).
Statin therapy to treat to target cholesterol levels, the 2013 acc/aha guideline on treating blood cholesterol focuses instead on the use of statin therapy to address the broader goal of reducing ascvd risk and events. The 2018 aha/acc cholesterol guidelines include many of these geriatric concepts when considering statins for primary prevention in older adults, citing functional decline (physical or cognitive), multimorbidity, frailty, or reduced life expectancy. The primary goal is an ldl cholesterol <100 mg/dl.
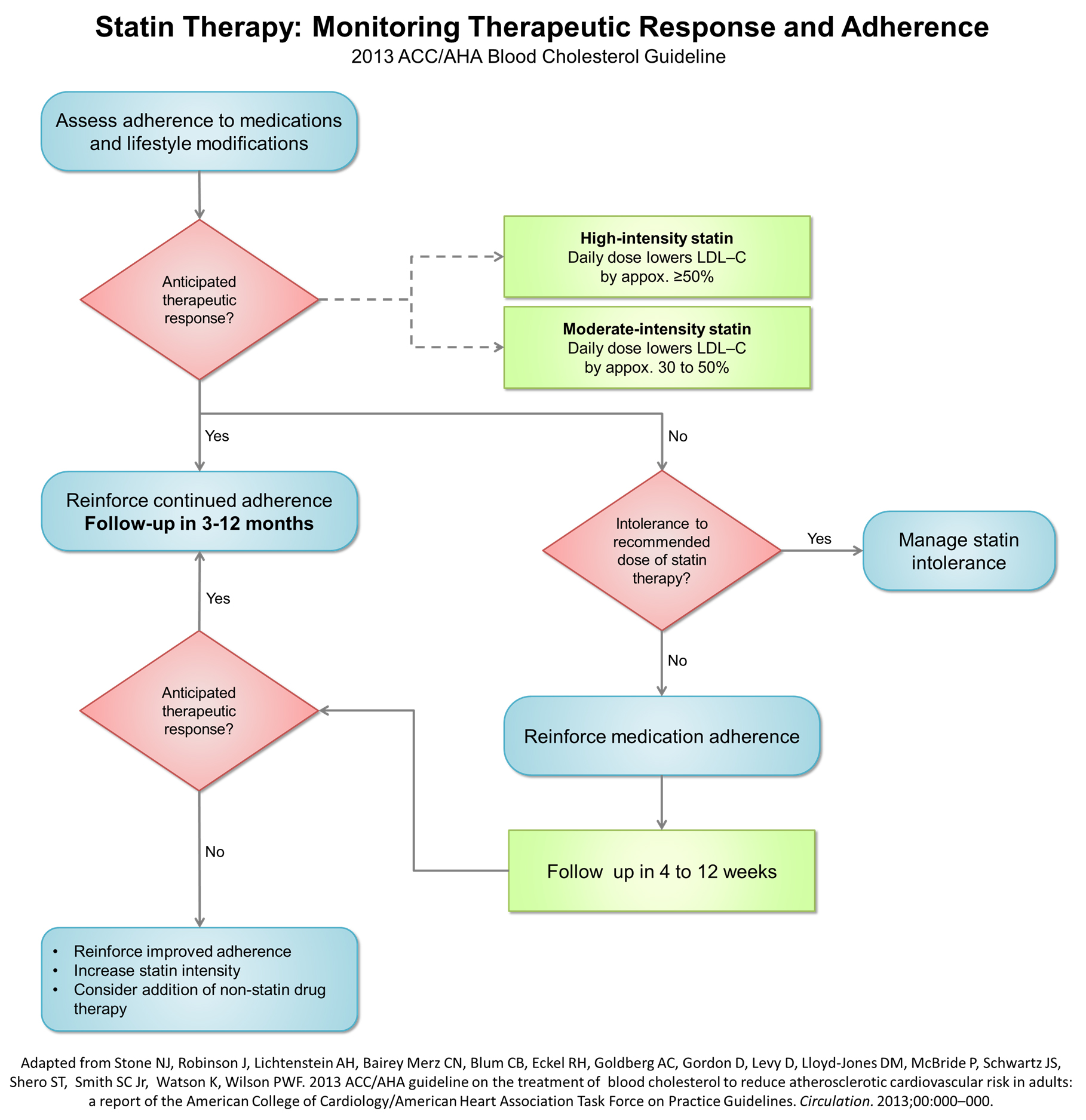
Do not routinely exclude from statin therapy people who have an alt that is raised but less The new guidelines proved more accurate and efficient at identifying people at increased risk of both cardiovascular disease and subclinical coronary artery disease. • start with the appropriate intensity of statin therapy to reduce ascvd risk, and regularly monitor patients for adherence to lifestyle changes and appropriate intensity of statin therapy.
• statin therapy is safe when used properly and monitored. Sexually active women on statin therapy are advised to use effective forms of contraception (class i recommendation). The more ldl‐c is reduced on statin therapy, the greater will be subsequent risk reduction.
The guidelines also give specific recommendations regarding statin therapy when planning or during pregnancy. Statin therapy for secondary prevention in patients with clinical In addition, we performed a synthesis of information from all other recommendations for older adults regarding statin treatment.
Statin therapy should be added to lifestyle therapy, regardless of baseline lipid levels, for diabetic patients: Measure alt within 3 months of starting treatment and at 12 months, but not again unless clinically indicated. The importance of using a high dose of a statin.
We selected all guidelines with recommendations (instructions and suggestions) on discontinuation of statin treatment applicable to older adults, published between january 2009 and april 2019. All of the ada recommendations and the following: Women planning to become pregnant should stop statin therapy 1 to 2 months before pregnancy is attempted.
Understanding of statin use, focused on myopathy, and to provide updated recommendations for the appropriate use of statins, including cautions, contraindications, and safety monitoring for statin therapy. 2.in patients with clinical ascvd, reduce low‐ density lipoprotein cholesterol (ldl‐c) with high‐intensity statin therapy or maximally tolerated statin therapy. The following are guideline recommendations for statin treatment:
• engage patients in the discussion before initiating statin therapy and lifestyle changes.