It works by activating antithrombin, which in turn inactivates thrombin and prevents clot formation. 1 one third of hospitalised patients in the usa,.

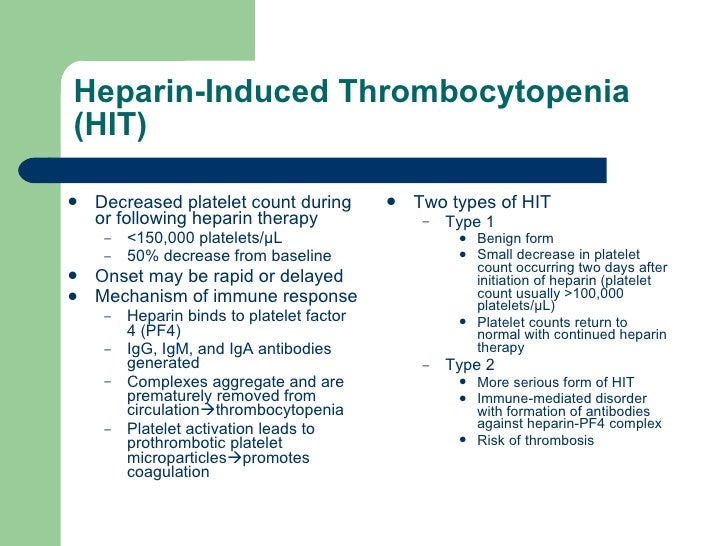
This is the time taken for hit antibodies to be formed.
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia treatment. Further, the therapy has showed some success in reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with thrombotic conditions. Stop all heparin exposure, including lmwh, prophylactic heparin, heparin locks or flushes, and remove heparin‐coated catheters. Recommendations address screening of asymptomatic patients for hit, diagnosis and initial management of patients with suspected hit, treatment of acute hit, and special situations in.
Patients who experience hit may also develop thromboembolic complications that are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Hit usually occurs after you are. The following guideline is intended to guide the management of heparin induced thrombocytopenia and includes recommendations for diagnosis and treatment agents.
15 mg twice daily × 3 weeks, then 20 mg daily isolated hit: 5 mg po twice daily until platelet recovery hitt: If a patient has been exposed to heparin within the past 100 days then thrombocytopenia can occur within 24 hours as a result of preformed antibodies.
It works by activating antithrombin, which in turn inactivates thrombin and prevents clot formation. 150 mg po twice daily until platelet recovery hitt: Heparin is widely used for thromboprophylaxis or treatment in many clinical situations, including cardiovascular and orthopaedic surgery and invasive procedures, acute coronary syndromes, venous thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, peripheral occlusive disease, dialysis, and during extracorporeal circulation.
Patients with hit are best managed by, or in consultation with, a specialist experienced in managing hit. It addresses the problem of thrombocytopenia developing in patients receiving heparin therapy and emphasises the importance of diagnosing heparin induced thrombocytopenia as a serious complication of therapy with a high morbidity and mortality. 3,4 hit is a profound hypercoagulability state 5.
Heparin is a widely used natural anticoagulant or �blood thinner�. 1 one third of hospitalised patients in the usa,. © 2015 thrombosis canada page 3 of 5.
150 mg twice daily until platelet count recovery none rivaroxaban1,2 hitt: Diagnosis rests on a clinical assessment of disease probability and laboratory testing. While the condition carries a high risk for morbidity and mortality, early detection and prompt treatment can greatly reduce the associated risk to life and limb.
Because it is so important to diagnose there is first a section on monitoring of patients at high. Patients who experience hit may also develop thromboembolic complications that are associated with morbidity and mortality. A number of thrombotic conditions need heparin therapy to reduce the risk of thrombosis.
10 mg po twice daily for 1 week then, 5 mg po twice daily isolated hit: This is the time taken for hit antibodies to be formed. Target population adult patients with suspicion or diagnosis of heparin induced thrombocytopenia key practice recommendations screening for hit 1.
A fall in platelet counts and a hypercoagulable state characterize hit. The risk is higher with the use of unfractionated heparin, longer duration of therapy, and among surgical patients and elderly women. Management involves immediate discontinuation of heparin and initiation of an.
Platelets help the blood clot. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia with thrombosis (hitt):