This long association with medicinal plant use may be a factor in the accumulation of antibiotic. However, evolution is rarely linear, and gene gain, duplication, loss, and horizontal gene transfer in bacteria confound.

The prevalence of antibiotic resistance in different countries layered according to the history of the introduction of antibiotics to their markets:
History of antibiotic resistance. Soon it got resistance to bacteria. However, very few new classes of antibiotics have been developed since the late 1960s, and. Policies recommended by the world health organization (who) include research on new antibiotics.
That means the germs are not killed and continue to grow. Brief history of resistance and antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance has been described as one of the greatest global threats of the 21st century.
Evolution and spread of resistance. It is possible to tie some of the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance determinants to major evolutionary events inferred by other phylogeneticists, such as divergence of major lineages or the emergence of large groups of organisms (battistuzzi and hedges 2009). At times in our history disease has
Antibiotic resistance is an increasing problem worldwide. Resistance genes to almost all classes of antibiotics have emerged. Historical contingency in the evolution of antibiotic resistance after decades of relaxed selection.
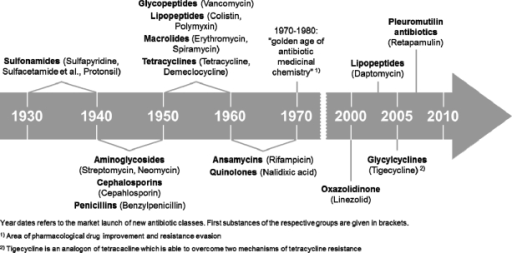
The first antibiotic marketed is penicillin in 1941; No new class has been discovered since daptomycin and linezolid in the 1980s, and only optimisation or combination of already known compounds has been recently commercialised. However, evolution is rarely linear, and gene gain, duplication, loss, and horizontal gene transfer in bacteria confound.
This paper traces the evolving response to antibiotic resistance through what at this point appear to be five eras: That between 1945 and 1963, a relatively optimistic period during which time the. 1 although it was recognized soon after antibiotics were first introduced, the impact was mitigated initially by the development and use of newer agents.
This battle has ranged throughout the centuries and across the globe. Our adversaries have been war, famine, death and disease…………. One interesting element to this puzzle is that bacteria acquire resistance to different antibiotics at different rates.
Drug resistant infections and why it matters to you since the very dawn of mankind the human race has struggled for survival. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria change in response to the use of these medicines. Antibiotic resistance has become a major threat to modern medicine.
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria grow and spread in the presence of antibiotics that are normally active against them. An illustrated history of antibiotic resistance. This long association with medicinal plant use may be a factor in the accumulation of antibiotic.
[1] ancient greeks, indians, and others, use mouldy bread, plants, soil, to treat infections. The natur al histor y of antibiotic resistance genes can be revealed through the ph ylogenetic rec onstruction and this kind of analysis suggests the. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
Ad stroke research and treatment invites cerebral circulation & associated disease research. Historical influences on antibiotic resistance. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance in different countries layered according to the history of the introduction of antibiotics to their markets:
For example, a history of adaptation to one antibiotic could alter resistance and subsequent evolution in the presence of a subsequent antibiotic. Antibiotic resistance happens when germs like bacteria and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. A brief history of antibiotic usage & resistance.
The history of antibiotics antibiotics have been used for millennia to treat infections, although until the last century or so people did not know the infections were caused by bacteria. By comparing thousands of bacterial genomes, researchers have traced back the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance genes. Hindawi�s academic journals cover a wide range of disciplines.
This review demonstrates a brief history of antibiotics, global strategies regarding this threat, mechanism of action of antibiotics as well as antibiotic resistance to the readers. Nat rev microbiol 15, 577 (2017).