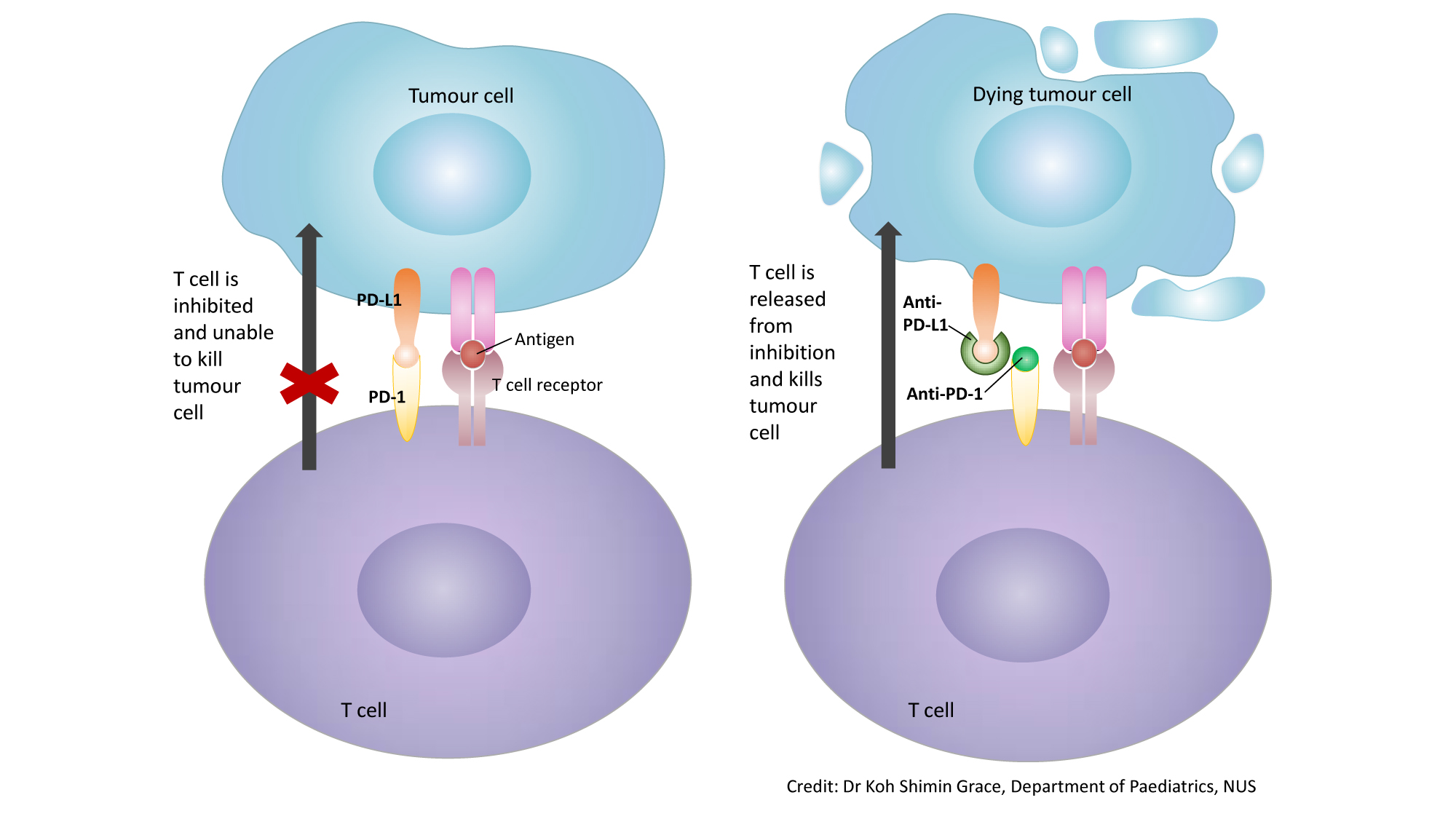
Immune checkpoint inhibitors stop the immune system from turning off before cancer is completely eliminated. Consequently, these drugs have dramatically increased in clinical use since being first approved for advanced melanoma in 2011.

Importance immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) are part of standard of care for patients with many advanced solid tumors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. These events, which may reflect enhanced t cell ac. Most of the benefit for checkpoint inhibitor drugs after 2015 was due to the responders with nsclc: These therapies are effective in multiple different tumor types.
It normally acts as a type of “off switch” that helps keep the t cells from attacking other cells in the body. Cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation (ctla4, pd1) a2ar : Multiple databases were searched for articles published until november 2020.
All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. In general, immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy may be continued while most grade 1 events are managed. The immune system relies on t cells to fight cancer.
These specialized cells are extremely powerful and have the potential to damage healthy cells. The adenosine a2a receptor is regarded as an important checkpoint in cancer therapy because adenosine in the immune microenvironment, leading to the activation of the a2a receptor, is negative immune feedback loop and the tumor microenvironment has relatively high. Patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction are traditionally ineligible to partake in pivotal randomized clinical trials of icis.
While management varies according to the organ system affected, in general, icpi therapy should be continued with close monitoring for grade 1 toxicities, except for some neurologic, hematologic, and cardiac toxicities. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with preexisting inflammatory bowel disease. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have emerged as a remarkable treatment option for diverse cancer types.
Icis act through a unique mechanism of action when compared with those of conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Immune checkpoint inhibitors stop the immune system from turning off before cancer is completely eliminated. 5.92% in 2016, 6.78% in 2017, and 7.09% in 2018, although the benefit of checkpoint inhibitors for nsclc was a lower proportion in later years than in earlier years, with the approval of multiple checkpoint inhibitors for more indications.
Consequently, these drugs have dramatically increased in clinical use since being first approved for advanced melanoma in 2011. Received immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy between january 2010 and february 2019. Importance immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) are part of standard of care for patients with many advanced solid tumors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy: T cell activity is controlled through “immune checkpoints,”. Backward selection and multivariate logistic regression were conducted to assess risk of gi adverse events.
Icpi therapy may be suspended for most grade 2 toxicities, with consideration of resuming when symptoms revert ≤ grade 1. The similarities and differences among the clinical guidelines for the management. Studies were deemed eligible if they compared overall survival (os),.
Methods a multidisciplinary panel of medical oncology, dermatology, gastroenterology, rheumatology, pulmonology, endocrinology, neurology,. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) have substantially changed the field of oncology over the past few years. I = immediate family member, inst = my institution.
Checkpoint inhibitor therapy appears to be safe in patients with baseline renal impairment from a nonimmune basis (eg, prior nephrectomy, old age, hypertension); In 5 out 47 vte patients (10.6%), the scheduled application of immune checkpoint. They’re a type of immunotherapy.
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. In recent years, the use of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ici) therapy has rapidly grown, with increasing u.s. Uses the immune system to attack malignancies.
This class of therapy will likely be used increasingly to treat other forms of cancer in the future. However, patients with a renal allograft are at high risk of rejecting the.