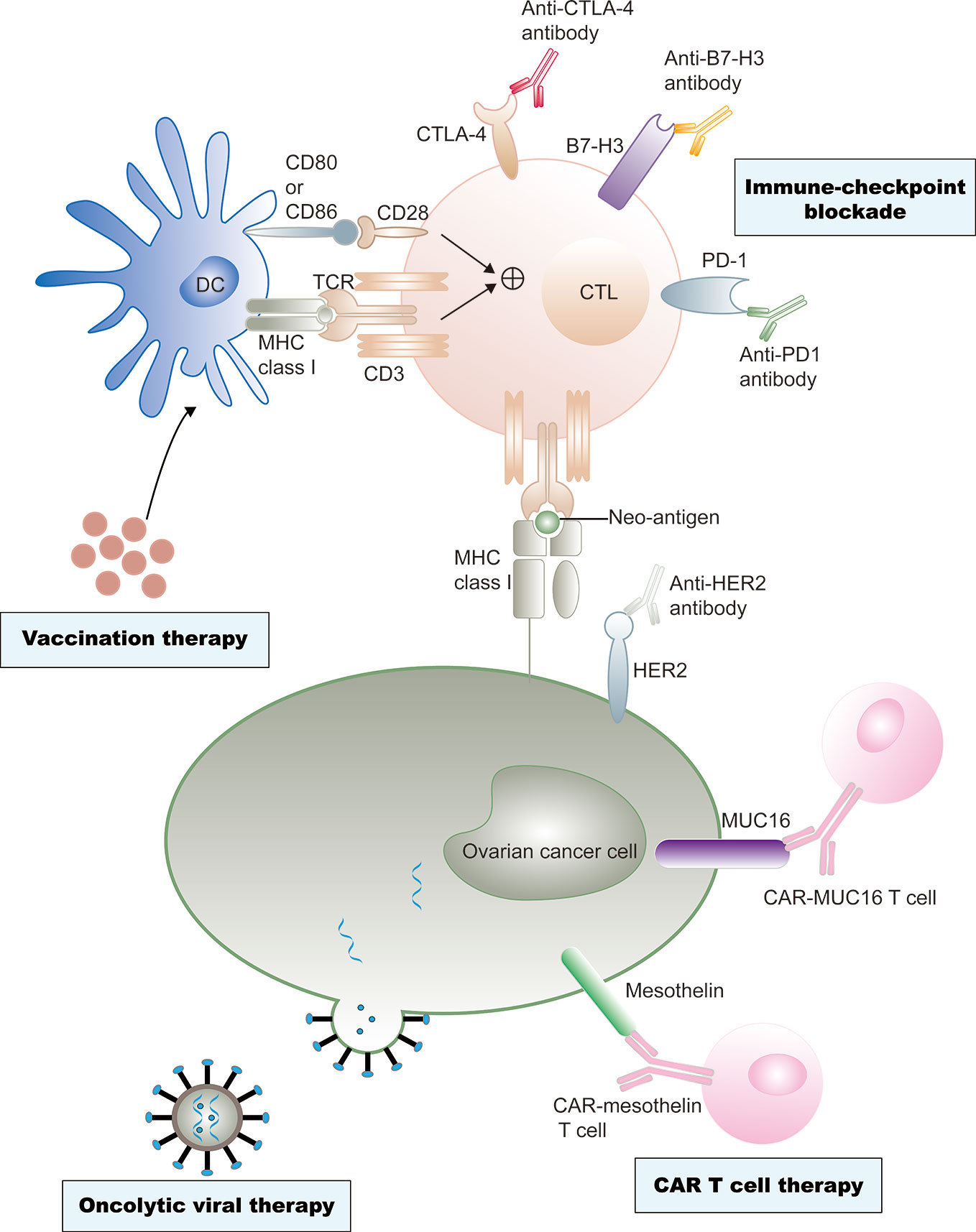
The first has the aim of stimulating an antitumor response from the patient’s own immune system itself inducing also an immunological memory. Although immunotherapy’s use in ovarian cancer lags other cancer types, matthew powell, m.d., believes there is still hope for checkpoint blockades in this field, likely in combination with other agents.
9 not only was the vaccine associated with an improved pfs, but it also enhanced preexisting and induced.
Immunotherapy and ovarian cancer. This treatment trains your immune system to remember cancer cells. Developments with immunotherapy, maintenance therapy, and novel strategies push the field of women’s cancers forward. Immunotherapy is a type of drug treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer.
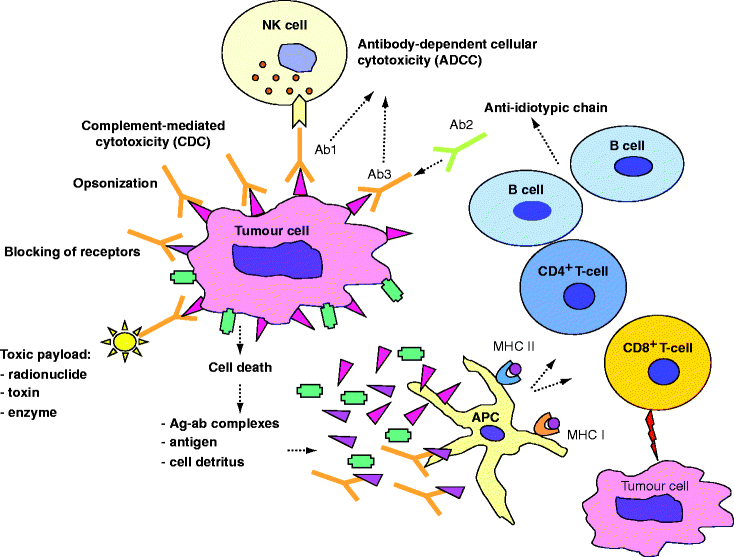
Ovarian cancer is one such example. Checkpoint inhibitors are a type of precision cancer immunotherapy that helps to restore the body’s immune system to fight the cancer by releasing checkpoints that cancer uses to shut down the immune system. Background immunotherapy knows three different strategies ( table 1 ):
However, it is important to mention the resistance of various cancer cells to immune checkpoints blockade treatment. The first has the aim of stimulating an antitumor response from the patient’s own immune system itself inducing also an immunological memory. A highly immunogenic subgroup of clear cell ovarian carcinoma with microsatellite instability has also been documented, which might comprise potentially good responders to immunotherapy [49].
Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer immunotherapy is the use of medicines to stimulate a person’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. Regulatory strategies for drug development sanjeeve bala, md, mph ovarian cancer endpoints workshop Ovarian cancer moon shot works to broaden immunotherapy impact.
9 not only was the vaccine associated with an improved pfs, but it also enhanced preexisting and induced. Ovarian cancer (oc) is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy, affecting approximately 1 in 70 women with only 45% surviving 5 years after diagnosis. In this review, the authors integrate emerging information on immunosuppressive mechanisms and t cell phenotype and discuss strategies of immunotherapeutic and vaccine regimens.
These responses were also seen in combination with immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy. Although immunotherapy’s use in ovarian cancer lags other cancer types, matthew powell, m.d., believes there is still hope for checkpoint blockades in this field, likely in combination with other agents.
The aim of this systematic review was to assess the clinical efficacy of specific immunotherapy in. Active immunotherapy, passive immunotherapy and immunomodulation. Ovarian cancer and modern immunotherapy:
A monoclonal antibody that targets the vegf/vegfr pathway and inhibits tumor blood vessel growth; One barrier to successful ovarian cancer treatment is that eventually the cancer becomes resistant to chemotherapy. In australia, immunotherapy drugs are currently available as treatment options for some types of cancer, such as melanoma and lung cancer.
Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer shows tremendous potential for addressing this devastating disease. Powell is a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and chief of the division of gynecologic oncology, washington university school of medicine, at. Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer.
These studies were preceded by small trials exploring. So far one immunotherapy drug, avastin, has been approved for. It is made up of white blood cells and organs and tissues of the lymph system.
The immune system helps your body fight infections and other diseases. Two key immunotherapy studies in ovarian cancer were presented during the american society of clinical oncology 2020 annual meeting. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most lethal gynecological cancer.
This treatment trains your immune system to remember cancer. Several approaches of active and passive immunotherapy for eoc have been studied. In the past two decades, immunotherapy has rapidly developed, and has revolutionized the treatment of various types of cancer.
Researchers suggest immunotherapy may be a way to overcome this. Surely, there would be a way to enhance the activity of immunotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer, a setting in which progress had remained elusive. Unfortunately, immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, are not very effective on their own in ovarian cancer.
At present, immunotherapy has not been proven to be an effective treatment for.