The catheter is inserted into the femoral vein and advanced through the inferior vena cava (or, if into an antecubital or basilic vein, through the superior vena cava), right atrium, and right ventricle and into the pulmonary artery. Left ventricular failure is often caused by chronic high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and faulty heart valves leading to the.

The heart is usually the size of a fist, but it has the ability to grow in response to the demands that are placed on it, as is the case during pregnancy, strenuous exercise, and when you have a heart condition.
Left sided heart enlargement. In the case of ph associated with lhd,. The right side of the heart is not able to cope with large pressures in the same way the left side does, so in periods of stress it may enlarge and fail immediately. This can occur either by an enlargement of the atrial chambers or the left ventricular chamber when heart failure develops.
In order to determine if echocardiographic left atrial enlargement is an early sign of hypertensive heart disease, we evaluated 10 normal and 14 hypertensive patients undergoing routine diagnostic cardiac catheterization for echocardiographic left atrial. Ecg signs of left atrial enlargement: Left atrial abnormality on the electrocardiogram (ecg) has been considered an early sign of hypertensive heart disease.
Right ventricular hypertrophy (also called right ventricular enlargement). Ad start your recertification in 60s. Hypertension (high blood pressure) left atrial enlargement is often present in.
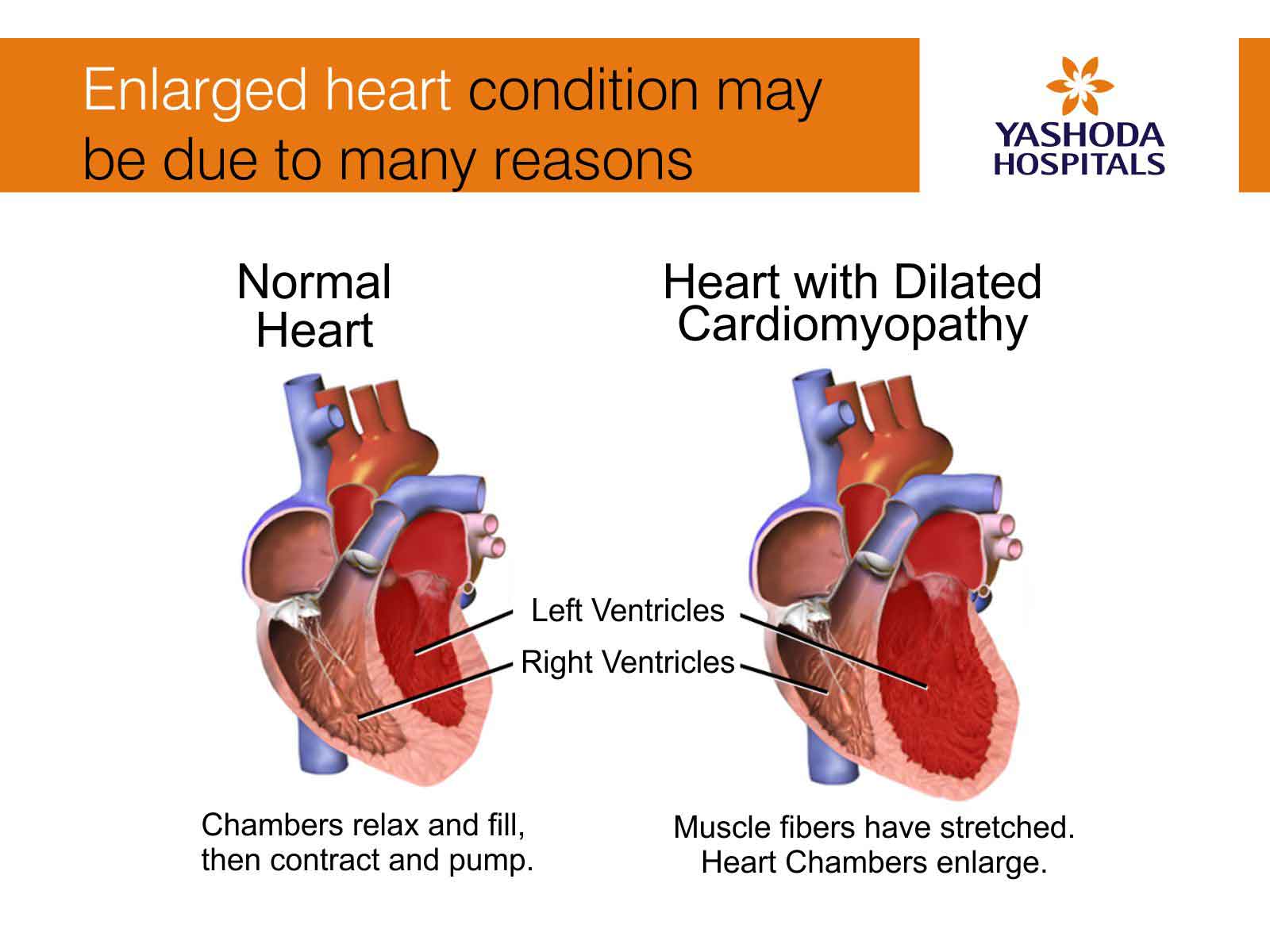
An enlarged heart, also known as cardiomegaly, is a condition that occurs when the heart has to work harder as a result of stress, infection, or heart disease. When this happens, it is called left atrial enlargement. Left atrial enlargement is a dilation of the heart�s left atrium.
The left side pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of your body. Alcohol, for example, can lead to enlargement and weakness of the left ventricle, resulting in cardiomegaly. In some cases, however, it can.
Over time, this enlargement can lead to congestive heart failure or the occurrence of arrhythmias (irregularities of the heart�s rhythm). Left atrial enlargement does not always cause symptoms, and someone may only discover it during a test for another problem. Pulmonary hypertension (ph) due to left heart disease (lhd) is the most common type of ph and is defined as mean pulmonary artery systolic pressure of >20 mm hg and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure >15 mm hg during right heart catheterization.
Sometimes referred to as left atrial dilation or left atrial hypertrophy , this condition is most often seen in obese individuals or in those who have an abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation. However, the right ventricle (rv) is unique in structure and function and is affected by a set of disease processes that rival that of the lv. Left atrial enlargement can occur in association with systemic hypertension, aortic stenosis, mitral incompetence, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
It also may double the. Sometimes, cardiomegaly can be transient. The heart is usually the size of a fist, but it has the ability to grow in response to the demands that are placed on it, as is the case during pregnancy, strenuous exercise, and when you have a heart condition.
♥common and can be very subtle.often the left atrium is not appreciably enlarged. Left heart disease (lhd) is the most frequent cause of pulmonary hypertension (ph), arising in response to increased left ventricular (lv) or left atrial filling pressure in a wide range of cardiac disorders [ 1 ]. Ph is defined by a mean pulmonary arterial pressure ( ppa) ≥25 mmhg;
Huge precordial r and s waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (sv2 + rv6 >> 35 mm). The catheter is inserted into the femoral artery or the antecubital artery. Left ventricular failure is often caused by chronic high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and faulty heart valves leading to the.
Aortic insufficiency generates left cavities overload propitiating left. The high pulmonary blood flow can also lead to volume overload in the left side of the heart, resulting in enlargement (dilatation) of the left atrium and left ventricle. The following conditions can lead to the enlargement of the left atrium:
This article will review the normal structure and function of the rv, describe the pathophysiology of rv failure. According to the american heart association, there are three major types of heart failure: Left atrial enlargement is the dilation of a person�s left atrium.
When addressing heart failure, most commonly, the left ventricle (lv) is the topic of discussion, and the right heart overlooked. Of, near, or relating to the heart: See usage note at coronary.
It is linked to several conditions, including atrial fibrillation and. Alterations of the mitral valve are the classic causes of left atrial enlargement, both mitral stenosis due to increased pressure, and mitral insufficiency due to volume increase. The catheter is inserted into the femoral vein and advanced through the inferior vena cava (or, if into an antecubital or basilic vein, through the superior vena cava), right atrium, and right ventricle and into the pulmonary artery.
Several heart problems can cause the left atrium to swell.