It’s here that a melanoma can form. To understand it, it helps to know how the eye works.
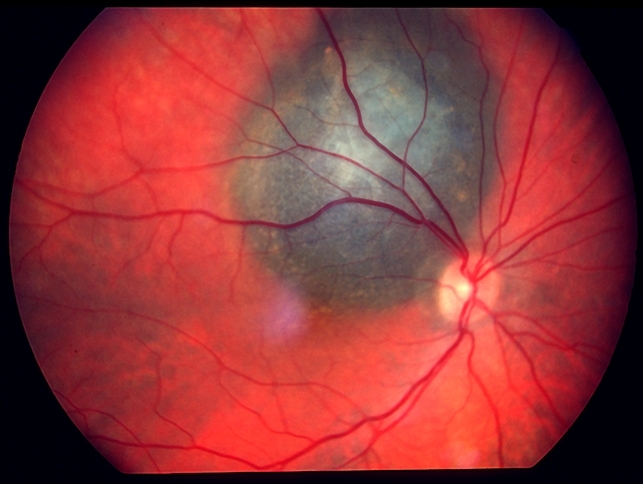
Metastatic malignant melanoma o f t h e retina* ella m.
Melanoma of the retina. Eye, or ocular, melanoma is the most common type of eye cancer. When symptoms of ocular melanoma occur, they may include: Tests that examine the eye are used to help diagnose intraocular melanoma.
When an ocular melanoma occurs in the ciliary body, it can displace the lens of the eye causing blurry vision from cataract or a rapid change in eyeglass prescription (astigmatism). Less commonly, it is found in the eye and other sites of the body. The cancer may only be in the eye.
Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma).in women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back. Intraocular melanoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the eye. Vasoproliferative retinal tumors associated with peripheral chorioretinal scars in presumed congenital toxoplasmosis.
[google scholar] laqua h, wessing a. Melanoma carries the potential to spread from the eye to other parts of the body. Metastatic malignant melanoma o f t h e retina* ella m.
Melanoma usually shows up on the skin, but it also can happen in your eyes. Also, eye melanoma typically doesn’t cause early signs or symptoms. To understand it, it helps to know how the eye works.
The middle layer between the sclera and retina is called the uvea. This is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the white of the eye and retina (back of the eye). Melanoma can also begin on the skin or.
The cancer may only be in the eye. Neovascular glaucoma in these cases may likely be. Ocular melanoma and other eye cancers may not cause symptoms early on unless the cancer grows in certain parts of the eye or becomes more advanced.
In these instances, the patient is typically referred to a retina specialist and often an ocular oncologist (eye cancer specialist). Because most eye melanomas form in the part of the eye you can’t see when looking in a mirror, they can be difficult to detect. A melanoma is a malignant tumor that most often arises in the skin.
Cutaneous malignant melanoma metastatic to the eye has a relatively greater preference for the retina and frequently presents with uveitis and glaucoma. This is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the white of the eye and retina (back of the eye). Rarely, eye melanoma can also occur on the conjunctiva.
Graefes arch clin exp ophthalmol. Signs of intraocular melanoma include blurred vision or a dark spot on the iris. The choroid layer is the most likely site of melanoma in the eye.
The american joint committee on cancer classification allows for categorization and staging of melanoma. Or, it may spread (metastasize) to another location in the body, most commonly the liver. Vision problems (blurred vision or partial or total sudden loss of vision) floaters or flashes of light
The choroid layer is the most likely site of melanoma in the eye. When it does, doctors call it ocular melanoma. In the eye, melanoma arises from the pigmented cells (melanocytes) of the uvea (iris, ciliary body, or choroid).
That�s why it is so important to see your. Melanoma of the eye can affect several parts of the eye, including the: It usually affects the uvea, which is the layer between the retina and the white of.
Peripheral retinal telangiectasis in adults simulating a vascular tumor or melanoma. Baltimore metastatic involvement of the retina by carcinoma or sarcoma is rare. It’s here that a melanoma can form.
Diagnosis of cutaneous malignant melanoma metastatic to the retina and vitreous was confirmed, and the patient expired shortly thereafter. What are symptoms of ocular melanoma? At diagnosis, choroidal melanoma usually appears as a pigmented (85%) tumor underlying the retina with a median basal dimension of 11 mm and a mean thickness of 4.5 mm.
As such, uveal melanoma is most often recognized by the primary eye care specialist. Being older and having fair skin may increase the risk of intraocular melanoma. Rarely is the eye red or painful.
This review will concentrate on choroidal melanoma.