
The bispecific antibodies are given continuously as compared to the car t therapies, which are a one and done treatment. Janssen recently submitted their biologics license application (bla) to the fda seeking for approval of teclistamab, a bispecific antibody for relapsed or refractory myeloma.
The bispecific antibodies are given continuously as compared to the car t therapies, which are a one and done treatment.
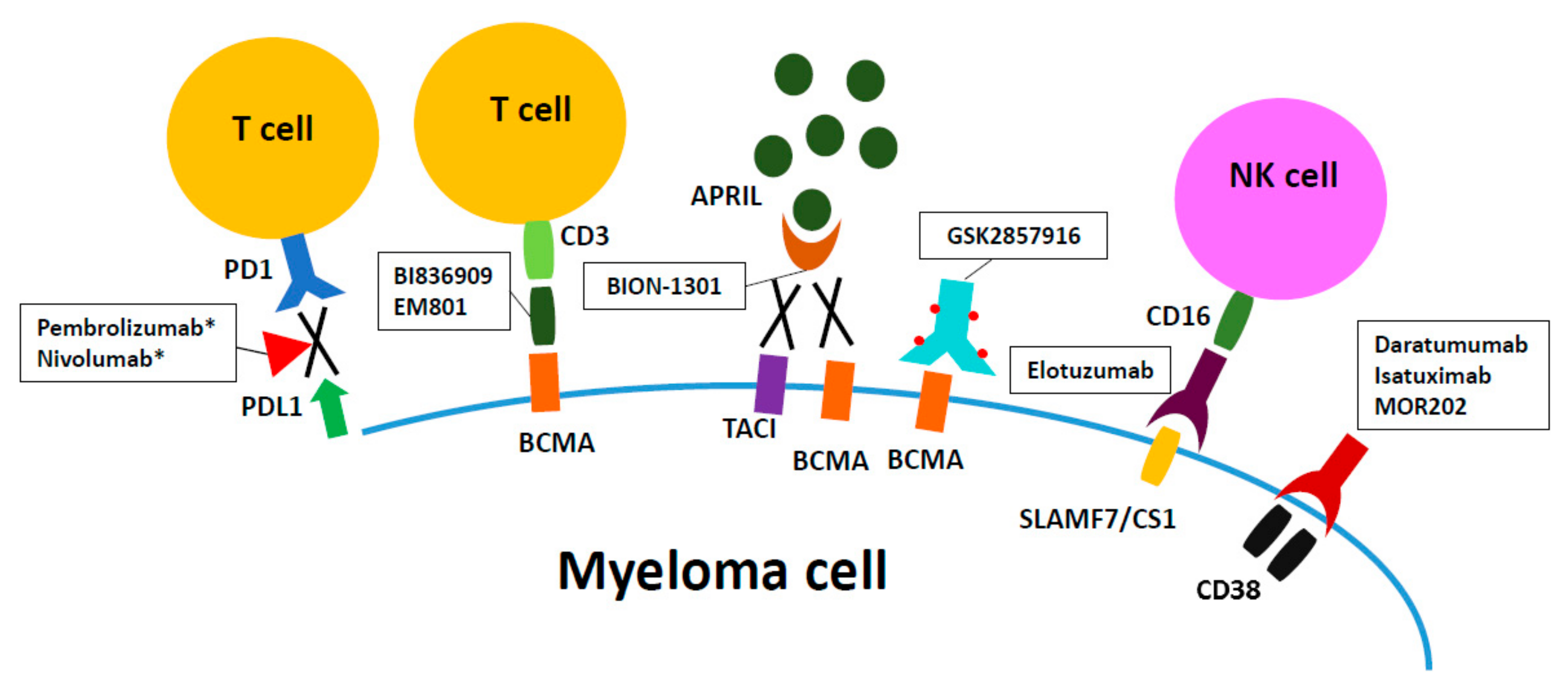
Multiple myeloma antibody treatment. Monoclonal antibodies (mabs) have broadened the treatment scope of numerous pathologies, including cancer. Since launch, daratumumab has become a foundational therapy in the treatment of multiple myeloma, having been used in the treatment of more than 227,000 patients worldwide.16 daratumumab is the. Bispecific antibodies are a novel immunotherapeutic modality with a favorable safety profile and impressive preliminary efficacy in heavily treated patients.
Each works in a different way, but with the common goal of controlling and destroying multiple myeloma cells. Daratumumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets cd38, a cell surface protein that is overexpressed on multiple myeloma (mm) cells. Drug therapies for multiple myeloma.
Janssen recently submitted their biologics license application (bla) to the fda seeking for approval of teclistamab, a bispecific antibody for relapsed or refractory myeloma. Monoclonal antibodies in multiple myeloma. In addition, drugs with a different.
1 globally, over 80 000 new cases of mm are reported each year, representing ~1% of all new cancer cases and 10% of all. I focused on treatment options for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients. The treatment options in multiple myeloma (mm) has changed dramatically over the past decade with the development of novel agents such as proteasome inhibitors (pis);
In multiple myeloma (mm), treatment selection and sequencing become increasingly complex with the increasing number of therapeutic options, including antibodies. The treatment landscape for patients with multiple myeloma (mm) is constantly evolving. A significant number of bispecific antibodies are being developed for multiple myeloma, going after a variety of targets including bcma.
Thalidomide, and lenalidomide which revealed high efficacy and improvement of overall survival (os) in mm patients. High expression of gprc5d has been associated with poor prognosis in multiple myeloma (59). Over the past decade, the introduction of novel agents such as proteasome inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs has led to notable changes in therapeutic strategy, and improvements in survival, yet mm remains incurable in the vast majority of cases.
Elotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting the extracellular domain of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule f7 (slamf7) highly expressed in multiple myeloma cells. Bortezomib and immunomodulatory drugs (imids); Isatuximab is a new antibody treatment that is used to treat multiple myeloma in adults where 3 other treatments have not worked.
Here are highlights from the ”a is for antibody” symposium: In the last years, one further therapeutic option for mm patients is represented by monoclonal antib. Despite continued and considerable progress following the introduction of proteasome inhibitors and immunomodulatory agents, multiple myeloma (mm) remains an incurable disease, and new therapeutic strategies are urgently needed.
Treatment of multiple myeloma (mm) patients has radically changed over the last years following the introduction of next generation proteasome inhibitors (pi) and immunomodulatory derivative (imids). It�s taken with pomalidomide and dexamethasone, and is in the same group of medicines as daratumumab. The first bispecific antibody for multiple myeloma may become fda approved in 2022.
Multiple myeloma is very different from individual to individual. It is approved for adult patients with myeloma in multiple disease settings, from the newly diagnosed to the relapsed/refractory. There are many ongoing clinical trials using novel t.
The number of drugs available now for treating myeloma makes it difficult to know which combination provides the best results. Although more data are needed, bispecifics will likely become an integral part of the multiple myeloma treatment paradigm in the near future. The bispecific antibodies are given continuously as compared to the car t therapies, which are a one and done treatment.
The main types of drug therapies used to treat multiple myeloma are proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs (imids), steroids, histone deacetylase (hdac) inhibitors, antibodies and chemotherapy.