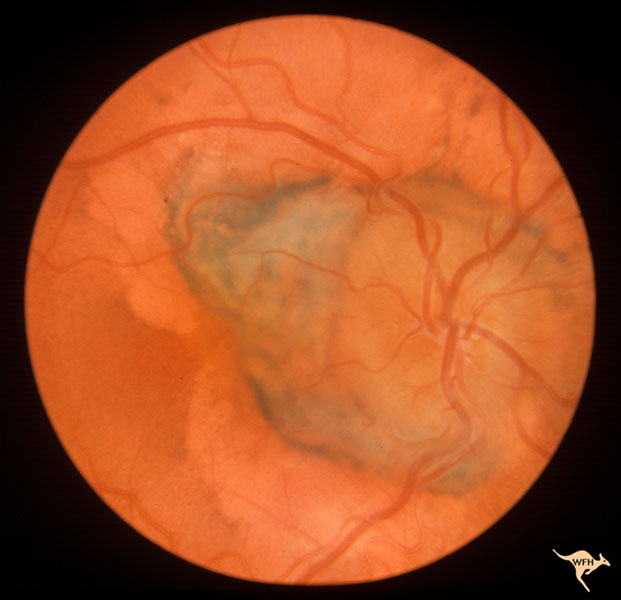
Where a prominent separate drusen body was placed far from the normal disc territory and bordered nasally by a small haemorrhage. Whenit wasseen 5 years later (1981) there wasa marked increase in size and number of these drusen.

Disc drusen gradually change in their ophthalmoscopic appearance throughout a patient’s lifespan.
Optic disc drusen complications. However, optic disc drusen can manifest with hemorrhagic complications. Vascular complications such as aion are common. In some individuals, the deposition of this material can be inherited, while in others it occurs without a family history.
[europe pmc free article] [google scholar] Whenit wasseen 5 years later (1981) there wasa marked increase in size and number of these drusen. Fluorescein angiography showed a diffuse pooling ofthe dye over all this area and the disc.
Retinal hemorrhages as one of complications of optic disc drusen during pregnancy Most patients with disc drusen are asymptomatic, but progressive visual field loss and vascular complications, including anterior ischemic optic neuropathy and choroidal neovascularization, may occur. Papillary hemorrhages and vascular shunts have been reported with disc drusen but their frequency and clinical significance is not well known.
In children, the odd are usually uncalcified and buried within the optic nerve head tissue. There are no treatments available to prevent or ameliorate the vision loss caused by odd. Drusen of the optic disc are associated with slowly progressive optic neuropathy, characterized by accumulation of acellular laminated concretions in the prelaminar portion of the optic nerve.
Ocular complications from disc drusen. Although not as common as visual field defects, retinal hemorrhages have been reported in 2% to 10% of patients with disc drusen. Optic discs with drusen have a higher incidence of vascular complications such as retinal artery occlusions, peripapillary haemorrhages, and anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy.
The cause of this material is unknown. All the visual information taken in by the eye is transmitted to the brain along the optic nerve. Patients with the optic disc drusen should regularly undergo ophthalmologic examinations focused on the intraocular pressure, visual field testing, and retinal fiber layer analysis.
Diagnosing disc drusen is critical because of the serious pathology they can mimic, including disc edema. Optic nerve drusen are abnormal collections of proteins and calcium salts which accumulate in the optic nerve. Drusen of the disc and retinal haemorrhages.
These drusen may change in appearance in early life, but are generally stable in adulthood, and may be associated with visual field defects, anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy, or rarer complications. There are no treatments available to prevent or ameliorate the vision loss caused by odd. Drusen of the optic nerve can cause severe defects of the visual field, decrease of the retinal nerve fiber layer, and may be accompanied by vessels complications.
The optic nerve is the physical connection between the eye and the brain. Patients with the optic disc drusen should regularly undergo ophthalmologic examinations focused on the intraocular pressure, visual field testing, and retinal fiber layer analysis. 10 three types of hemorrhages have been reported in association with disc drusen.
We observed visual field loss (vfl) in 64% (49 of 77) of our patients. Initially, papilledema is often diagnosed an. Optic nerve drusen what are optic nerve drusen?
Although typically benign, patients with disc drusen should be monitored on a regular basis to rule out ocular complications, which can be potentially sight threatening. Most patients with disc drusen are asymptomatic, but progressive visual field loss and vascular complications, including anterior ischemic optic neuropathy and choroidal neovascularization, may occur. Hemorrhagic complications of drusen of the optic disk.
In both cases visual acuity was 20/100 in. Prevent serious complications from bleeding. Sanders te, gay aj, newman m.
Ancillary testing, including ultrasonography, fluorescein angiography, fundus autofluorescence, and optical coherence tomography, may aid in the correct diagnosis of optic disc drusen. Disc drusen gradually change in their ophthalmoscopic appearance throughout a patient’s lifespan. Where a prominent separate drusen body was placed far from the normal disc territory and bordered nasally by a small haemorrhage.
This case highlights the possible ocular complications of disc drusen and the complexity in their treatment because of the risk of visual acuity loss. Drusen of the optic nerve can cause severe defects of the visual field, decrease of the retinal nerve fiber layer, and may be accompanied by vessels complications.