Epithelial ovarian cancer (oc) is the most lethal gynaecological malignancy worldwide with 22,530 estimated new cases in 2019, 13,980 deaths in 2019 and a median overall survival (os) of less than 5 years (1). Immunotherapy is an emerging area within gynecologic malignancies.
Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer shows tremendous potential for addressing this devastating disease.
Ovarian cancer and immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is an emerging area within gynecologic malignancies. Intraperitoneal radiation therapy is being studied to treat advanced ovarian cancer. It uses your body’s immune system to prevent, control, and get rid of.
Renewed optimism arose around the possibility that combination treatments would deliver the positive results the community was waiting for. In 2014, the first immunotherapy treatment for ovarian cancer was approved by the fda. Immunotherapy may overcome chemotherapy resistance.
Ca125 velocity at relapse is a highly significant predictor of survival post relapse: Is there a role for immunotherapy in ovarian cancer? At present, immunotherapy has not been proven to be an effective treatment for.
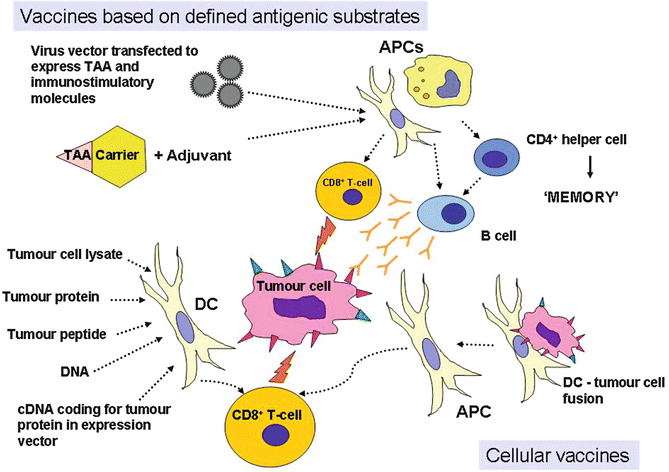
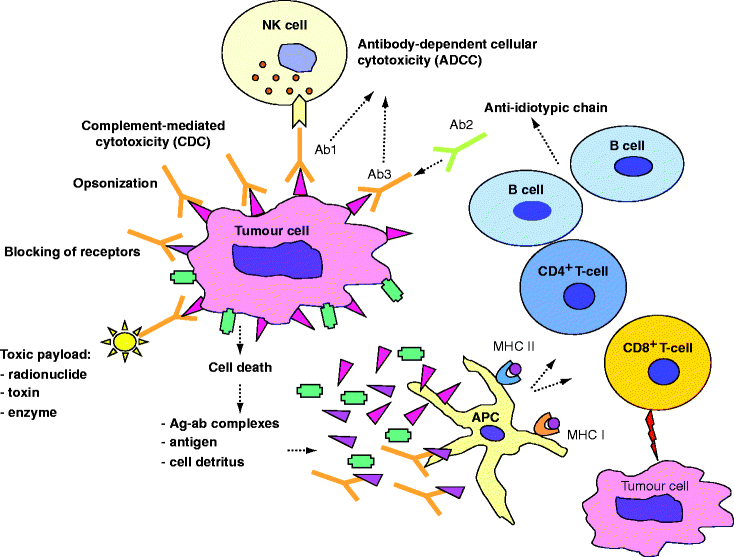
Ovarian cancer moon shot works to broaden immunotherapy impact. Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment. Background immunotherapy knows three different strategies ( table 1 ):
We found that immune checkpoint genes correlate negatively with a higher risk score. In recurrent ovarian cancer, 1,2. Known and feared for vague and uncharacteristic symptoms that often mean the disease is.
Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer shows tremendous potential for addressing this devastating disease. New type of immunotherapy hinders the spread of ovarian cancer. Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight cancer.
Surely, there would be a way to enhance the activity of immunotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer, a setting in which progress had remained elusive. A monoclonal antibody that targets the vegf/vegfr pathway and inhibits tumor blood vessel growth; The purpose of immunotherapy in ovarian cancer treatment is to remove the cancer cells or control the growth of the cancer cells by restoring the natural function of the immune cells, t cells are stimulated and strengthened in vitro, so that after being introduced back to patient’s body, they will be able to identify the ovarian cancer cells and destroy them.
Unfortunately, immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, are not very effective on their own in ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed when it is at an advanced stage, so chemotherapy is a key part of treatment. Ovarian cancer is one such example.
Unfortunately the immune checkpoint inhibitors don�t work for most cases of ovarian cancer. There�s a lot of interesting enthusiasm for developing this further. This treatment has led to improved survival in patients with malignancies such as melanoma and lung cancer but, disappointingly, its benefits have not been as forthcoming in ovarian cancer.
In australia, immunotherapy drugs are currently available as treatment options for some types of cancer, such as melanoma and lung cancer. Surely, there would be a way to enhance the activity of immunotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer, a setting in which progress had remained elusive. Malignant ovarian cancer is insidious:
Active immunotherapy, passive immunotherapy and immunomodulation. Immunotherapy hinges on stimulating patients’ immune system to fight cancer. So far one immunotherapy drug, avastin, has been approved for.
Immunotherapy is a type of drug treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. The first has the aim of stimulating an antitumor response from the patient’s own immune system itself inducing also an immunological memory. In the past two decades, immunotherapy has rapidly developed, and has revolutionized the treatment of various types of cancer.
Epithelial ovarian cancer (oc) is the most lethal gynaecological malignancy worldwide with 22,530 estimated new cases in 2019, 13,980 deaths in 2019 and a median overall survival (os) of less than 5 years (1). Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer immunotherapy is the use of medicines to stimulate a person’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. Berek js, taylor pt, nicodemus cf.
First of all, its immunotherapy. Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body’s natural defenses against cancer.