In this lesson, we�ll look at the three types of atrial fibrillation and then look at a typical ecg readout for a patient in afib and provide a cardiac. Thus, the simultaneous recording of the p waves during af on the baseline ecg was a contradictory finding.
Afib is not defined as the absence of p waves.
P waves in afib. Chest lead v1 (septal precordial) generally presents with a biphasic p wave, meaning a p wave with an initially positive portion and a negative terminal portion. That is one of the deciding factors for junctional. P waves are generated by organized activation of both atria during sinus rhythm, whereas fibrillatory waves are caused by disorganized and chaotic atrial electric activity during af.
Patient’s with new onset afib and those who are currently experiencing accelerated rates of afib (call afib with rapid ventricular response/afib rvr) shouldn’t do a lot of walking and moving around, as this can. At times, the p wave activity may be observed as “coarse fibrillatory waves,” and the term “coarse atrial fibrillation” is used, though there is no clinical significance to this finding. If there are no p waves, it�s one of the two.
In most ecg�s, afib results in a rapid irregular pulse (qrs signal), while vfib results in no pulse (no clear qrs signal) so the ecg�s are quite different. A highly organized reentrant rhythm, usually atrial. In afib, abnormal p waves precede the qrs signal on the ecg.in vfib, there is a rapid irregular tracing but p waves and the qrs signal are unidentifiable.
The evaluation of atrial fibrillation involves a determination of the cause of the arrhythmia, and classification of the arrhythmia. The atria quiver rapidly, with most electrical impulses being blocked before reaching the ventricles. Patient’s with new onset afib and those who are currently experiencing accelerated rates of afib (call afib with rapid ventricular response/afib rvr) shouldn’t do a lot of walking and.
We propose a deep learning enabled method for af risk prediction. The p wave may also be hidden within the qrs complex. The key characteristics of atrial rhythms are abnormal p waves, or p waves that are replaced by flutter or fibrillation waves.
An isoelectric baseline between p waves; Wide (≥ 0.12 sec), bizarre st/t wave: With sinus rhythm, the p waves will be in place with equal pr intervals.
This encounter shows an irregular rhythm with no p waves present. And qrs complex will measure less than 0.12 seconds. Sinoatrial arrest (with a secondary escape rhythm)
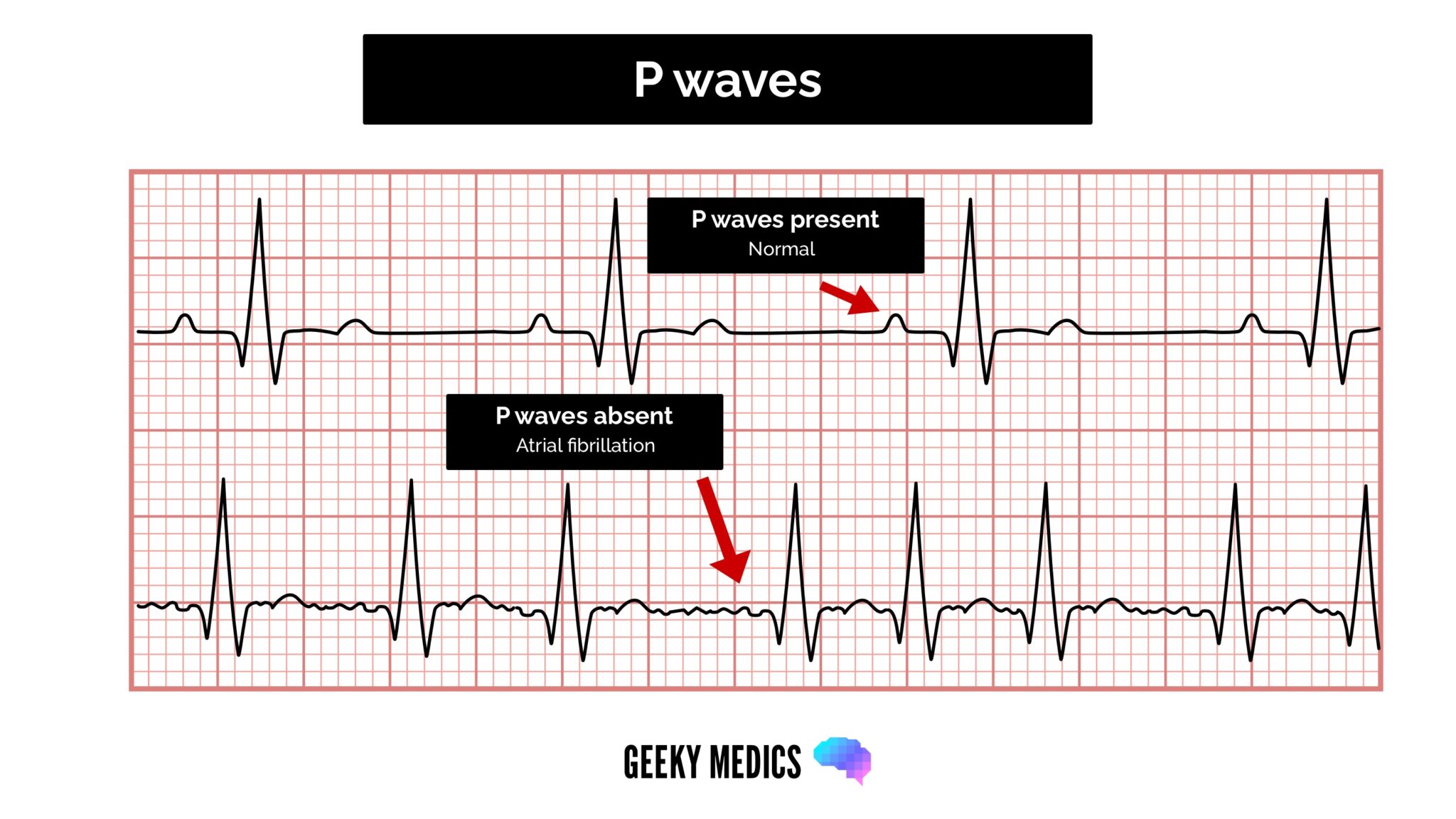
Absence of the p wave with a flat baseline may indicate: Atrial fibrillation has no p waves. [patient.info] ⚕ symptoma®️ is a digital health assistant but no replacement for the opinion and judgement of medical professionals.
If a pt is in a regular rhythm and has no p waves, that means the pt is in a junctional rhythm. Acute myocardial infarction untreated ventricular They may or may not be buried in the preceding t waves.
P waves in mat are well formed and discrete, compared to afib where p waves are characterized as continuous, undulating, and changing. Sinoatrial arrest (with a secondary escape rhythm) In most ecg�s, afib results in a rapid irregular pulse (qrs signal), while vfib results in no pulse (no clear qrs signal) so the ecg�s are quite different.
Atrial flutter will produce sawtooth like “flutter waves” along the baseline. Afib is not defined as the absence of p waves. Difference between atrial flutter and afib atrial fibrillation is caused by multiple ectopic action potentials coming from various areas dotted around the atria.
∅ p waves or if present, not associated with qrs qrs: In afib, abnormal p waves precede the qrs signal on the ecg. This may occur with sinus dysfunction or in the presence of fibrillation or flutter waves.
In this lesson, we�ll look at the three types of atrial fibrillation and then look at a typical ecg readout for a patient in afib and provide a cardiac. Sinus tach and most svts have only one p wave for each qrs complex. Thus, the simultaneous recording of the p waves during af on the baseline ecg was a contradictory finding.
Absence of the p wave with a flat baseline may indicate: This table lists key features of mat, afib, and af. In vfib, there is a rapid irregular tracing but p waves and the qrs signal are unidentifiable.
Identifying the susceptibility to af based on routine or continuous ecg recording is of considerable interest. Ecg typically shows absent p waves with escape rhythm: Make sure there aren’t any!
Clear flutter waves can be seen. In atrial fibrillation the p waves, which represent depolarization of the top of the heart, are absent. The aim of this paper was to assess the potential of the analysis of the p.
Opposite direction of qrs a group of three pvcs in a row or more at a rate greater than 100/ minute or more constitutes ventricular tachycardia. After all, an upright p wave in lead ii is one of the best pieces of evidence suggesting an impulse of normal sinus origin; These deflections respectively show the depolarisation of the right.
A form of electrical chaos in either the atria or ventricles, resulting in the absence of definable p waves (in atrial fibrillation) or qrs complexes (in ventricular fibrillation) flutter. These signs are indicative of atrial fibrillation or afib. A lack of visible p waves preceding qrs complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats;