60% of patients are metastatic (advanced stage). It develops from cells that make mucus.
However, human evaluation of pathology slides cannot accurately predict patients� prognoses.
Prognosis for non small cell lung cancer. The condition has several subtypes, and the subtype of lung cancer affects its treatment and overall prognosis (disease outlook). In comparison, brain cancer is a. The lungs bring oxygen into the body as you breathe in.
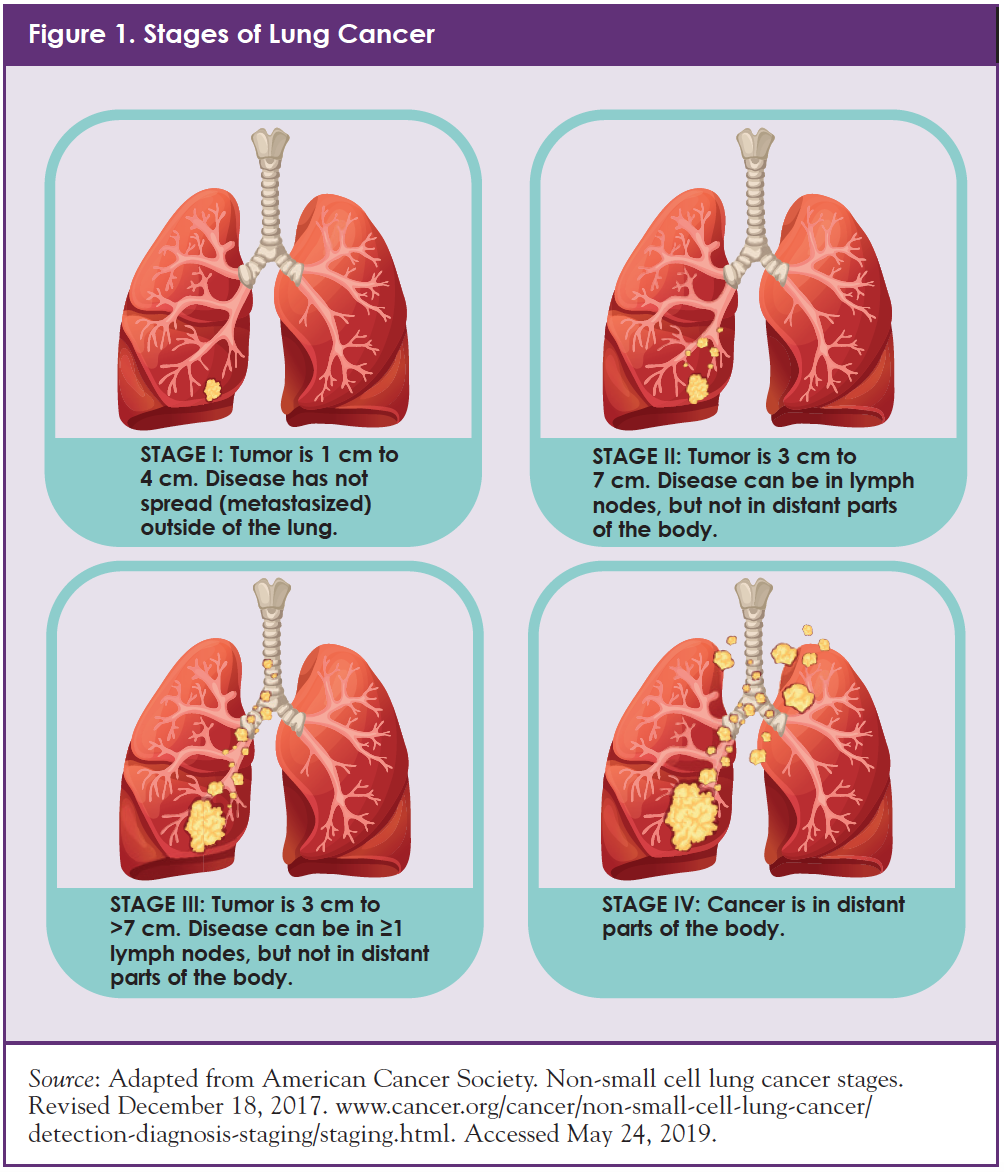
The stage of lung cancer is the most important prognostic factor. Small tumours in the lung are often asymptomatic, so the majority of patients have either locally advanced or metastatic disease at diagnosis. The loss of smad4 on immunohistochemical staining is often used to suggest a pancreaticobiliary differentiation in evaluating a metastatic adenocarcinoma with unknown origin.
Metastasis refers to the process of cancer cells leaping to the lymph nodes or to another part of the body, through the bloodstream. There are cases where you may have a. Most common presenting symptoms are cough, chest pain, haemoptysis, dyspn.
It usually grows more slowly than small cell lung cancer. Nsclc makes up 80 percent to 85 percent of lung cancer diagnoses. With small cell lung cancer, limited stage cancers have a.
However, human evaluation of pathology slides cannot accurately predict patients� prognoses. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular person’s chances of survival. Once your doctor makes a prognosis, they’ll develop a treatment plan.
The cells of a nsclc tumor are typically larger in size. It develops from cells that make mucus. There are several treatment options available.
However, some reports suggest that patients with brain metastases at the time of initial diagnosis have a more favourable survival than do patients with advanced nsclc without brain metastases. The most common form of. There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics.
Like most cancers, the prognosis of nsclc depends significantly on the stage in which the cancer is diagnosed. Nsclc grows and spreads less aggressively than small cell lung cancer. Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of nsclc.
Like all cancers, nsclc begins at the cellular level and causes abnormal cells in the lungs to reproduce rapidly and out of control. Stage description* occult (hidden) cancer. The main—really the sole—risk factor for small cell lung cancer is smoking.
These include the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. It is more often found in the outer area of the lung. That is not the case for small cell.
Nsclcs are carcinomas, which are cancers of the cells lining the surface of the lung airways. There are three main subtypes of nsclc: In 2012, lung cancer was diagnosed in 1.8 million people and caused approximately 1.6 million deaths.when someone is diagnosed with lung cancer, one of the first steps is to stage the disease in order to determine both treatment.
It constitutes 80% to 85% of lung cancers. The main tumor can’t be assessed for some reason, or cancer cells are seen in a sample of sputum or other lung fluids, but the cancer isn’t found with other tests, so its location can’t be determined (tx). There are two types of lung cancer:
Lung cancer is the most prevalent cancer worldwide, and histopathological assessment is indispensable for its diagnosis. There are three main types: I would say probably 95% to 98% of all small cell lung cancer patients have a smoking history and a heavy smoking history.
They release carbon dioxide, a waste product of the body’s cells, as you breathe out.each lung has sections called lobes. 60% of patients are metastatic (advanced stage). Adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and large cell carcinomas.
However, it is important to note that survival rates depend on several factors, including the subtype of lung cancer, and the stage of disease.