Immunotherapy side effects happen when the immune system that has been prompted to act against the cancer also acts against healthy cells and tissues in the body. Immunotherapy can be called biological therapy and it uses
For some sufferers, tolerance can last even longer.
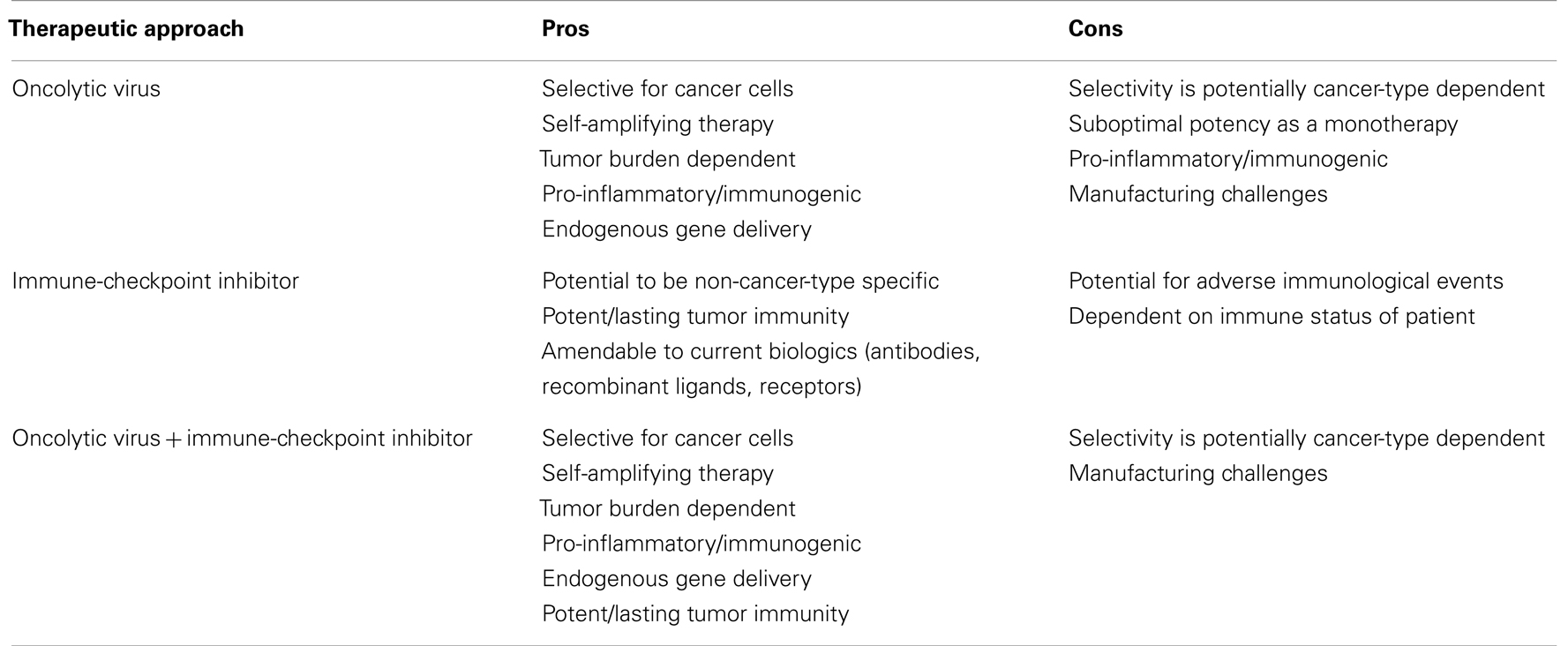
Pros and cons of immunotherapy. Immunotherapy may help slow or stop the growth of cancer cells and. The cons of topical minoxidil include its inability to work for extensive hair loss and, if too much is used, its association with weight gain, headaches, and irregular heartbeat. Cancer immunotherapy is an innovative treatment for tumors today.
Immunotherapy using t lymphocytes is an attractive strategy to treat many types of malignancies. Side effects such as lung problems (coughing, shortness of breath), liver and kidney problems, changes in eyesight, and. Pros and cons of rituximab maintenance in follicular lymphoma cancer treat rev.
Possible side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Pros and cons of treating cancer some oncologists choose not to mention immunotherapy to dying patients, arguing that scientists first must gather rigorous evidence about the benefits and pitfalls. The advantages of immunotherapy the disadvantages of immunotherapy;
Learn about the types of side effects that immunotherapy might cause and where to go for more information. Some types of immunotherapy rev up your immune system and make you feel like you have the flu, complete with fever, chills,. For some sufferers, tolerance can last even longer.
The two main advantages are that no injections are necessary and treatment can be administered at home. This is more common while the drug is first being given. Other recommended treatments include prescription medications.
There are limitations in the treatment objects and. Immunotherapy — treatment that uses certain parts of a person’s immune system to fight diseases such as cancer — isn’t a new concept. Authors lu zhang 1 , michele ghielmini 2 , bruce d cheson 3 , chaitra ujjani 4 affiliations 1 oncology institute of southern.
Using substances made by the body or in a laboratory, immunotherapy boosts the body’s natural defenses to combat cancer. Immunotherapy, on the other hand, targets your body’s sensitivity to allergens. Still being studied and refined by researchers, this process involves “engineering,” or genetically modifying, a patient’s own immune t cells to specifically recognize and attack cancer cells.
Immunotherapy side effects happen when the immune system that has been prompted to act against the cancer also acts against healthy cells and tissues in the body. Immunotherapy can train the immune system to remember cancer cells. “when you have immunotherapy, your immune system learns to go after cancer cells if they ever come back.
“the idea that we could use the body’s own natural defense mechanisms to attack cancer cells has actually been around for quite some time, since the 1960s,” says len lichtenfeld, m.d., deputy chief medical officer of the american. Immunotherapy can make the immune system respond to diseases or improve the immune system’s opposition to agile diseases like cancer. Many clinical trials tried to eliminate potentially harmful cells using suicide genes.
The last and arguably the biggest benefit of immunotherapy is that it has a higher success rate for whether or not the cancer will return. The pros include easy accessibility, few adverse effects if used as directed, and relatively low cost. Immunotherapy can be called biological therapy and it uses
Immunotherapy can be called biological therapy and it uses Over time, you become less reactive to the things that trigger your symptoms. The antibodies themselves are proteins, so giving them can sometimes cause something like an allergic reaction.
“when you have immunotherapy, your immune system learns to go after cancer cells if they ever come back. Monoclonal antibodies are given intravenously (injected into a vein). Immunotherapy can make the immune system respond to diseases or improve the immune system’s opposition to agile diseases like cancer.
Frey and porter in this issue of oncology,[1] it involves genetic manipulation of autologous cytotoxic t cells to create a product capable of targeting specific tumor antigens. The last and arguably the biggest benefit of immunotherapy is that it has a higher success rate for whether or not the cancer will return.