However, symptoms can appear by adolescent and adult age. If the left atrium is enlarged, then the patient.

Small physiological, or normal, shunts are seen due to the return of bronchial artery blood and coronary blood.
Right to left cardiac shunt symptoms. Hypoxemia manifests as cyanosis, causing blue babies. diagnosis. A flow phenomenon, with preferential flow from the inferior vena cava directly through the pfo; This syndrome usually manifests in young adulthood.
1 assessing left atrial enlargement is useful for distinguishing between left and right shunts. Irrespective of different type of cardiac defects that may cause right to left shunt, the symptoms of these condition remain common. Forward systemic flow can be reduced if the shunt is large resulting.
In a large pda, the ekg will demonstrate right ventricular hypertrophy, left ventricular enlargement, and left atrial enlargement, due to volume overload. In certain cases, the magnitude of the shunted blood can be large enough to result in a reduction in the partial pressure of arterial oxygen such that hypoxemia arises. Lesions resulting in left to right shunts include:
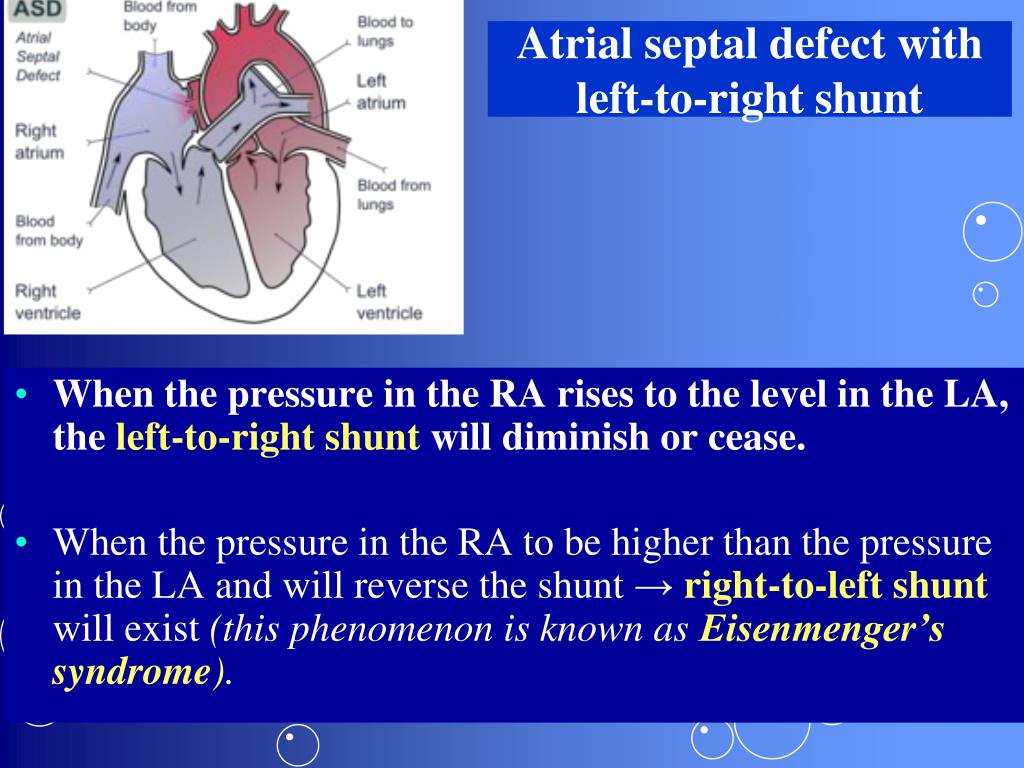
For example, while haemodynamically relevant ventricular septal defects (vsds) nowadays typically are managed during childhood, atrial septal defects. A decrease in right ventricular compliance,. Because of the extra flow that goes to the “right heart” and the pulmonary circulation, which are not built to handle that much extra blood, one can hear abnormal heart sounds (“murmurs”), and if not treated this part of the heart may start to fail.
If the left atrium is enlarged, then the patient. Left to right shunts are often asymptomatic in childhood; [amboss.com] pathophysiology significant left to right shunting can occur resulting in a high left ventricular cardiac output.
Dyspnea, fatigue, and cyanosis develop. A cardiac shunt is when blood follows a pattern that deviates from the systemic circulation, i.e., from the body to the right atrium, down to the right ventricle, to the lungs, from the lungs to the left atrium, down to the left ventricle and. 1 depending on location and size of the shunts, haemodynamic effects and presentation vary considerably.
Atrial septal defects can result in a shunt in either direction. Transient, rather than prolonged, mean interatrial pressure differentials that occur during the normal cardiac cycle; [tandurust.com] in newborns, the oxygen deprivation causes a bluish discoloration of the skin known as cyanosis and this is often referred to a cyanotic congenital heart disease.
There is an opening or passage between the atria, ventricles, and/or great vessels; There are a many symptoms that a person can feel if a vp shunt is not draining fluid properly or underdraining though many of these symptoms can occ. Causes of right to left cardiac shunt right to left cardiac shunt is congenital heart malformation which is present since birth.
Presentation often includes shortness of breath, exercise intolerance, and easy fatigability. Small physiological, or normal, shunts are seen due to the return of bronchial artery blood and coronary blood. Williams, md, ms iib6@columbia.edu learning objectives ¥learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance ¥review the transition from fetal to mature circulation ¥correlate clinical signs and symptoms with cardiac physiology as it relates to left to right shunt lesions:
Left to right shunts ismee a. Patient presents with following symptoms. Increase in blood volume to the lungs may result in pulmonary hypertension and, without treatment, permanent damage to.
Cyanotic heart diseases signs and symptoms may include shortness of breath, very low levels of oxygen ‘spells’, loss of weight, puffy face and eyes, clubbed fingers, dizziness, and fainting. In these defects, the right side of the heart receives more blood, which causes pulmonary hypertension over time in some patients. However, symptoms can appear by adolescent and adult age.
Blue discoloration of skin, lips and tongue. When cardiomegaly is present, the amount of cardiac enlargement is generally proportional to the increase in pulmonary vascularity. In a small pda, the ekg is usually normal.
Simple shunt lesions are among the most common forms of congenital heart disease.