
But inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity are also signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd), sometimes known as attention deficit disorder or add. The symptoms continue, can be severe, and can cause difficulty at school, at home, or with friends.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd) is a neurodevelopmental disorder with symptoms commonly starting during childhood.
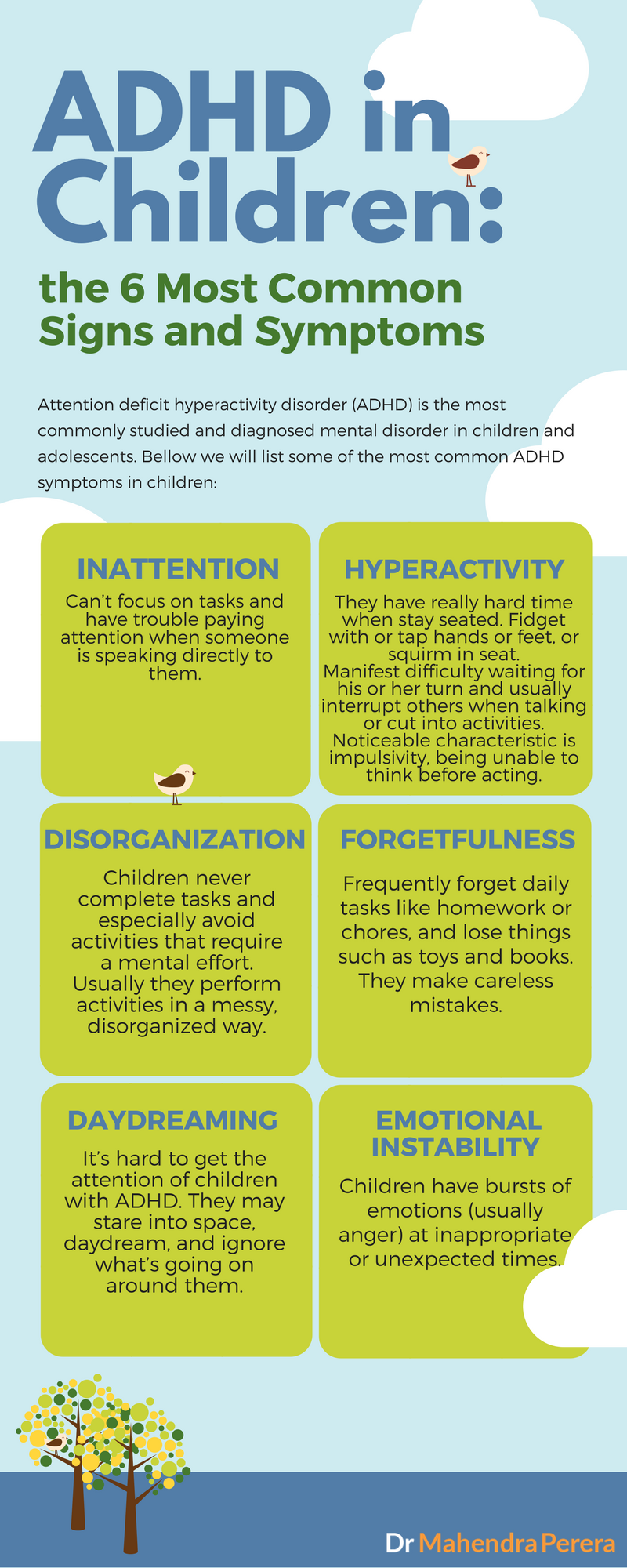
Signs of childhood adhd. For this reason, you may find that a child with adhd struggles to form and maintain relationships, as well as struggles to participate in certain activities that demand a high. Exhibit excessive energy (e.g., excessive running, climbing, jumping) interrupt frequently, blurt out answers, or talk excessively. Kids with adhd will likely struggle in school, may have trouble with friends, and as a result could experience low.
The child’s head is bobbing, occasionally to an inaudible rhythm. The signs of adhd are easier to pick up on than attention deficit disorder, where attention issues are mostly happening inside a child’s head, said melissa derosier, clinical. Childhood trauma is linked to adhd, and vice versa.
Adhd includes a combination of persistent problems, such as difficulty sustaining attention, hyperactivity and impulsive behavior. Are impatient and/or easily bored. Although not always the case, some children may also have signs of other problems or conditions alongside adhd, such as:
Everyone shows signs of adhd at one time or another. Knees and legs are twitching and wiggling, arms are moving, sometimes in someone else’s face. These are just a few reasons why clinicians must increase their understanding of trauma and adopt an informed approach when assessing and treating children for adhd.
The key symptom is trouble with focus. Children with adhd have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors (may act without thinking about what the result will be), and in some cases, are overly active. Symptoms in the attention deficit adhd subtype in girls can be daydreaming in the class, anxiety or grief, inattention, shyness, problems in keeping friendly relations, recrimination.
Each also amplifies symptom severity in the other. It may also cause physical symptoms, such. The symptoms continue, can be severe, and can cause difficulty at school, at home, or with friends.
A child with adhd might: Have trouble staying in one place. Forget or lose things a lot
Patient clinical data such as diagnosis was obtained from patients’ files. Another sign of adhd is being quieter and less involved than other kids. Older children with adhd frequently jump out of their seats to sharpen a pencil, talk to a classmate, grab a book, get a drink of water, or visit the bathroom.
If your child shows signs of. What follows these comments and observations may be denial. Some of the early signs of adhd in babies are :
But kids with adhd struggle a lot more with them than other kids their age. Have difficulty waiting their turn. Symptoms can include difficultly focusing on tasks and trouble controlling impulsive behaviors.
Adhd is a chronic condition that affects millions of kids. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd) is a neurodevelopmental disorder with symptoms commonly starting during childhood. However, children with adhd do not just grow out of these behaviors.
Often runs about or climbs in situations when it is not appropriate (adolescents or adults may be limited to feeling restless) is often unable. The child mostly exhibits symptoms characteristic of inattentive adhd. ️ babies that are angry, fussy, and difficult to.
But inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity are also signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd), sometimes known as attention deficit disorder or add. A child with adhd may stare into space, daydream , and ignore what’s going on around them. Children with adhd have a pattern of inattention, hyperactivity or impulsivity—sometimes all three combined—which interferes with functioning, development and relationships.
That someone may even be yourself or your child. Adhd is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that typically appears in early. A kid displays most signs of inattention but isn’t hyper or impulsive.
They share similar symptoms that are often confused and misdiagnosed. It is normal for children to have trouble focusing and behaving at one time or another. But it does start with someone — an attentive doctor, an observant teacher, a caring friend, or a family member — who takes notice of your child’s behaviors and struggles.
Your child may have signs of hyperactive and impulsive adhd if they: Fidget, squirm, or can’t sit still. In contrast, in children with adhd it is common to see the child struggle with focus of attention and hyperactivity, going from early childhood and into later childhood.
Blanca fresno of children�s physicians medical group (cpmg) explains the signs, symptoms and treatment for the different types of childhood adhd. They have symptoms from both sides of the disorder.