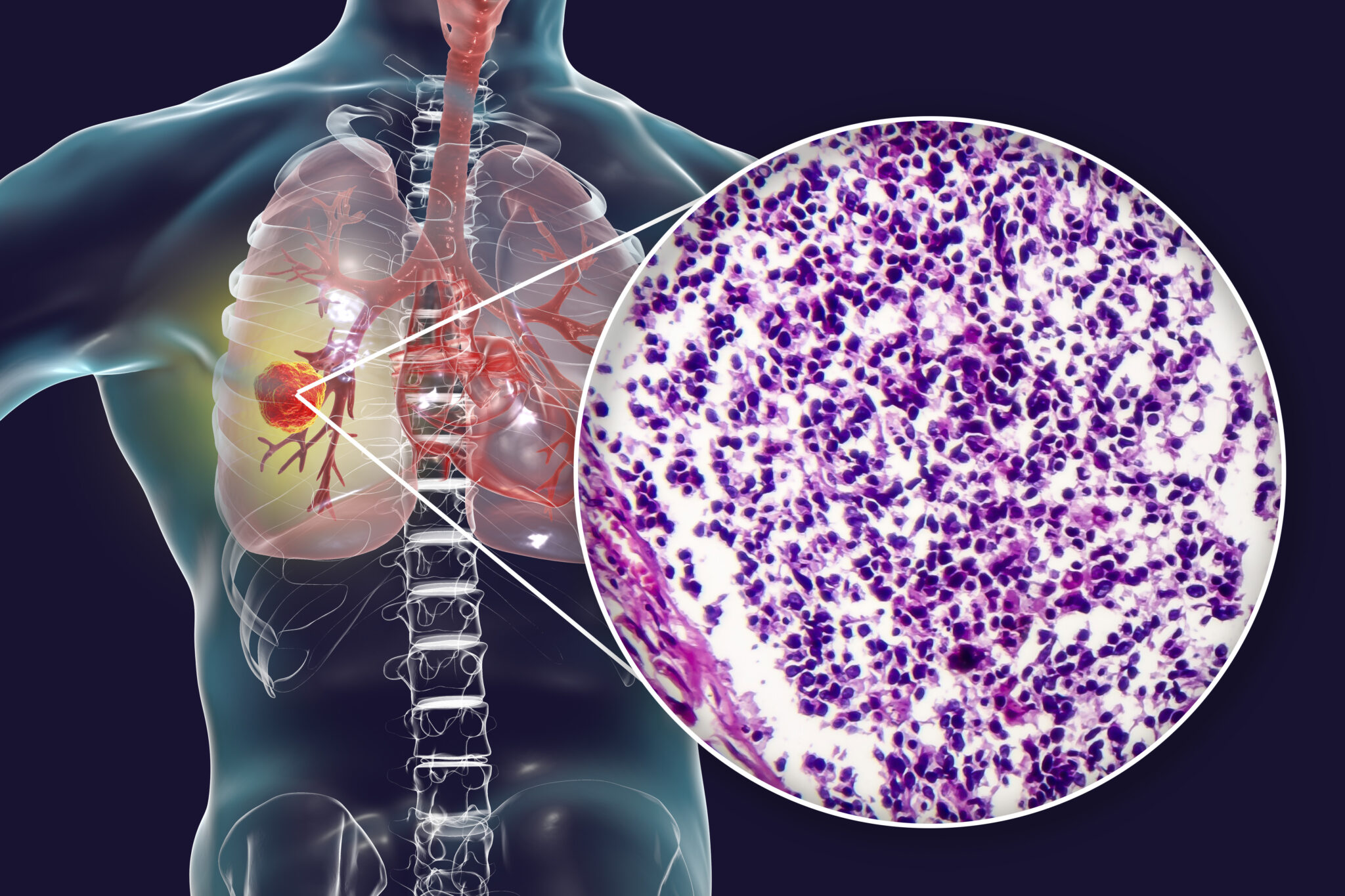
By the time a person gets a diagnosis, small cell lung cancer has typically spread (metastasized) outside of the lungs. What is small cell lung cancer (sclc)?
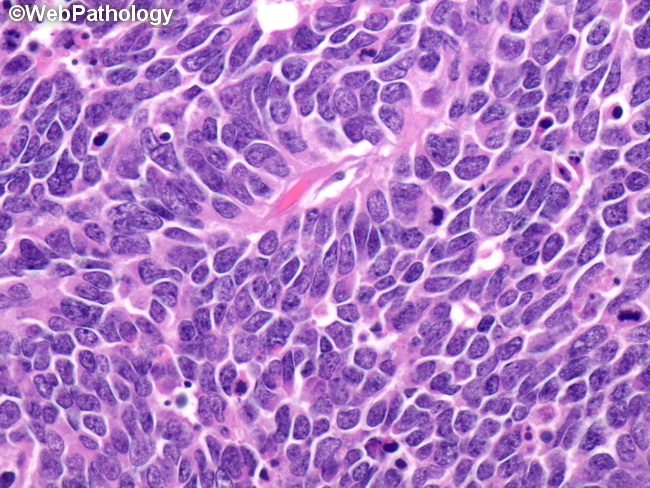
The nuclei have finely dispersed or salt and pepper chromatin and absent nucleoli.
Small cell ling cancer. Small cell lung carcinoma (sclc) arises in peribronchial locations and infiltrates the bronchial submucosa. Small cell lung cancer (sclc) is an aggressive. This means that you have chemotherapy at the same time as radiotherapy.
Composed of small, ovoid cells with. Sclc usually starts in the bronchi, located in the middle of the chest. It starts in nerve cells or cells that make hormones.
Or, you can choose another section to learn more about a specific question you have. Small cell lung cancers are staged as limited stage and extensive stage. Use the menu below to choose the introduction section to get started.
It’s also known as “oat cell” cancer, because the cells may resemble oats. What is small cell lung cancer (sclc)? It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of certain cells in the lungs.
The term small cell refers to the size and shape of the cancer cells as seen under a microscope. Small cell lung cancer (sclc) gets its name from how the cancer looks under a microscope. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body.
Typically, doctors first treat it. It can cause increased intracranial pressure, headaches, and changes in consciousness. Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
Limited stage means that the cancer is only in one lung and maybe in lymph nodes on the same side of the chest. Sclc is a heterogeneous disease including extremely chem. These cells can be carried away in blood or float away in the fluid, called lymph, that surrounds lung tissue.
Each guide is reviewed by experts on the cancer.net editorial board, which is composed of medical, surgical,. When a cancerous lung tumor grows, it can shed cancer cells. Small cell lung cancer is histologically described as small round / oval cells with high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio.
This cancer is also more likely than other. It makes up about 1 in 7 lung cancers (about 15%). Eventually, a tumor forms and the cancer can spread (metastasize) to other areas of the body.
Small cell lung cancer is a form of neuroendocrine cancer that often grows rapidly and quickly spreads to other organs. Adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas and large cell carcinomas. You usually then have radiotherapy to the chest.
Small cell lung cancer (sclc) is an aggressive cancer of neuroendocrine origin, which is strongly associated with cigarette smoking. Growth of the tumor can cause compression of the superior. Sclc is strongly associated with exposure to tobacco carcinogens.
Sclc accounts for about 13 percent of all lung cancers. About 10% to 15% of lung cancer cases are. Like its name suggests, small cell lung cancer contains cells that are smaller in size.
Types of small cell lung cancer Cancer that starts in the lung is called primary lung cancer. The nuclei have finely dispersed or salt and pepper chromatin and absent nucleoli.
Small cell lung cancer (sclc) is an aggressive form of lung cancer. This process is called staging. It helps determine how serious the.
Small cell lung cancer is most often located at the hilum and grows along the bronchi. The lungs bring oxygen into the body when you breathe in and take out carbon dioxide when you breathe out. It takes its name from the typically small size and shape of these tumor cells, as seen under a microscope.
The cancer is in a single area that can be treated with radiotherapy. The main treatment for limited disease small cell lung cancer is chemotherapy. There are two main types of primary lung cancer:
If you are fit enough, you might have chemoradiotherapy. The biggest risk factor for developing lung cancer is smoking, however there are people who have never smoked that still develop lung cancer. Widespread metastases occur early in the course of the disease, with common spread to the mediastinal lymph.
By the time a person gets a diagnosis, small cell lung cancer has typically spread (metastasized) outside of the lungs. After someone is diagnosed with small cell lung cancer (sclc), doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far.