
In september 2017, the fda granted accelerated approval for the use of the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab in unresectable hcc patients who. Sorafenib reduces cell viability, clonogenic survival and induces apoptosis in hcc cells.
Essentially, they block tyrosine kinases that are very active in angiogenesis, cancer development and growth, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment.
Sorafenib mechanism of action. If playback doesn�t begin shortly, try restarting your device. Sorafenib is unique in targeting the raf/mek/erk pathway. Laboratory studies demonstrated the biological plausibility of sorafenib in treating osteosarcoma by measuring its success in various in vitro and in vivo studies.
Mechanism of action of sorafenib. Mechanism of action stivarga ® (regorafenib) is an oral inhibitor of multiple kinases target normal cellular functions and pathological processes such as oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and tumor immunity 1,2 Cell proliferation was determined by estimating the amount of bromodeoxyuridine (brdu.
Mechanism of multikinase inhibitor action. The majority of these are tyrosine kinase receptors, and the primary mechanism is inhibition of the mapk/erk pathway. Sorafenib is also an inhibitor of kit, a cytokine receptor inhibitor.
Sorafenib is small molecule inhibitor approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer and advanced primary liver cancer. Tumour development involves the dysregulation of normal cell processes such as cell growth and proliferation, as well as angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels). Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor capable of facilitating apoptosis, mitigating angiogenesis and suppressing tumor cell proliferation.
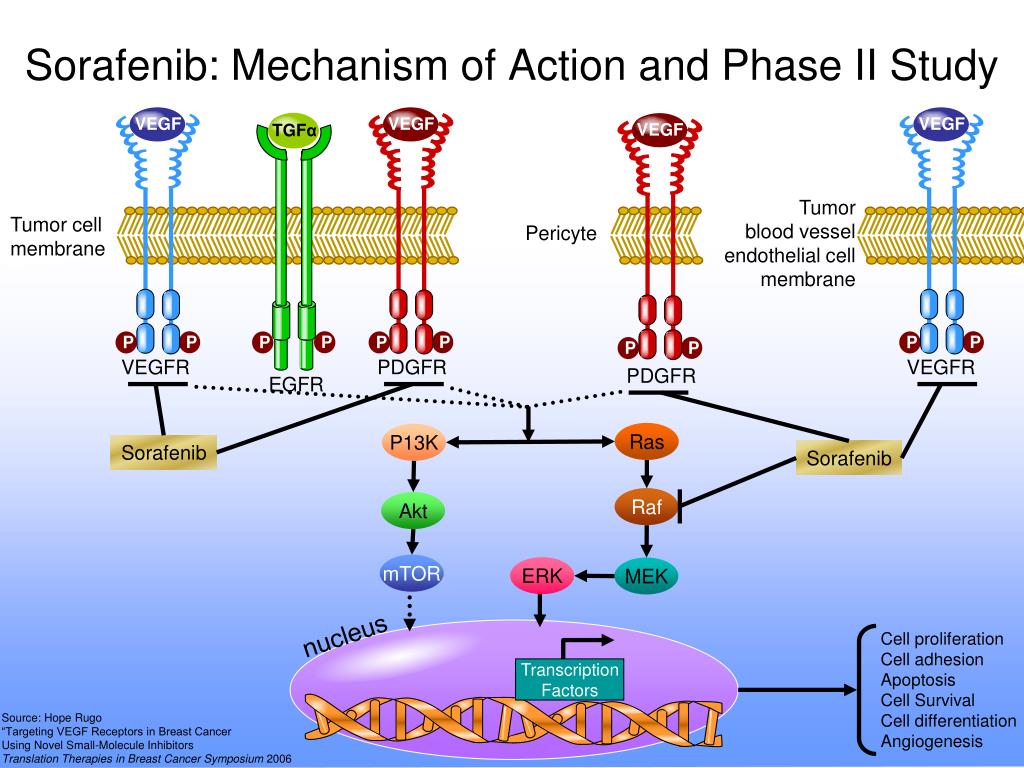
It works by inhibiting or blocking the pathways that involves the. Inhibition of pdgfr and vegfr results in reduced tumor vascularization and cancer cell death. Sorafenib mechanism of action in treating advanced hepatocellu designed by asuka ccp.
Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, recently received fda approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc). Sorafenib inhibits the action of tyrosine kinase raf and other factors involved in vasculogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet. It was well tolerated at a dose of 400 mg twice daily and permanent discontinuation of the drug was rarely required.
Sorafenib blocks the enzyme raf kinase, a critical component of the raf/ mek /erk signaling pathway that controls cell division and proliferation; Cfthe mechanism of action of regorafenib (stivarga, bayer) is very similar to that of sorafenib (nexavar, bayer). They are both oral multikinase inhibitors.
In september 2017, the fda granted accelerated approval for the use of the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab in unresectable hcc patients who. Sorafenib binds the atp binding site of pdgfr & vegfr, peventing the receptor kinase from binding atp and phosphorylating their respective tyrosine target residues. Hence, the molecular mechanism of action of this drug in otherwise classically refractory solid tumors, such as rcc and hcc, warrants further investigation.
Essentially, they block tyrosine kinases that are very active in angiogenesis, cancer development and growth, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. The global community for designers and creative professionals. Sorafenib works by inhibiting a variety of proteins.
Sorafenib tosylate is identifiable through the serial modification of the commercial raf kinase inhibitor. Sorafenib exerts its action through inhibition of several kinases involved in both tumour cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Sorafenib reduces cell viability, clonogenic survival and induces apoptosis in hcc cells.
Connect with them on dribbble; Several of these kinases are thought to be involved in angiogenesis, thus sorafenib reduces blood flow to the tumor.