There are two types of lung cancer: There are a number of variants of lung cancer and these are named for their microscopic appearance, the main ones being:

Defined as tumor 2 cm or less in peripheral lung with no lymph node or distal metastases only rarely identified in practice, since these tumors grow rapidly often have glandular cell characteristics.
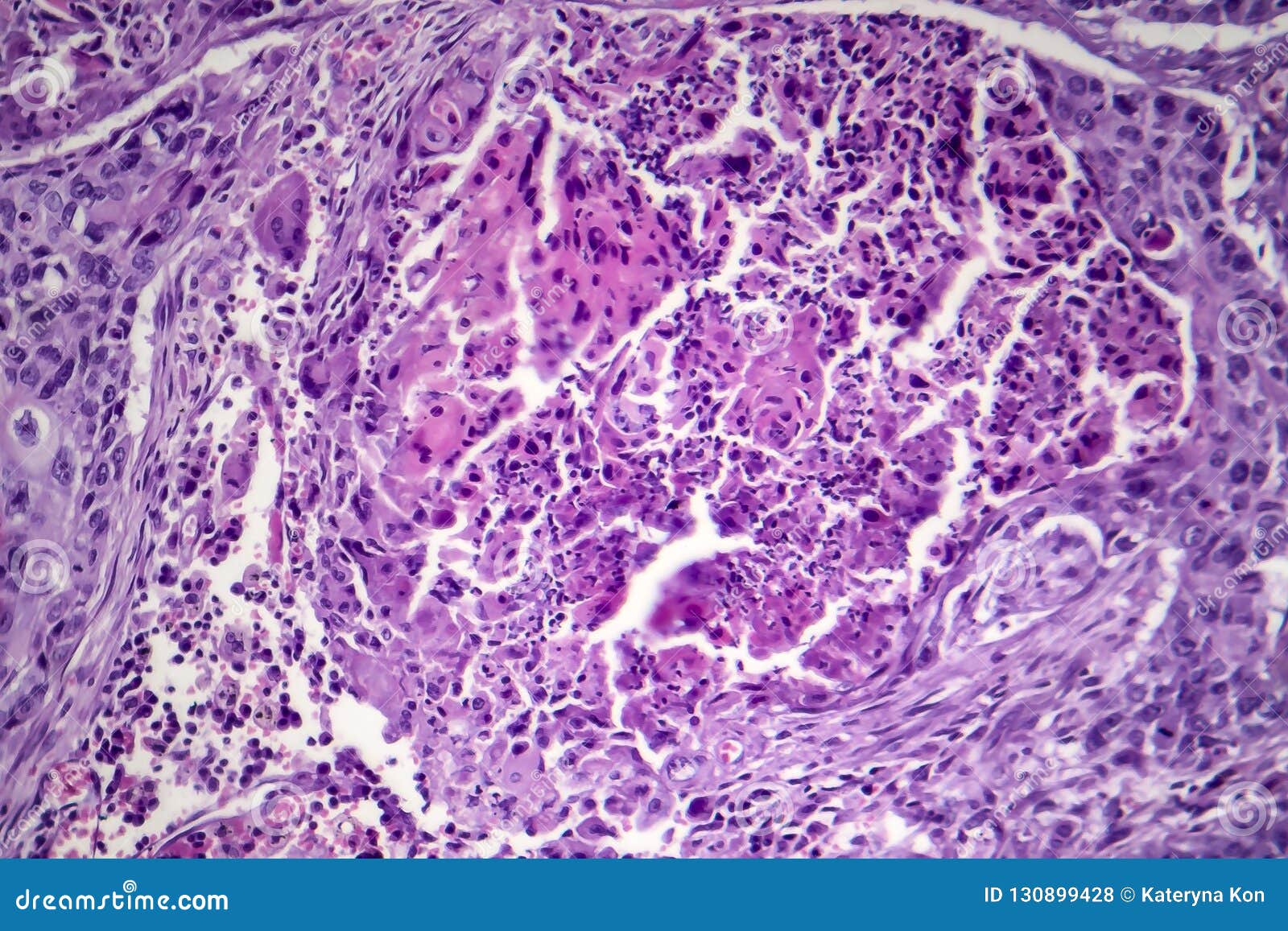
Squamous cell lung carcinoma. What is squamous cell carcinoma? This is curious, as there is no normal squamous tissue in the lung. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Lymph nodes around and between the lungs; The most common subtypes of lung cancers are lung adenocarcinoma (luad) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (lusc), classified together as. Squamous cell lung cancer is categorized as such.
Lung scc is a tumor characterized by squamous epithelial differentiation. Early squamous cell carcinoma of peripheral type: These are thin, flat cells that line the airways, much like the lining of a pipe.
Nevertheless, lung scc remains a common. Squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, small cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma.in squamous cell cancer, the tumor cells resemble skin cells.this type of tumor is commonly seen in smokers. In response to specific types of epithelial.
It occurs when abnormal lung cells multiply out of control and form a tumor. Squamous cell carcinoma lung cancer can spread in bones, liver, glands and also brain. Defined as tumor 2 cm or less in peripheral lung with no lymph node or distal metastases only rarely identified in practice, since these tumors grow rapidly often have glandular cell characteristics.
Lung cancer can start from the cells lining the bronchi, bronchioles or alveoli. It can metastasize or spread to other parts of the body or organs other than the lungs. What is squamous cell carcinoma lung cancer?
They provide a barrier between the air in the lungs and the lungs themselves. Squamous cell lung carcinoma accounts for roughly 30 percent of all lung cancers. The tissue that most closely resembles a squamous pattern is the pseudostratified epithelium of the trachea and upper bronchi.
It is caused by abnormal lung cells forming a tumor. Squamous cell lung tumors often occur in the central part of the lung or in the main airway, such as the left or right bronchus. According to the american cancer society , about 80 to 85 percent of.
The main causative agent of cellular transformation is tobacco smoke. Nearly 80% of all lung cancer cases in men and 90%. Lung squamous cell carcinoma (lscc) remains a leading cause of cancer death with few therapeutic options.
There are two types of lung cancer: Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of lung cancer with relatively better survival rates. Tumors may also contain keratin pearls, and larger tumors may have extensive necrosis.
Squamous cell carcinoma (scc) of the lung, also known as epidermoid carcinoma, is a form of lung cancer. Whether the expression of these markers in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma is a prognostic factor has been a matter of debate. There are a number of variants of lung cancer and these are named for their microscopic appearance, the main ones being:
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, also known as epidermoid carcinoma, is a cancer that originates from the squamous cells. Squamous cell carcinoma is often a centrally located tumor close to the hilum. A type of skin cancer squamous.
Eventually, tumor cells can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body including the. Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinomas, also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that result from squamous cells.
Histologic hallmarks of squamous cell carcinoma are polygonal cells with intercellular bridges, crisp eosinophilic cytoplasm. We characterized the proteogenomic landscape of lscc, providing a deeper exposition of lscc biology with potential therapeutic implications. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung is a type of lung cancer.