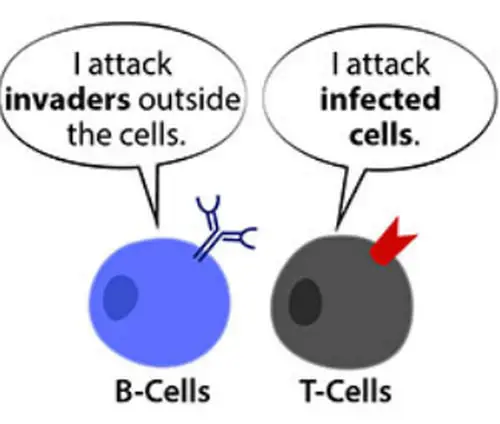
The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs). B cells and t cells are both lymphocytes, or white blood cells produced in bone marrow and maturing in the organs of the body�s lymphatic system.
One type, known as t helper cells, coordinate the body�s various immune responses.
T cells and b cells. B lymphocytes collect in tighter groups. Since both t cells and b cells are subtypes of white blood cells, both cells occur in the blood. They help to shape, activate and regulate the adaptive immune response.
B cells are produced in the b one marrow. One type, known as t helper cells, coordinate the body�s various immune responses. The second, called cytotoxic t cells or killer t cells,.
The lymphocytes also learn to recognize a specific antigen and bind to it. Both t cells and b cells are the two types of lymphocytes. B lymphocytes (often simply called b cells) and t lymphocytes (likewise called t cells).
B cells are the foundation of humoral immunity. T lymphocytes tend to be more diffusely distributed in the lymph nodes; Cd4+ cells are targeted by hiv.
(9, 10) composition/proportion in the blood. There are many more t cells than b cells. When there’s a change in the dna, it can cause a cell to divide more quickly and, in some cases, lead to cancer.
T cells and b cells differ in their functions, like t cells are known to develop various immune response such as invading bacteria from body’s immune system, virus attacks, not supporting the organ transplant, etc., while b cells produce antibodies against the antigen. B cells mature in the bone marrow while the t. Both t cells and b cells are involved in the adaptive immunity.
Regulatory t cells may be similar to cytotoxic t cells, but they are detected by their ability to suppress the action of b cells or even of helper t cells (perhaps by killing them). During maturation, the lymphocytes learn to differentiate between foreign cells and self. The t cells attack the foreign organ tissue as the transplant organ is identified as infected tissue.
T cells and b cells are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. Despite showing variance in their working, t and b cells struggle with the same aim of destroying the. B cells and t cells are the white blood cells of the immune system that are responsible for adaptive immune response in an organism.
T cells make up around 80% of all circulating lymphocytes. Specific cd4 + t cells are important for eliciting potent b cell responses that result in antibody affinity maturation, and the levels of spike. Igg + and igm + memory b cells have a distinct.
The precursors of t cells are also produced in the bone marrow but leave the bone marrow and mature in the t. The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs). 2 these cells first find cancer cells and can also be stimulated to kill cancer cells.
These memory b cells may maintain broad reactivity to the activating pathogen. Dna provides the instructions for a cell’s growth, survival and reproduction. However, the absence of specific antibodies in the serum does not necessarily mean an absence of immune memory.
B cells and t cells are both lymphocytes, or white blood cells produced in bone marrow and maturing in the organs of the body�s lymphatic system. Both t cells and b cells also occur in the lymphatic system. Both the cells are made in the bone marrow.
Regulatory t cells thus act to damp down the immune response and can sometimes predominate so as to suppress it completely. Basic concepts in t cell memory. Cd4+ t cell functions include activating other immune cells, releasing cytokines, and helping b cells to produce antibodies.