The adaptive immune system includes the t cells and b cells. This click & learn describes key elements of the adaptive immune system, including b cells and antibody molecules, helper t cells and cytotoxic t cells, and antigen presentation.

Whether this decrease in thymus function explains the drop in t cells or whether other changes play a role is not fully understood.
T cells in the immune system. For your immune system to fight off any kind of invader, such as a virus, you need a kind of white blood. Break bloodborne pathogens into small amino acid chains → move to lymph node → present antigens to t cells macrophages: This click & learn describes key elements of the adaptive immune system, including b cells and antibody molecules, helper t cells and cytotoxic t cells, and antigen presentation.
Vertebrates have an additional powerful immune response called adaptive immunity. But the details of this immune response and how long it lasts after infection have been unclear. It has been shown that tregs are able to inhibit t cell proliferation and cytokine production.
00:01:43.09 plasma cells are the immune cells that are responsible for secreting antibodies, 00:01:47.10 an important component of adaptive immunity. The tcr is a dimer composed of 2 chains, usually α and β. The accompanying worksheet guides students’ exploration.
T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes—b cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune responses to antigens (foreign substances) in the body. Different types of t cells help recognize and kill pathogens. Both send out signals to attract macrophages and neutrophils to the site of the infection.
Whether this decrease in thymus function explains the drop in t cells or whether other changes play a role is not fully understood. As the infection progresses, responding cells become more specialized, developing different effector functions that optimize how the immune system attacks it. B cells make new antibodies when the body needs them.
Cd8+ t cells also are called cytotoxic t cells or cytotoxic lymphocytes (ctls). 8.1 shows the involvement of the different effector t cells in the immune responses to. These two mechanisms of antigen presentation reflect the different roles of.
This article discusses t cell production, the different t cell types and relevant clinical conditions. Others are interested in whether the bone marrow becomes less efficient at producing the stem cells that give rise to the cells of the immune system. Dna provides the instructions for a cell’s growth, survival and reproduction.
A rapid way to track an elusive part of. Cd8+ cytotoxic t cells, on the other hand, directly kill infected cells. Killer t cells only recognize antigens coupled to class i mhc molecules, while helper t cells and regulatory t cells only recognize antigens coupled to class ii mhc molecules.
The adaptive immune system includes the t cells and b cells. T cells (also called t lymphocytes) are major components of the adaptive immune system. One type, known as t helper cells, coordinate the body�s various immune responses.
Not in blood lymphoid cells:. T cells carry out multiple functions, including killing infected cells and activating or recruiting other immune cells. 00:02:00.29 t cells arise from a common progenitor.
Their roles include directly killing infected host cells, activating other immune cells, producing cytokines and regulating the immune response. The second, called cytotoxic t cells or killer t cells,. During a viral infection, t.
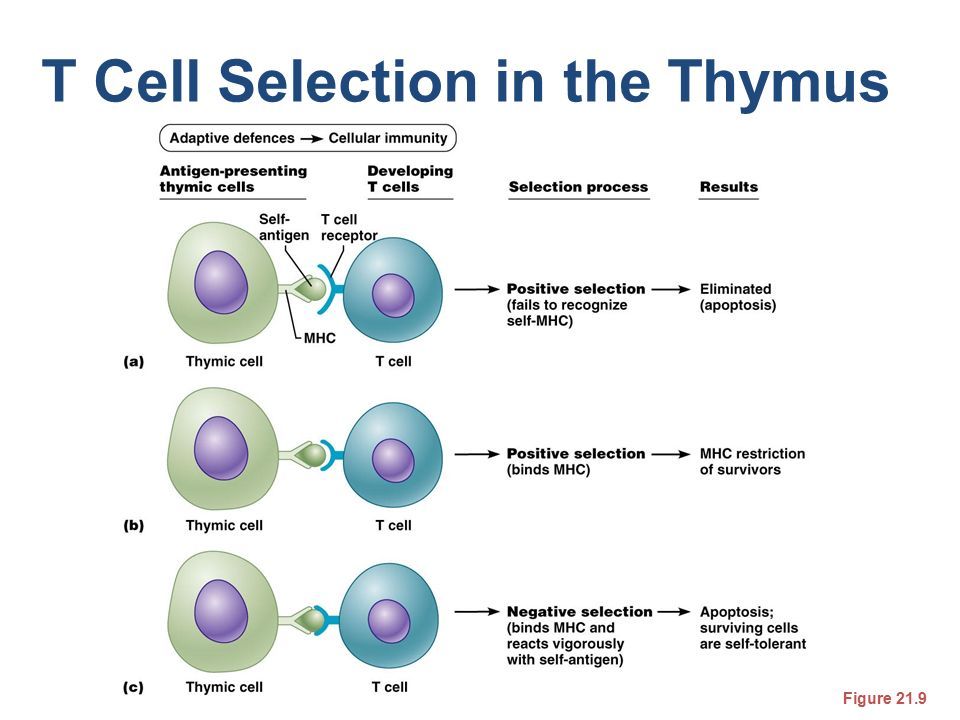
00:01:52.05 natural killer cells are cytotoxic cells of the innate immune system. Central tolerance is achieved through negative selection of autoreactive t cells, while peripheral tolerance is achieved primarily via three mechanisms: Consume large proteins in interstitial fluid;
The other type—humoral immunity—protects our bodies from these invaders by making antibodies. What are t cells and why are they important? Stay in connective tissue, lymphoid organs;
T cell, type of leukocyte (white blood cell) that is an essential part of the immune system. Release cytokines to recruit other cells; But pharmaceutical corporations are trying to suggest that the only way to prevent this from happening is for people to get third or booster doses of their vaccines.
The immune system has evolved a variety of mechanisms to achieve and maintain tolerance both centrally and in the periphery. These t h 2 cells can subsequently stimulate the production of different isotypes, including iga and ige, as well as neutralizing and/or weakly opsonizing subtypes of igg. Similar to the bcr, each one of these chains includes a variable and a constant domain.