Qrs duration 130 ms (favours svt); (1) the r wave in v1 was, during the tachycardia, clearly higher than the r wave in v1 during sinus rhythm.
In certain cardiac alterations, wide qrs complex tachycardias of another etiology can be observed.
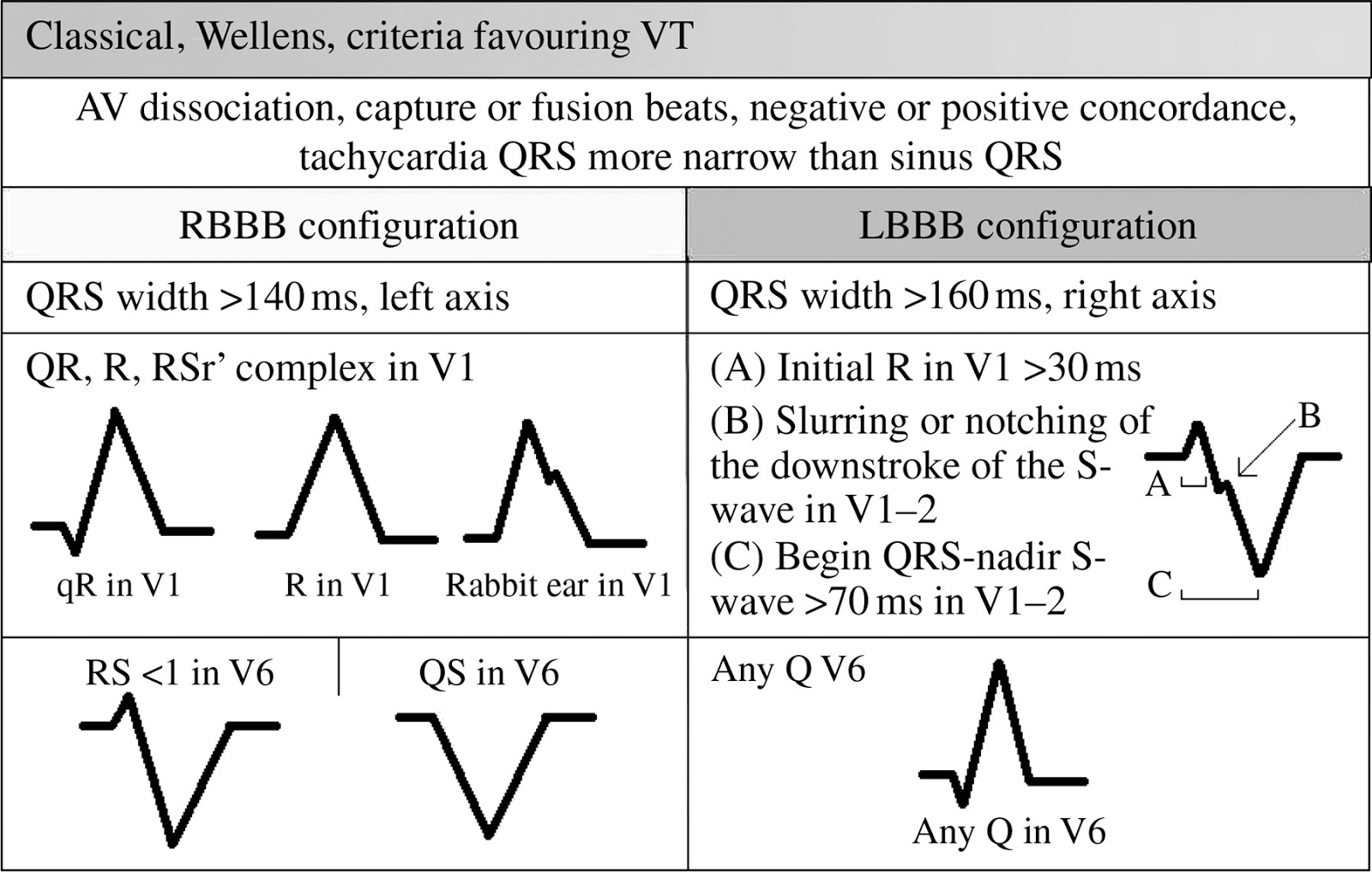
Ventricular tachycardia ecg criteria. Ecg criteria to identify epicardial ventricular tachycardia in nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Antidromic tachycardia is a supraventricular tachycardia with wide qrs complexes. Slurred or notched downstroke of the s wave in v1 or v2 favors vt.
Rapid ventricular paced rhythm (e.g. Electrocardiogram features of antidromic tachycardia: S (v3) + r (avl) > 28mm;
Ecg criteria for ventricular tachycardia ecg features of ventricular tachycardia. The brugada criteria were derived to assist clinicians at the bedside when assessing sick patients with a wide complex tachycardia on their ecg. Despite the fact that the ecg pattern is of lbbb type and the patient presented with baseline lbbb, we diagnose ventricular tachycardia (vt) because of the following:
Differential diagnosis of supraventricular tachycardia (svt) and ventricular tachycardia (vt) is of paramount importance for appropriate patient management. Absence of an rs complex in all precordial leads all qrs complexes completely upright or completely downward in precordial leads: This is the most important classification clinically and influences immediate management.
Several diagnostic algorithms for discrimination of vt and svt based on surface electrocardiogram. Ventricular tachycardia with rate 100 to 120 beats per minute is. Ventricular tachycardia refers to a wide qrs complex heart rhythm — that is, a qrs duration beyond 120 milliseconds —.
Duration of onset of the qrs complex to. Ublished ecg criteria for identifying an epicardial (epi) origin of ventricular tachycardia (vt) include interval slowing in the initial portion of qrs and morphological Misdiagnosis in slow vt may be deadly!
Percutaneous epicardial radiofrequency (rf) ablation of ventricular tachycardia (vt) has been introduced as an approach for the treatment of recurrent vt refractory to endocardial ablation [1,2,3,4].the ecg criteria for identifying an epicardial origin of vt include slowing and unusual notching in the initial portion of qrs [5,6,7].these criteria are region. (1) the r wave in v1 was, during the tachycardia, clearly higher than the r wave in v1 during sinus rhythm. Whenever we have a wide qrs complex tachycardia on an electrocardiogram, we must assume by default that it is a ventricular tachycardia, although this is not always true.
Wide qrs complex tachycardia with hr between 200 and 300 bpm; • av dissociation is highly suggestive of ventricular tachycardia, as a part of the brugada and vereckei criteria used to differentiate vt from svt with aberrancy. Haemodynamically unstable — e.g hypotension, chest pain, cardiac failure, decreased conscious level;
To reevaluate ecg criteria for distinguishing supraventricular tachycardia (svt) with aberrant conduction from ventricular tachycardia (vt), 133 wide qrs tachycardias were recorded in patients undergoing invasive electrophysiological (ep) study. Left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) modified sgarbossa criteria; R avl > 11 mm;
A wide r wave in lead v1 or v2 of 40 ms or more favors vt. In certain cardiac alterations, wide qrs complex tachycardias of another etiology can be observed. Qrs onset to peak in.
Criteria incorrectly suggests supraventricular tachycardia in this patient with idiopathic left bundle branch block ventricular tachycardia a: 6 usually these vas are asymptomatic but sometimes patients report. The specificity is high (>85%).
Ekg criteria for ventricular tachycardia. Qrs duration 130 ms (favours svt); Ventricular tachycardia (vt) ecg review.
Specifically, they help differentiate between. Multifocal atrial tachycardia (mat) narrow qrs bradycardia; S (v3) + r (avl) > 20 mm
Ventricular tachycardia classification is based on: Avr with wide q wave (favours vt); R to s interval >100 ms in one precordial lead distance between r and s waves in each precordial lead:
Supraventricular & ventricular tachycardia • when there is a block (or aberrancy) in the conduction pathway to the ventricles (either a bundle branch block or intraventricular conduction delay) or preexcitation, supraventricular tachycardia (svt) will be associated with widened qrs complexes and the resulting rhythm can be difficult to distinguish from monomorphic ventricular.