
Natural killer (nk) cells were discovered more than 30 years ago. Instead, these cells appear to detect surface markers on cells which indicate immunologically irregular behavior.
Nk cells in the uterus are known as unk cells.
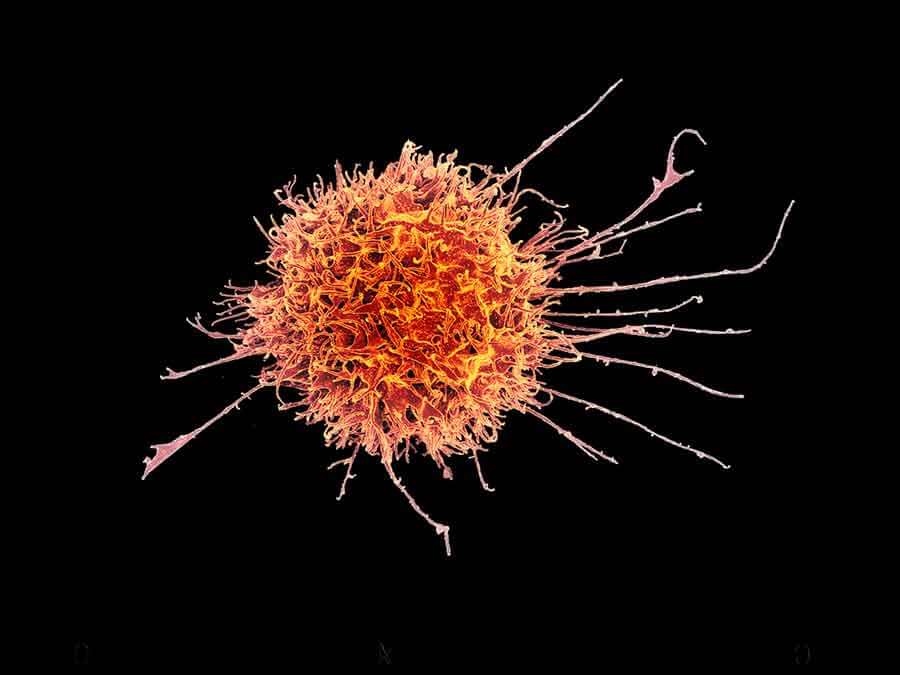
What are natural killer cells. Natural killer (nk) cells were originally described in the 1970s as large granular lymphocytes able to develop natural cytotoxicity against tumour cells without a prior encounter. The tumor microenvironment is highly complex, and immune escape is currently considered an important hallmark of cancer, largely contributing to tumor progression and metastasis. Nk cells are best known for killing virally infected cells, and detecting and controlling
Instead, these cells appear to detect surface markers on cells which indicate immunologically irregular behavior. Named for their capability of killing target cells autonomously, natural killer (nk) cells serve as the main effector cells toward cancer in innate immunity and are highly. Natural killer (nk) cells are lymphocytes that were first identified for their ability to kill tumor cells without deliberate immunization or activation.
They play an important role in. Natural killer cells (also known as nk cells, k cells, and killer cells) are a type of lymphocyte (a white blood cell) and a component of innate. Recent research highlights the fact that nk cells are also regulatory cells engaged in reciprocal intera.
Natural killer (nk) cells are large granular lymphocytes derived from the common lymphoid progenitor cells (lymphoblasts). Natural killer cells (nk cells) form part of the body’s immune system. Nk cells can also use perforin to kill cells in the absence of antibody.
Nk cells in the uterus are known as unk cells. Biotechnology jamia hamdard university 2. Natural killer cells are cytotoxic cells that defend the body against viral infections.
Small granules in their cytoplasm contain proteins. They help the body fight infection and cancer. Subsequently, they were also found to be able to kill cells that are infected with certain viruses and to attack preferentially cells that lack expression of major histocompatibility complex.
Natural killer (nk) cells are described as a type of toxic lymphocytes that are critical to the immune system [ 1 ]. Natural killer (nk) cells are lymphocytes in the same family as t and b cells, coming from a common progenitor. Natural killer (nk) cells are effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system that control several types of tumors and microbial infections by limiting their spread and subsequent tissue damage.
Natural killer (nk) cells are granular lymphocytes that play important roles in immunity against viruses and in the immune surveillance of tumors. Natural killer cells (identified by the surface marker cd56) are the dominant type of maternal immune cell populating the uterine mucosa during formation of the placenta. Research is in progress looking at ways to both boost the function of these cells and increase their numbers as a method of fighting cancers.
Natural killer (nk) cells are effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system that control several types of tumors and microbial infections by. Nk cells are produced in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and thymus, from where they then enter into the circulation [ 1 ]. Killing may occur without previous.
Natural killer (nk) cells were discovered more than 30 years ago. However, as cells of the innate immune system, nk cells are classified as group i innate lymphocytes (ilcs) and respond quickly to a wide variety of pathological challenges. Nk (natural killer) cells are a population of lymphocytes with both innate and adaptive immune features.
Granzymes are enzymes that enter the target cell via the holes created by the. They produce cytotoxic molecules and can eliminate infected cells or cancer cells. Nkt cells are rapid responders of the innate immune system and mediate potent immunoregulatory and effector functions in a variety of disease settings [64].
Perforins are proteins that form pores in the cell membrane of the target cell. Every organ has nk cells to protect it, including the uterus (womb).