These combinations are called monoclonal antibody cocktails. Although the food and drug administration gave these treatments — like regeneron — emergency use authorization in 2020, the criteria for who is eligible to receive them has expanded.
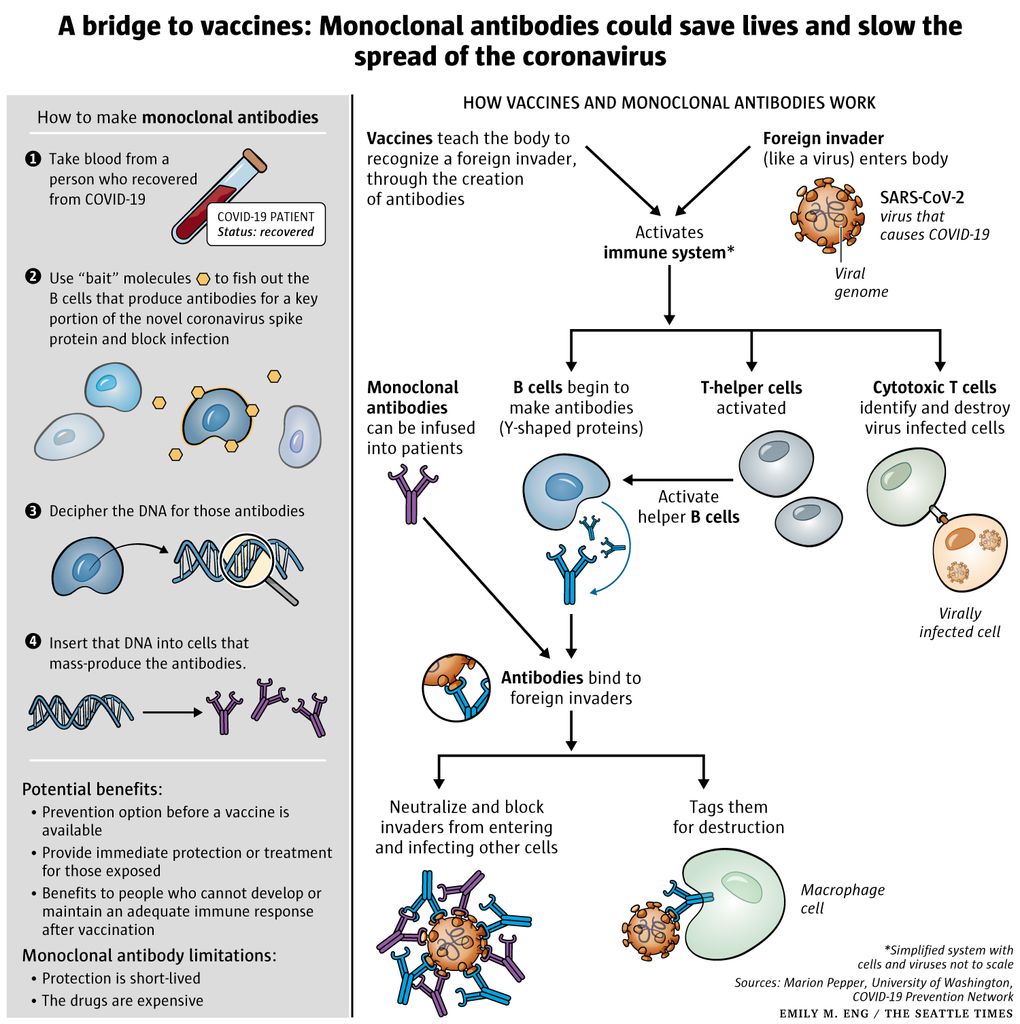
Monoclonal antibodies are like the antibodies your body makes to fight other viruses, but they are made in a lab and are designed to target the coronavirus spike protein.
What is a monoclonal antibody. Monoclonal antibodies act in a similar way to the antibodies your body makes—these are just generated in a lab. Producing monoclonal antibodies (mabs) is initially done by identifying a specific antigen, immunizing an animal with the antigen multiple times. Polyclonal antibodies are synthesized from different immune cells and the antibodies produced bind to multiple antigens.
Monoclonal antibodies (mab) are specific antibodies produced in a laboratory. Extensive research has shown decreased. Who benefits from monoclonal antibody treatment?
The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads and lessen symptom severity. So the mab treatment may help if. Monoclonal antibodies are like the antibodies your body makes to fight other viruses, but they are made in a lab and are designed to target the coronavirus spike protein.
So the mab treatment may help if you are at high risk for serious symptoms or a hospital stay. Mon·o·clo·nal an·ti·bod·y (mab, moab), an antibody produced by a clone or genetically homogeneous population of fused hybrid cells, that is, hybridoma. These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in.
The mechanism by which therapeutic mabs protect against infectious diseases is similar. The technique for producing monoclonal antibodies, invented in 1975. They are created from cells harvested from people who have recovered from a particular illness.
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Our bodies naturally make antibodies to fight infection. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune system recognize germs that cause disease, such as bacteria and viruses, and mark them for destruction.
The spike protein is further divided into two subunits, s1 and s2, that mediate host cell attachment and invasion. Monoclonal antibodies plus a vaccine. There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of.
When they are given to an individual, monoclonal. When activated by an antigen, a circulating b cell multiplies to form a clone of plasma cells,. What is monoclonal antibody therapy?
Monoclonal antibodies (mabs) are laboratory synthesized to mimic these natural antibodies. 542 rows this is a list of therapeutic, diagnostic and preventive monoclonal antibodies,. Spike (s), envelope (e), membrane (m), and nucleocapsid (n), as well as nonstructural and accessory proteins.
The most commonly used animal models are laboratory mice. The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads, and lessen symptom severity. Monoclonal antibodies are carefully designed to recognize a single target (for example, a specific part of a specific virus).
Although the food and drug administration gave these treatments — like regeneron — emergency use authorization in 2020, the criteria for who is eligible to receive them has expanded. Production of monoclonal antibodies was one of the most important techniques of biotechnology to emerge during the last quarter of the 20th century. Some monoclonal antibodies block the connection between a cancer cell and proteins that promote cell growth — an activity that is necessary for cancer growth and survival.
What are monoclonal antibody treatments, again? These combinations are called monoclonal antibody cocktails. In order for a cancerous tumor to grow and survive, it needs a blood supply.
This treatment works as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance, or mimic the way your immune system tackles invading pathogens, the food and drug administration (fda) explains. Monoclonal antibodies will be able to complement vaccines by offering rapid protection against infection. Hybrid cells are cloned to establish cell lines producing a specific antibody that is chemically and immunologically homogeneous.
Monoclonal antibody, antibody produced artificially through genetic engineering and related techniques. When the antibodies bind to the spike protein, they block the virus from entering your body’s cells. Sometimes two monoclonal antibodies, targeting different parts of a virus, are given in combination to increase the effectiveness of the treatment;