Monoclonal antibodies (mabs) are laboratory synthesized to mimic these natural antibodies. These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in.
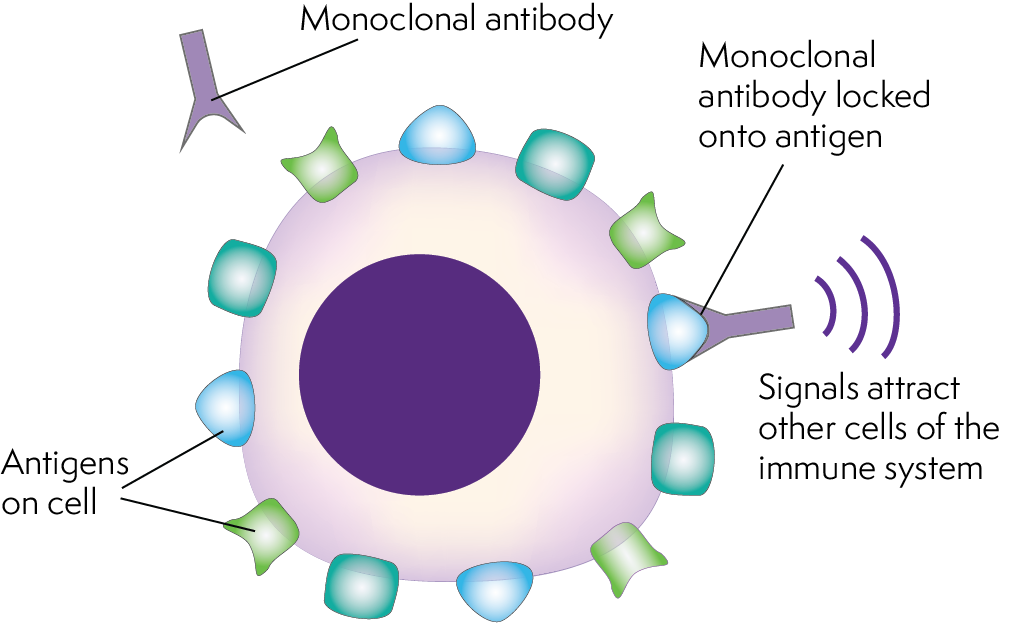
Monoclonal antibody (mab) therapy is one way to help the body skip the training and head straight to the battlefront.
What is monoclonal antibody. If your health care provider recommends a monoclonal antibody drug as part of your cancer treatment, find out what to. Sometimes two monoclonal antibodies, targeting different parts of a virus, are given in combination to increase the effectiveness of the treatment; Polyclonal antibodies are synthesized from different immune cells and the antibodies produced bind to multiple antigens.
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). So, a monoclonal antibody is made so that it binds to only one unique substance. These antibodies are synthetic versions of the body�s natural line of defense, meant for covid patients early on in their infections and who are at high risk of getting even sicker in.
These combinations are called monoclonal antibody cocktails. When they are given to an individual, monoclonal. The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads, and lessen symptom severity.
Monoclonal antibody therapy uses manufactured antibodies that mimic the immune system’s method of fighting off harmful pathogens like viruses. Monoclonal antibodies (mabs) are laboratory synthesized to mimic these natural antibodies. Some monoclonal antibody drugs may be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
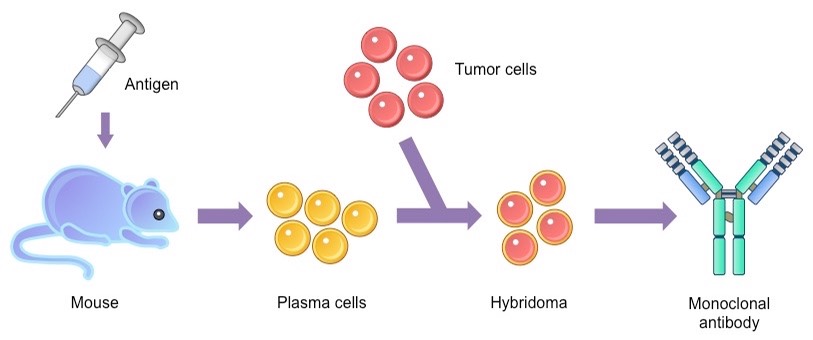
Monoclonal antibodies are like the antibodies your body makes to fight viruses and other bugs, but they are made in the labs of pharmaceutical companies, like regeneron. Mon·o·clo·nal an·ti·bod·y (mab, moab), an antibody produced by a clone or genetically homogeneous population of fused hybrid cells, that is, hybridoma. Monoclonal antibodies are similar to the natural antibodies produced by the body to help fight and protect against infections.
The regeneron cocktail is an “investigational” medicine. Spike (s), envelope (e), membrane (m), and nucleocapsid (n), as well as nonstructural and accessory proteins. Monoclonal antibodies must be administered within 10 days of when symptoms develop, before the body’s inflammatory response to the virus is triggered.
There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. The difference, in this case, is that monoclonal antibodies are artificial and are usually created in a lab and are customized. People who have been hospitalized or prescribed oxygen are not eligible for monoclonal antibody therapy as it is too late for the treatment to make an impact.
Monoclonal antibodies are carefully designed to recognize a single target (for example, a specific part of a specific virus). 1,2 what is the difference between a monoclonal antibody treatment and a vaccine? The mechanism by which therapeutic mabs protect against infectious diseases is similar.
Monoclonal antibodies will be able to complement vaccines by offering rapid protection against infection. Although the food and drug administration gave these treatments — like regeneron — emergency use authorization in 2020, the criteria for who is eligible to receive them has expanded. Hybrid cells are cloned to establish cell lines producing a specific antibody that is chemically and immunologically homogeneous.
Monoclonal antibodies plus a vaccine. These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in. How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer and the drug you’re receiving.
So the mab treatment may help if you are at high risk for serious symptoms or a hospital stay. There are many type of antibodies that are each uniquely tailored to each type of foreign substance, to offset the invasion. The medicine used during this treatment is called the regeneron cocktail (a mix of two antibodies:
The spike protein is further divided into two subunits, s1 and s2, that mediate host cell attachment and invasion. Monoclonal antibody (mab) therapy is one way to help the body skip the training and head straight to the battlefront. The technique for producing monoclonal antibodies, invented in 1975.