The length of a gene is about a few hundreds of bases. The rna genome is bound to the nucleocapsid protein.
The length of the genome of a higher organism is about billion base pairs.
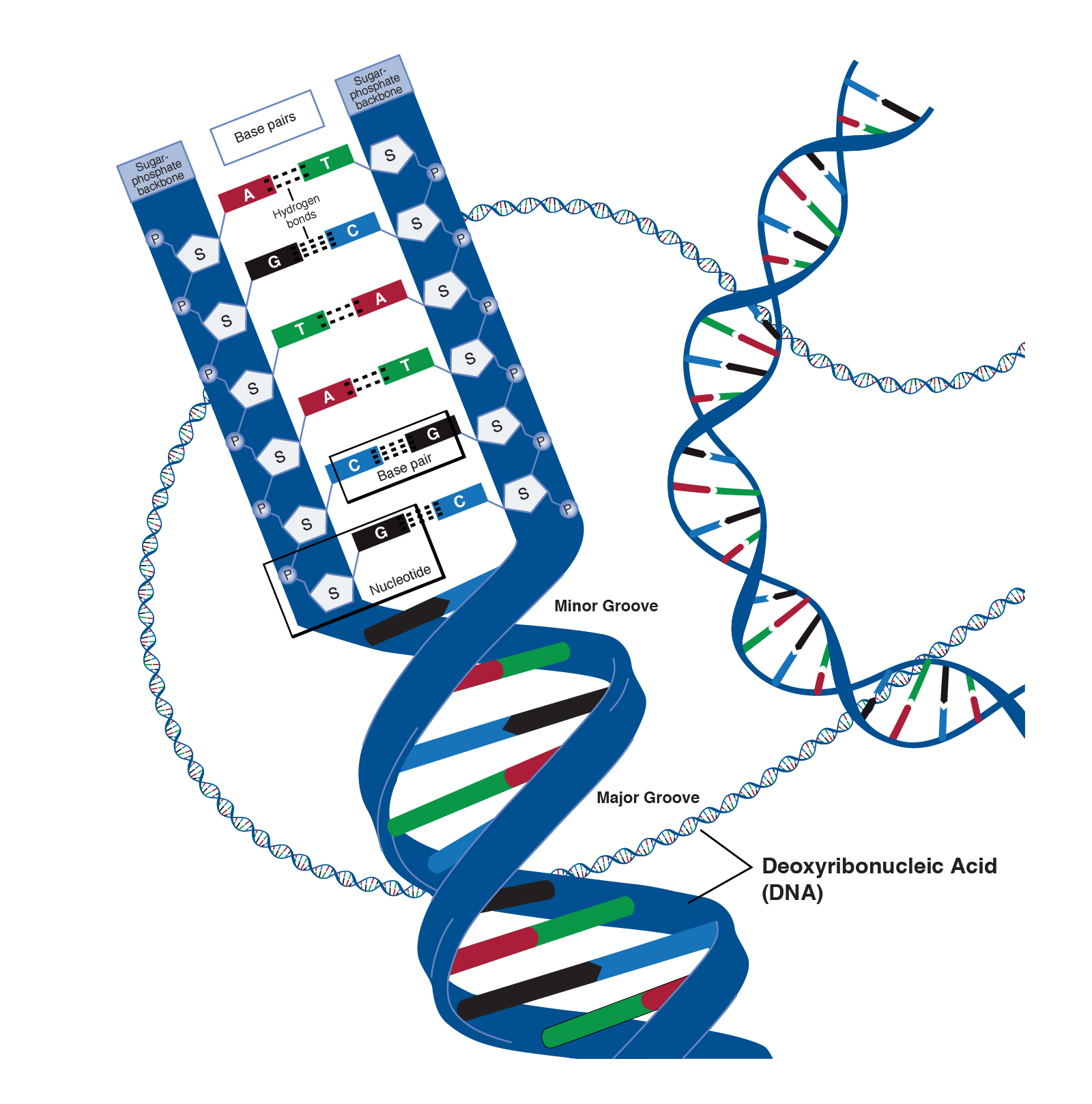
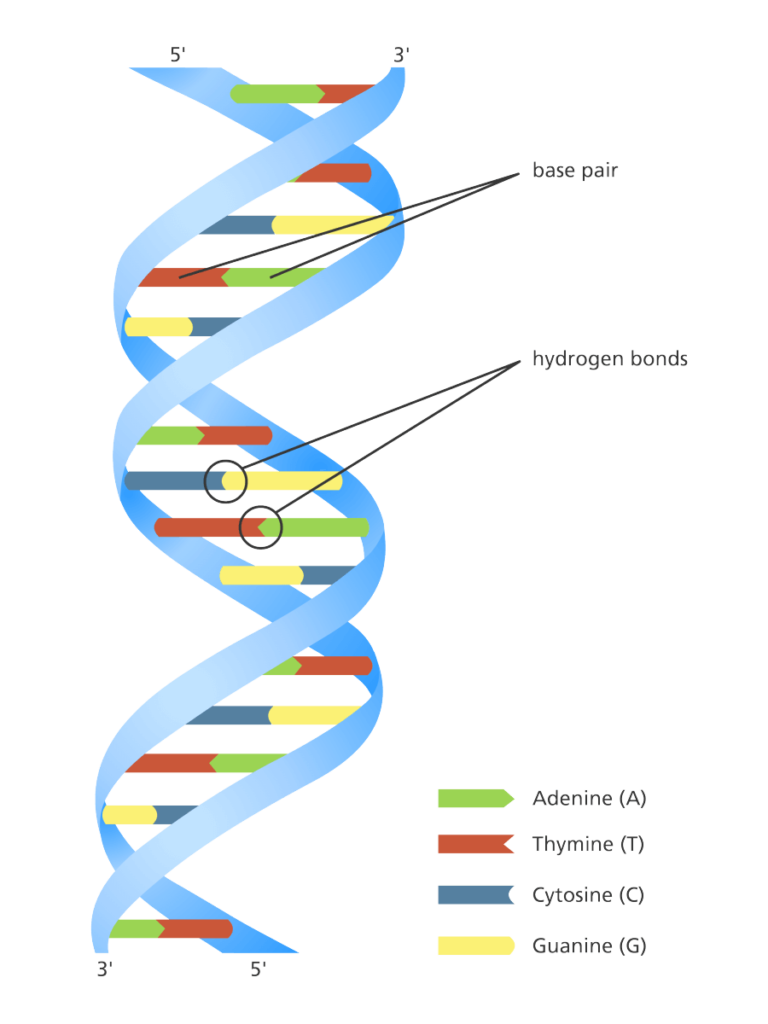
What is the structure of a genome. A genome is composed of one or more dna molecules, each organized as a chromosome. Lec., 2 the organization and structure of genomes fgenetics: 22 in a haploid cell, 44 in a diploid cell.
A gene encodes protein synthesis. The genome is the total dna in a cell. The basic watson and crick structure of dna is identical in you, your dog, and the bacteria.
How many autosomes do we have. Interestingly, most bacterial genomes are organized into a circular chromosomal structure. The circular structure of a bacterial genome, however, enables its dna replication to start and stop at the same location — a feature not seen in the linear genomes of other organisms.
See the image below, a brief overview of the structure of coronavirus. Is the entire genetic material of an organism. Influenza a viruses (iavs) constitute a major threat to human health.
The genome is packed by viral nucleocapsid (n) proteins as a large ribonucleoprotein (rnp) complex and enclosed by an envelope membrane with lipids and viral proteins s. Prokaryotic genomes are mostly single circular chromosomes. • the genome is all the dna in a cell.!
An organism�s complete set of dna is called its genome. A genome encodes both proteins and regulatory elements for protein synthesis. The rna genome is bound to the nucleocapsid protein.
How long is the human genome. These polymers are maintained in duplicate copy in the form of chromosomes in every human cell and encode in their sequence of constituent bases ( guanine [g], adenine [a], thymine [t], and cytosine [c]) the details of the molecular and. Just like you, bacteria have dna that stores genetic information.
Terms in this set (89) what is the genome. Humans, by contrast, have a linear chromosomal structure. Virtually every single cell in the body contains a complete copy of the approximately 3 billion dna base pairs, or letters, that make up the human genome.
The genome of an organism is its hereditary information encoded in dna. The human genome, like the genomes of all other living animals, is a collection of long polymers of dna. The viral mrnas are transcribed from both strands of the dna genome, as two.
A human haploid cell, consist of 23 nuclear chromosome and one mitochondrial chromosome, contains more than 3.2 billion dna base pairs. A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic information. It is found in the nucleus of a cell, and is composed of a chemical called dna.
Genomes are tightly packed inside the capsids and frequently the genome and the capsid are collectively called nucleocapsid. The genome is made up of genes that code for. The study of the structure and function of the genome is.
All regulatory elements, including the replication origin 5 (ori), promoter of early genes, and promoter of late genes, are clustered within a segment called the regulatory region. The envelope made up of lipid bilayer has a membrane, envelope and anchored spike proteins. What is the structure of a genome?
It deals with the study of the structure of entire genome of a living organism. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. The length of a gene is about a few hundreds of bases.
Amazingly, viruses are able to execute productive infection and of course make us sick with very limited genetic information. Dna is the language of life. In other words, it deals with the study of the genetic structure of each chromosome of the genome.
The s protein is homotrimeric in structure with s1 and s2 subunits. Normal diploid cells contain two copies of the nuclear genome and a much larger but variable number of copies of the mitochondrial genome. • specifically, it is all the dna in an organelle.!
The genome is the full complement of genetic information in a cell, and contains the programme required for that cell to function. All the genetic material in an organism. The phrase “the human genome” normally refers to the nuclear genome but should also include the mitochondrial genome.
Humans have two genomes, nuclear and mitochondrial. A genome includes all of the hereditary instructions for creating and maintaining life, as well as instructions for reproduction. The length of the genome of a higher organism is about billion base pairs.