
Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi. Done as a preventive measure for control of gingivitis.
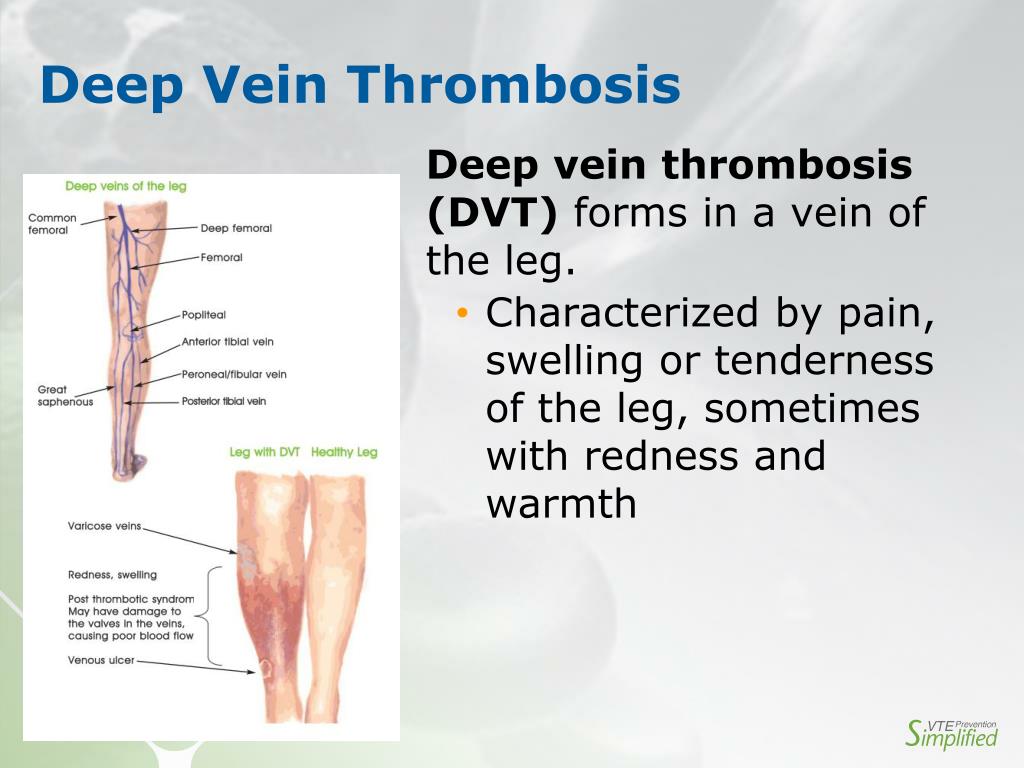
Deep vein thrombosis (dvt) is the formation or presence of a thrombus in the deep veins.
What is thrombosis prophylaxis. Apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, edoxaban, and betrixaban are alternatives to warfarin for prophylaxis or treatment of deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe). Primary prophylaxis is the preferred method with the use of medications and mechanical methods to prevent dvt. Commonly used to treat heart attack, acute myocardial infarction, arterial thromboembolism prophylaxis.
Dvt of the leg is the development of a blood clot in one of the major deep veins in the leg or thigh, which leads to impaired venous blood flow, usually causing leg swelling and pain. Apixaban, edoxaban, rivaroxaban, and betrixaban inhibit factor xa, whereas dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor. Commonly used to treat stroke, heart attack, peripheral artery disease, myocardial infarction prophylaxis, thrombosis prophylaxis, acute myocardial infarction, stemi.
We evaluated the benefit/risk ratio of different anticoagulant regimens in the prevention of vte in patients with ais. A pe most commonly occurs when a thrombus, usually from a dvt, travels in the blood (embolus) and obstructs blood flow to the lungs causing respiratory dysfunction. Oral prophylaxis cleaning of the teeth by a dentist or dental hygienist, including removal of plaque, materia alba, calculus, and extrinsic stains;
Dvt prophylaxis can be primary or secondary. Thrombosis is the occlusion of a blood vessel caused by the formation of a blood clot (thrombus). The risk of venous thrombosis in patients admitted to hospital depends on medical versus surgical admission and, among.
In patients with dvt, a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the arm or leg, occluding blood flow and potentially leading to complications. Deep vein thrombosis (dvt) prophylaxis is medical treatment to prevent the development of dvt in a patient at risk of this condition. Venous thromboembolism (vte) prophylaxis includes both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic steps to reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe).
Prevention of venous thromboembolism has become routine in all surgical disciplines and consists of physical and pharmacological measures. Thromboprophylaxis is the most important patient safety strategy in patients admitted to hospital. Symptoms of a pe include chest pain, shortness of breath, and/or haemoptysis.
Deep vein thrombosis (dvt) is the formation or presence of a thrombus in the deep veins. Currently, there is no standardized recommendation for the use of vte prophylaxis during anterior cruciate ligament (acl) reconstruction. The benefit from pharmacological prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism (vte) is uncertain probably due to doubts about the optimal agent and dose.
On completion of this article, the reader should be able to determine risks profiles for venous thromboembolism and pulmonary embolism in patients undergoing colon and rectal surgery, and to discuss the benefits of mechanical and pharmacologic venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. Obstruction of a blood vessel with thrombotic material carried by the blood from the site of origin to plug another vessel. Done as a preventive measure for control of gingivitis.
This usually causes swelling and pain in the leg. Venous thromboembolism (vte) is a significant perioperative risk with many common orthopaedic procedures. The best theoretical approach to thrombosis prophylaxis would be to address all of the virchow postulates starting before the anticipated confinement or surgery and continuing throughout the entire period of risk.
Secondary prophylaxis is a less commonly used method that includes early detection with screening methods and the treatment of subclinical dvt. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi. The deep veins in the leg and pelvic area are most frequently affected.
Venous thromboembolism (vte) is common after major general surgery. © 2003 by saunders, an imprint of elsevier, inc. Dvt occurs mostly in the lower extremities and to a lesser extent in the upper extremities.
Extended prophylaxis with bemiparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after abdominal or pelvic surgery for cancer: The indications and choice of prophylaxis modality depend on the individual patient risk profile which is determined by the combination of exposing and predisposing risk factors. Venous thromboembolism (vte) prophylaxis consists of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to diminish the risk of deep vein thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe).
Dvt of the leg occurs when there is a blood clot in the major veins in the leg or thigh, which impairs venous blood flow.