The antibodies enter the bloodstream and prevent a specific disease from recurring. This triggers our immune system to produce antibodies and activate other immune cells to fight off what it thinks is an infection.
B cells have b cell receptors (bcrs) on their surface, which they use to bind to a specific protein.
What kind of cells produce antibodies. Neutralization by antibodies is also important in preventing bacterial toxins from entering cells. Your immune system can also safely learn to make antibodies through vaccination. What the antibody recognises, is determined by the shape of its variable region (figure 1);
B cells have b cell receptors (bcrs) on their surface, which they use to bind to a specific protein. B cells and t cells. Next, our cells display the spike protein piece on their surface.
B lymphocytes, also known as b cell, don�t attack and kill cells, viruses or bacteria themselves. Antibodies otherwise known as immunoglobulins are soluble glycoprotein.they are secreted or produced by plasma cells.plasma cells precursors are in turn produced by b cells also known as b lymphocytes,a type of immune cell.b cells are produced from haematopoetic stem cells in bone marrow where they mature. The specificity of a particular antibody, i.e.
The antibodies enter the bloodstream and prevent a specific disease from recurring. When you are infected with a virus or bacteria, your immune system makes antibodies specifically to fight it. Booster shots are a type of secondary vaccine that allow for longer lasting protection against a particular virus.
This is achieved either by direct attack of antibody on pathogens (usually when pathogens are viruses) or by binding to pathogen’s surface (when. Antibodies that bind to the pathogen can prevent this and are said to neutralize the pathogen. B cells are a part of the adaptive immune system and can only impact extracellular threats, which are outside of our cells.
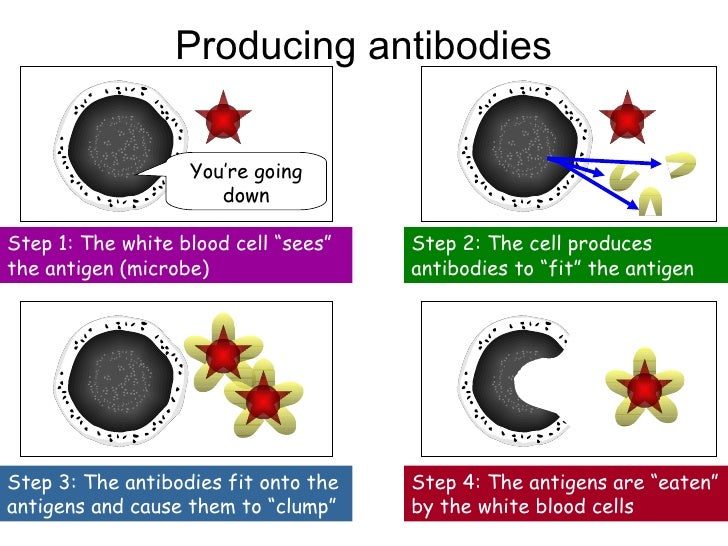
The antigen produces and displays specific molecules on its cell. A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system. Instead, they manufacture proteins called antibodies that actually stick to the surface of invaders, disabling those invaders and spotlighting them for clean.
Antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called a b cell (b lymphocyte). The first antibodies made by a newly formed b cell are not secreted. When b cells become activated due to the presence of a particular antigen, they develop into plasma cells.
Once the encoding is done by b cells, it releases antibodies which then bind with specific pathogens resulting in their elimination from our bodies. Part of humoral response and differentiate into plasma cells in lymph tissue (white pulp of spleen, follicles of lymph nodes) to produce antibodies. B cells develop from stem cells in bone marrow.
This phenomenon is called “gene rearrangement.” Each lymphocyte of b cells generates a unique antibody against a unique epitope. This triggers our immune system to produce antibodies and activate other immune cells to fight off what it thinks is an infection.
After the protein piece is made, our cells break down the mrna and remove it. This switching process allows the immune system to customize its response to incoming. Our immune system recognizes that the protein doesn’t belong there.
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins are glycoproteins produced by the b lymphocytes upon encountering a pathogenic substance. These antibodies can in turn bind with the specific antigens, and stop the infection. 9.1).to enter cells, viruses and intracellular bacteria bind to specific molecules on the target cell surface.
One type of white blood cells, called b cells, manufacture and. Antibodies are proteins that your immune system makes to help fight infection and protect you from getting sick in the future. These antibodies have immunological, scientific, commercial, and industrial uses and are a major part of our ability to carry immunity.
Specifically plasma cells (a type of b cells, which are meant to produce large quantities of b cells very quickly, and memory b. What kind of cell will produce such antibodies? Marita�s body has just been exposed to a number of foreign invaders, but her immune system is activing a certain type of cell that will produce antibodies to fight these toxins.
White blood cells produce antibodies to diseases. The t cells destroy the body�s own cells that have themselves been taken over by viruses or become cancerous. There are two main types of lymphocytes:
Booster shots are a type of secondary vaccine that allow. The b cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins. Antibodies contribute to immunity in three main ways (see fig.
B cells (the precursors to plasma cells) are the source of antibodies within the body.