They are activated when they encounter antigens—any foreign substances outside of cells or proteins, peptides, or polysaccharides on the surface of a pathogen. B lymphocytes (or b cells) are each programmed to make one specific antibody.

Lymphocytes are one of the main types of immune cells.
Which lymph cells produce antibodies. They also mediate the immune response. They are activated when they encounter antigens—any foreign substances outside of cells or proteins, peptides, or polysaccharides on the surface of a pathogen. C) remove debris and pathogens from the lymph.
These cells are made up of two types made by a mitotic division process in the bone marrow, namely: Which lymph cells produce antibodies? When b cells become activated due to the presence of a particular antigen, they develop into plasma cells.
They can travel through the lymphatic and circulatory systems. E) remove excess nutrients from the lymph. T and b lymphocytes are the only lymphoid cells that produce and express specific receptors for antigens.
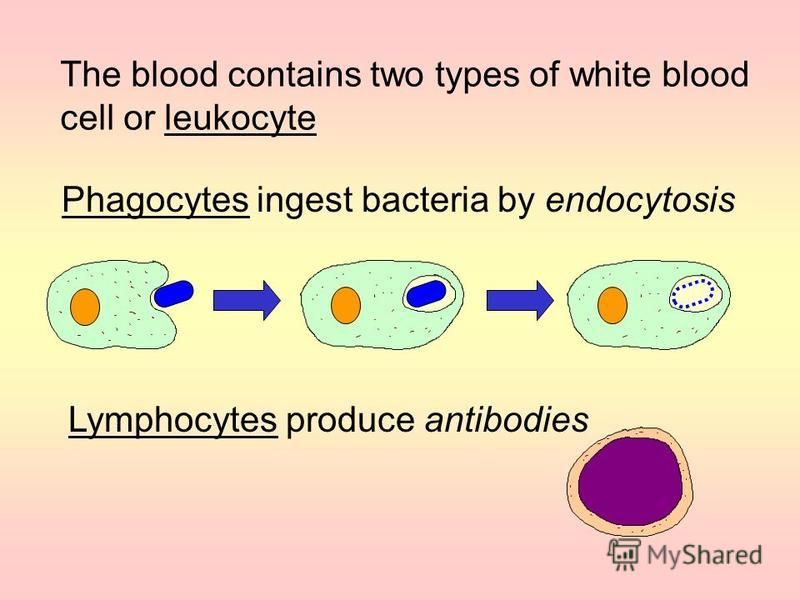
Antibodies are manufactured by the lymph system. Cells manufactured in the bone marrow that create antibodies for isolating and destroying invading bacteria and viruses. All of these lymphocyte cells contribute to the body’s immune response.
B cells produce plasma cells, which secrete antibodies in the blood. B cells make up nk cells make 10. The plasma cells produce antibodies to that particular antigen.
When the same antigen enters the body for the second time, the memory cells responds quickly and produces the antibodies against them. Antibodies are specialized proteins that the body produces in response to invasion by a foreign substance. B) monitor the contents of lymph.
Lymphocytes are divided mainly into b and t cells. Antibodies are proteins produced by certain lymphocytes in response to a specific antigen. Antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called a b cell (b lymphocyte).
The memory cells are specific cells which remain inactivated and remembers the antigen. Activated b cells produce and secrete proteins called antibodies, which target specific antigens to flag,. B cells develop from stem cells in bone marrow.
The process of antibody formation begins. B lymphocytes (or b cells) are each programmed to make one specific antibody. Ige is produced by plasma cells located in lymph nodes draining the site of antigen entry or locally, at the sites of allergic reactions, by plasma cells derived from germinal centers developing within the inflamed tissue.
Lymphocytes are white cells found in lymph tissues and blood that are parts of the body’s main immune system. The lymph nodes act as filters. A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the immune system of jawed vertebrates.
Natural killer (nk) cells attack and destroy foreign microbes. Lymphocytes are divided mainly into b and t cells. Other activated t cells remain in the lymphoid organ and help b cells respond to the microbial antigens.
Specific type of acquired immunity involved in the production of antibodies by derivatives of b lymphocyte known as plasma cells A) produce antibodies through b cells. •function of the lymphatic system •to produce, maintain, and distribute lymphocytes •lymphocyte production •lymphocytes are produced •in lymphoid tissues (e.g., tonsils) •lymphoid organs (e.g., spleen, thymus).
Swollen or painful lymph nodes are a sign that the immune system is active, for example to fight an. Lymphocytes are activated & fixed plasma cells produce antibodies to foreign antigens These cells are involved in the regulation of the immune response and in cell mediated immunity and help b cells to produce antibody (humoral immunity).
Vertebrates inevitably die of infection if they are unable to make antibodies. Lymphocytes are one of the main types of immune cells. B) monitor the contents of lymph.
D) act as a way station for cancer cells. Lymph nodes do all of the following, except that they a) produce antibodies. Various immune system cells trap germs in the lymph nodes and activate the creation of special antibodies in the blood.
The binding of antibodies to invading pathogens also recruits various types of white blood cells and a system of blood proteins, collectively called complement (discussed in chapter 25). C) remove debris and pathogens from the lymph. The activated b cells secrete antibodies that circulate in the body and coat the microbes, targeting them for efficient phagocytosis.