
These cells start life inside bone marrow, before maturing as they circulate through the body�s blood vessels. The b cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
B cells develop from stem cells in bone marrow.
White blood cells that produce antibodies are called. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called b lymphocytes (or b cells). Because some white blood cells called neutrophils have a short life less than a day, your bone marrow is always making them. Antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called a b cell (b lymphocyte).
An antibody is produced by t cells and an antigen is a foreign protein. What are white blood cells (wbcs)? Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called b lymphocytes (or b cells).
Lymphocytes are another type of white blood cell. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called b lymphocytes (or b cells). Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called b lymphocytes (or b cells).
This hybridoma, or monoclone, is an inexhaustible generator of exactly the same antibody, over and. Adnan i qureshi, in ebola virus disease, 2016. White blood cells, also called leucocytes, detect and deal with infections or foreign molecules that enter your body.
The t cells destroy the body�s own cells that have themselves been taken over by viruses or become cancerous. Part of their development involves assembling key segments of immunoglobulin genes to churn out antibodies with random structures. B cells and t cells.
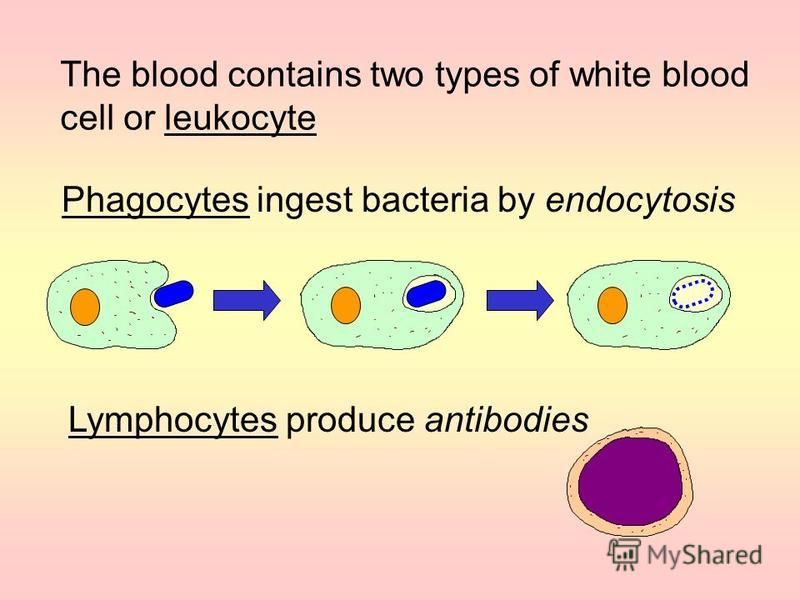
Bone marrow, lymph glands, and nodes are the primary sources where wbcs gets produced. The b cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins. A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system.
An antigen is presented by antigen presenting cells to plasma cells, which produce antibodies. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor b cell. They pass directly to the bloodstream and live from several days to many years.
Antibodies attack antigens by binding to them. White blood cells will produce antibodies to fight the infection and help with other immune responses. From there, that cell is fused to a blood cancer cell, producing something called a hybridoma.
They are stored in your blood and lymph tissues. B cells develop from stem cells in bone marrow. T cells only make memory cells, antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells or wbcs called b lymphocytes or b cells, hence,the type of white blood cells which produce antibodies are called lymphocytes, accounting for about 1 percent of your blood, they use the blood as a transport medium, the body identifies antigens as dangerous.
They recognise proteins on the surface of pathogens called. When b cells become activated due to the presence of a particular antigen, they develop into plasma cells. These cells start life inside bone marrow, before maturing as they circulate through the body�s blood vessels.
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called b lymphocytes (or b cells). There are two main types of lymphocytes: The white blood cells (wbcs) or leukocytes are the type of cells that have a nucleus and float freely in your bloodstream.
White blood cells are made in the bone marrow. A medical illustration of a lymphocyte. He used the term “colorless cells” for.
An antibody is one response to an antigen. The major difference between monocytes and lymphocytes is that monocytes are large phagocytic white blood cells with a simple oval nucleus and lymphocytes are small white blood cells with a single round nucleus.