There is another very commonly used induction therapy, azacitidine (vidaza) and venetoclax (venclexta). The goal of induction treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia (aml) is to clear the blood and bone marrow of immature blood cells (called blast cells, or blasts) and bring about a complete remission, or complete response.
This is the first phase of treatment.
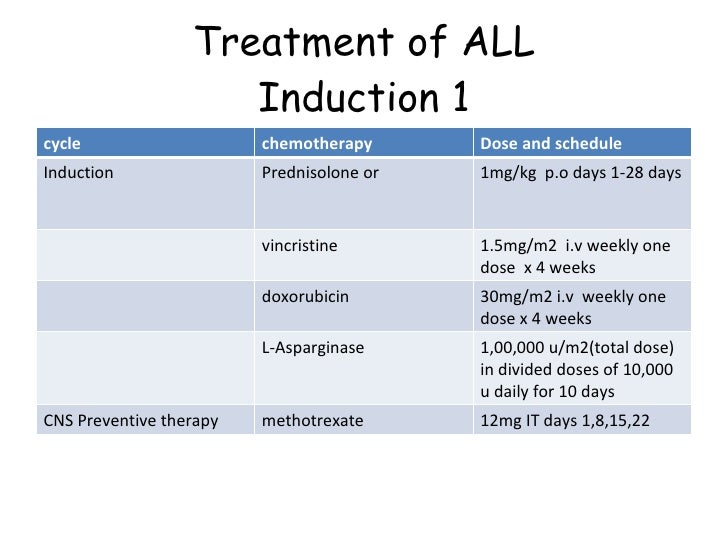
Induction therapy for aml. New agents that are targeted to specific molecular abnormalities in the aml cell are being studied as additions to induction therapy. Except when given into the csf, these drugs enter the bloodstream and reach all areas of the. Results from the uk ncri aml17 trial in 1206 patients.
The efficacy and safety of daunorubicin versus idarubicin combined with cytarabine for induction therapy in acute myeloid leukemia: Treatment protocols for acute myeloid leukemia (aml) are provided below, including a general treatment approach and treatment recommendations for relapsed or refractory disease. The intensive induction therapy (combination of anthracycline and cytarabine) for young patients with good performance status has remained.
You may also be given targeted therapy drugs as part of your induction and consolidation therapy. A randomized comparison of daunorubicin 90 mg/m2 vs 60 mg/m2 in aml induction: The goal is to kill the leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow.
Azacitidine and venetoclax as induction therapy with venetoclax maintenance in the elderly with aml the safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. General treatment approach for acute myeloid leukemia. What type of treatment is used for aml induction therapy?
This is called the “7 + 3” regimen, because cytarabine is most often given by continuous intravenous (iv) infusion over 7 days, while the anthracycline drug is given by an iv infusion in a single. Standard therapy was applied according to the german aml cooperative group 1999 protocol for elderly patients ≥60 years of age as follows: About 60% to 80% de novo aml will achieve cr with induction therapy.
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (aml) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes a large number of abnormal blood cells. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (mylotarg®) and midostaurin (rydapt®). Due to aggressive induction therapy, patients with aml are having better remission and survival outcomes.
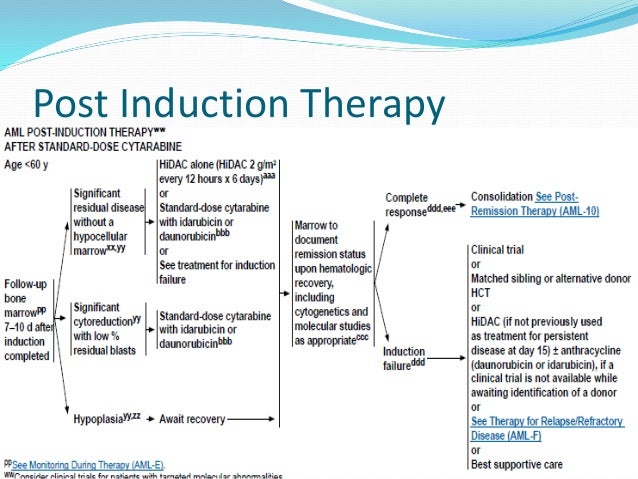
Approaches such as consolidation treatment, prolonged maintenance, and autologous or allogeneic transplantation in first remission are directed against the minimal residual disease. Induction treatment is also called remission induction therapy. Hetty carraway is director of the leukemia program at cleveland clinic.
And then the venetoclax is a pill that�s taken every day by mouth. Induction treatment is also called remission induction therapy. There is another very commonly used induction therapy, azacitidine (vidaza) and venetoclax (venclexta).
The most common induction regimen for aml includes cytarabine and an anthracycline drug, such as daunorubicin or idarubicin. This is the first phase of treatment. Carraway cares for patients with acute leukemia and bone marrow failure states.
So, one of the medicines is given usually as a subcutaneous injection for seven days in a row. The goal of induction treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia (aml) is to clear the blood and bone marrow of immature blood cells (called blast cells, or blasts) and bring about a complete remission, or complete response. The goal of induction treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia (aml) is to clear the blood and bone marrow of immature blood cells (called blast cells, or blasts) and bring about a complete remission, or complete response.
So, this other arm of induction therapy is given a little bit differently. There are two types of targeted therapy drug offered to people with aml: Burnett ak, russell nh, hills rk, et al.
What is induction therapy aml? Hetty carraway, an aml specialist at cleveland clinic, provides an explanation of the role of induction and consolidation therapy in aml patients. Although the knowledge of the underlying biology and molecular abnormalities has evolved tremendously, this has not been accompanied as quickly by translational changes in the early management of aml patients.