Ecg changes in myocardial infarction. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi.
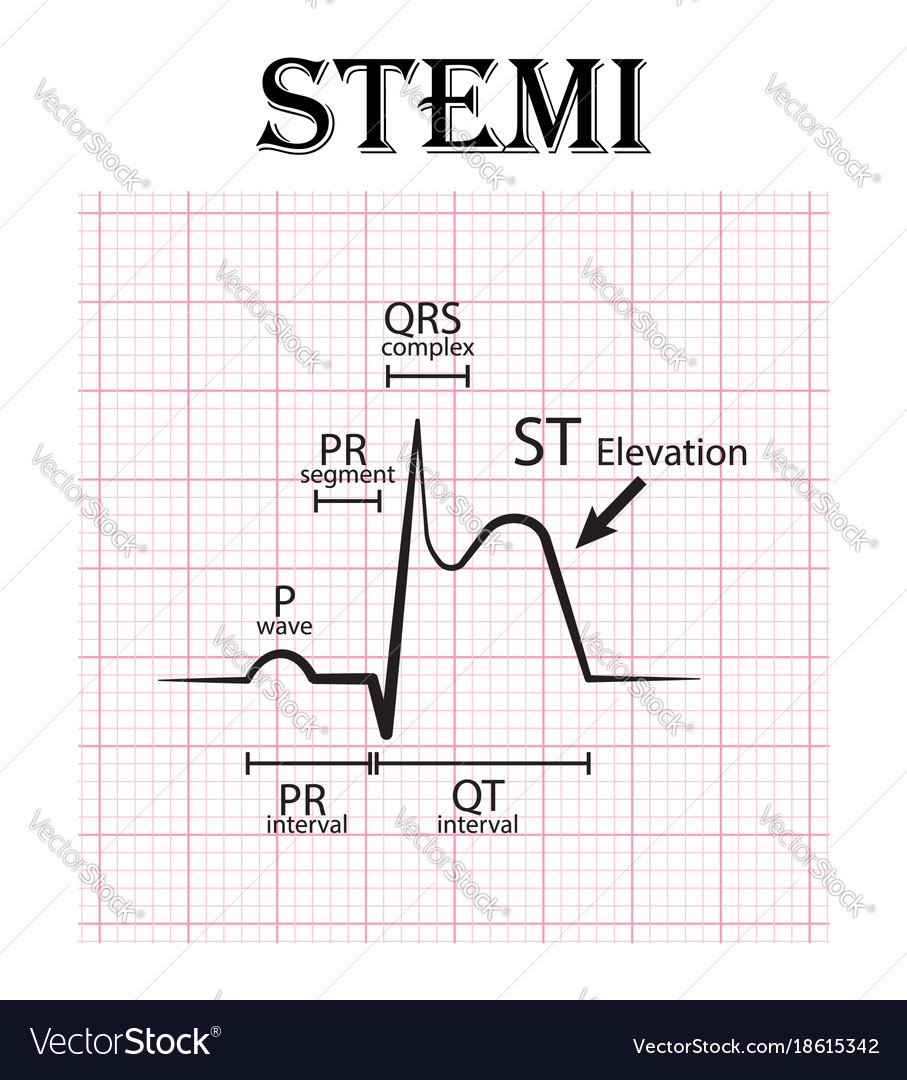
Isoelectric line, q wave, r wave, and st segment.
Myocardial infarction ecg interpretation. Now, insights from angiography and advances in electrocardiogram (ecg) interpretation have led to the new paradigm of occlusion myocardial infarction (omi), creating the possibility of further qi. Electrocardiogram (ecg) interpretation is widely performed by emergency physicians. The first ecg finding in acute myocardial infarction is hyperacute t waves, which are tall and symetrical and occur within the first few minutes.
Ecg interpretation of st segment elevation and possible stemi by dr. Fat deposits, fibrosis, calcification, and/or platelet aggregation), which results in. This occurs because these ecg leads will see the mi backwards;
Electrocardiographic differentiation among occlusion of the left anterior descending, first diagonal, and first obtuse marginal coronary arteries. These then resolve and st elevation develops in affected leads over minutes to hours, with st depression in reciprocal leads. It is often important to be able to determine the localization of myocardial infarction and ischemia, as well as being able to determine which coronary artery that is iccluded, and where the occlusion may be located.
Introduction to ecg recognition of myocardial infarction when myocardial blood supply is abruptly reduced or cut off to a region of the heart, a sequence of injurious events occur beginning with subendocardial or transmural ischemia, followed by necrosis, and eventual fibrosis (scarring) if the blood supply isn�t restored in an appropriate period of time. The leads are placed anteriorly, but the myocardial injury is posterior. Describe the ecg characteristics of a normal 12 lead ecg.
Most acute mis are caused by atherosclerosis (e.g. The reader will gradually notice that ecg interpretation is markedly facilitated by using an algorithm, as it minimizes the risk of missing. This lecture series is aimed primarily at medical/nursing/paramedicine students and junior trainees, but will hopefully be useful as a refresher course for the more experienced.
Rapid diagnosis of myocardial infarction (mi) using electrocardiography (ecg) is the cornerstone of effective treatment and prevention of mortality; Birnbaum y, hasdai d, sclarovsky s, herz i, strasberg b, rechavia e. Ad a forum for research on vascular biology, physiology, imaging and disease.
Correctly identify the following normal ecg components: Isoelectric line, q wave, r wave, and st segment. St segment elevation over area of damage st depression in leads opposite infarction inverted t waves pathological q waves.
The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi. Providers rely heavily on ecg interpretation of these leads for the detection of irregular cardiac rhythms, conduction abnormalities, and myocardial infarction as well as to explore and better understand several other cardiac diseases, like valvular heart disease and pericarditis (prutkin, 2019).
Acute myocardial infarction (mi) is actual necrosis of myocardial tissue as a result of relative or absolute lack of blood supply to the myocardium. A r/s wave ratio greater than 1 in leads v1 or v2. The ecg must always be interpreted systematically.
This article reviews the current stemi paradigm, the emergence of the omi paradigm, and the use of qi to continuously improve care for acute myocardial infarction. Systematically assess and interpret a 12 lead ecg for abnormal patterns of ischemia, injury, and infarction. Risk stratification using the ecg.
Using the ecg to localize myocardial infarction / infarction and determine the occluded coronary artery. Failure to perform a systematic interpretation of the ecg may be detrimental. During this acute phase, the cardiologist or emergency department physician.
Participants were asked to focus on. Ecg changes in myocardial infarction. The ecg is used to quickly risk stratify and subsequently implement the best treatment strategy for the individual patient.